前缀和(一维、二维)c++实现
文章目录
-
- 一维前缀和
-
- 是什么?
- 有什么用?
-
- 怎么用?
- 代码实现
- 二维前缀和
-
- 是什么?
- 有什么用?
- 怎么用?
- 代码实现
代码实现中我使用的头文件是
,如果运行不成功请注意更换。
一维前缀和
是什么?
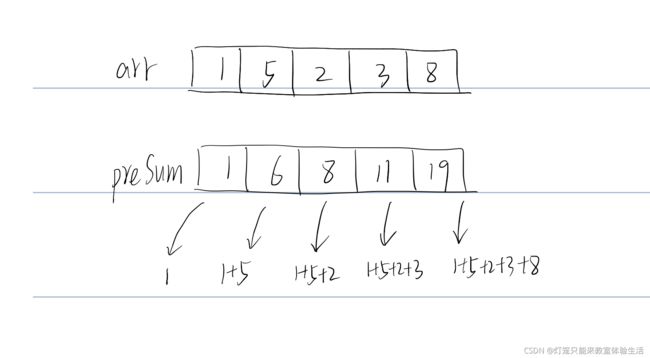
一个数组中,从【第一个元素】到【当前元素】的【数值和】,通常简写为preSum
有什么用?
能够快速查询一个数组中[L,R]范围内的【数值和】。
怎么用?
根据前缀和的定义,preSum[index]就是从数组在[0,index]范围上的【数值和】。
-
preSum[R] = arr[0] + arr[1] + … + arr[L] + … + arr[R]
-
preSum[R] = arr[0] + arr[1] + … + arr[L]
-
所以[L,R]上的数值和就是 :preSum[R]-preSum[L-1]。
-
要注意数组是否越界。
代码实现
输入的数据从1开始,而非0
#include 二维前缀和
是什么?
一个二维数组中,从【第一个元素】到【当前元素】范围内的【数值和】
有什么用?
给定【起点坐标】和【终点坐标】,能够快速查询两点范围内的【数值和】
怎么用?
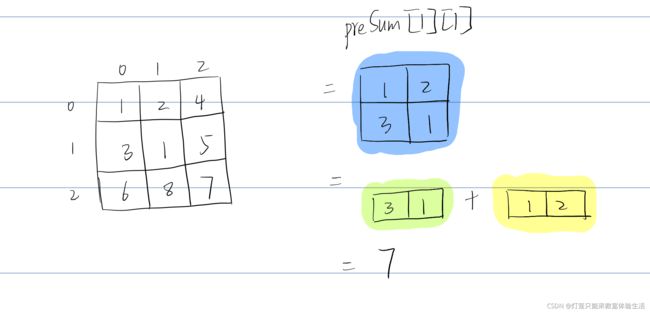
以上图举例:
-
对于某一行,比如第一行,【数值和】其实就是一维的前缀和,这个很好理解。
-
对于多行,比如前两行,相当于当前行的【一维前缀和】+上一行的一维【前缀和】。
- 此时再看看:起点为[1,1],终点为[2,2]的数值和

很清晰了:
假设:行为x轴,列为y轴,起点为(x1,y1),终点为(x2,y2)。
那起点到终点的数值和就是:
result = preSum[x2][y2] - preSum[x2][y1-1] - preSum[x1-1][y2] + preSum[x1-1][y1-1]
当然,要注意数组越界问题。
代码实现
输入的坐标原点是(1,1),符合用户直觉,而非(0,0)
/*
* 给定【起点坐标】和【终点坐标】返回两点范围内的【数值和】
*
* */
#include