深度学习之OCR识别
写在前面,最近两天在做ocr识别相关内容,趁有时间来记录一下。本文的代码是基于Pytorch框架mobilenetv3基础网络的CRNN+CTC网络实现
文字检测与识别介绍
文字识别也是图像领域一个常见问题。然而,对于自然场景图像,首先要定位图像中的文字位置,然后才能进行识别。
所以一般来说,从自然场景图片中进行文字识别,需要包括2个步骤:
在自然场景图片中的文字检测算法比较好用的有PSENET、DBNET等。
本文的重点是如何对已经定位好的文字区域图片进行识别,即假设之前已经文字检测算法已经定位图中的“subway”区域(红框),接下来就是文字识别。

文字识别
1. 背景介绍
基于RNN的文字识别算法主要有两个框架,本文主要介绍CRNN模型:
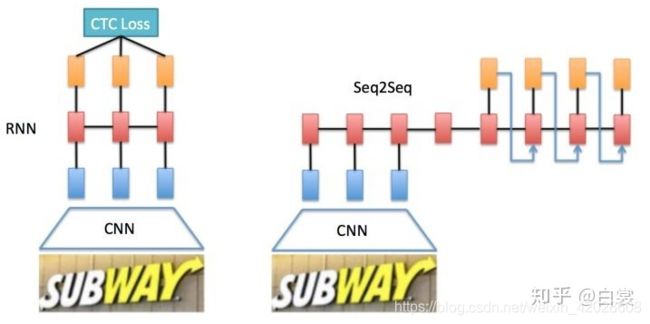
- CNN+RNN+CTC【CRNN】
- CNN+Seq2Seq+Attention【ED】
注:两种算法在使用过程中的发现:ED模型对英文识别效果会稍微好一些,但是在推理阶段耗时也更大。对于中文识别来说,两者效果相差不大,但CRNN相对来说解码阶段简单了很多,所以在中文识别方面,CRNN使用的更多些
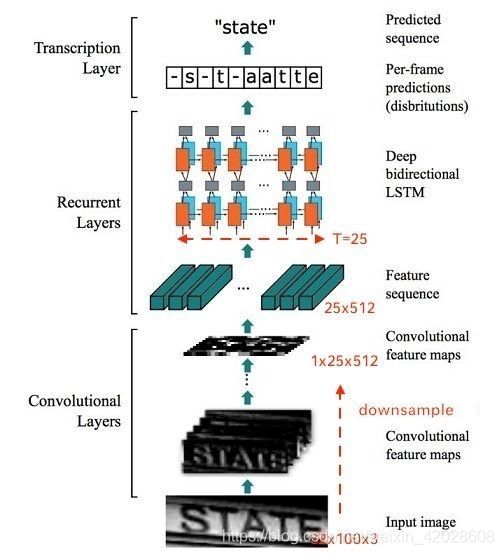
2. CRNN网络结构介绍
整个CRNN网络主要可以分为四个部分:
- Convlutional Layers
【输入:待识别图片(2, 32, 280),输出:图像卷积特征(2, 96, 1,70)】
这里用一个普通的CNN网络去提取图像特征,本文考虑到时间耗时和精度两方面因素,使用了Mobilenetv3,详细代码见下文
- Recurrent Layers & 3. Transcription Layers
【输入:图像卷积特征(2, 96, 1,70),输出:预测结果(70, 2, 90)】
这里用一个双向LSTM网络在卷积特征的基础上继续提取文字序列特征,对RNN的输出做softmax,来作为对应时序特征块的输出
- 计算loss or 解码
在训练阶段,将预测结果与gt做CTC loss;
在预测阶段,直接对预测结果进行解码
3. 基本设置
- 任务背景: 数据集icdar2015,提取所有出现字符,加一个blank共90个字符
- 图片大小:resize为32 * 280
- 网络输出:T =70(输入LSTM的数据的时间步, CNN 部分输出序列长度) * 90(一共90个不同的字符, 有多少字符此处数字为多少)
4. 网络构造
- RCNN整体模型
# RCNN模型
class RecModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super(RecModel, self).__init__()
self.algorithm = config['base']['algorithm']
self.backbone = create_module(config['backbone']['function'])(config['base']['pretrained'],config['base']['is_gray'])
self.head = create_module(config['head']['function'])(
use_conv=config['base']['use_conv'],
use_attention=config['base']['use_attention'],
use_lstm=config['base']['use_lstm'],
lstm_num=config['base']['lstm_num'],
inchannel=config['base']['inchannel'],
hiddenchannel=config['base']['hiddenchannel'],
classes=config['base']['classes'])
def forward(self, img):
x = self.backbone(img)
x = self.head(x)
return x
- 以mobilenet为backbone的模型
class MobileNetV3_Small(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, is_gray):
super(MobileNetV3_Small, self).__init__()
if(is_gray):
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
else:
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
self.hs1 = hswish()
self.bneck = nn.Sequential(
Block(3, 16, 16, 16, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(16), (2,1)),
Block(3, 16, 72, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 1),
Block(3, 24, 88, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, (2,1)),
Block(5, 24, 96, 40, hswish(), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(5, 40, 240, 40, hswish(), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(5, 40, 240, 40, hswish(), SeModule(40), 2),
Block(5, 40, 120, 48, hswish(), SeModule(48), 1),
Block(5, 48, 144, 48, hswish(), SeModule(48), (2,1)),
Block(5, 48, 288, 96, hswish(), SeModule(96), 1),
Block(5, 96, 576, 96, hswish(), SeModule(96), 1),
Block(5, 96, 576, 96, hswish(), SeModule(96), 1),
)
self.init_params()
def init_params(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.hs1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.bneck(out)
return out
- 以双向LSTM及全连接为head的结构
class BLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nHidden, nOut):
super(BLSTM, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(nIn, nHidden, bidirectional=True)
self.embedding = nn.Linear(nHidden * 2, nOut)
def forward(self, input):
recurrent, _ = self.rnn(input)
T, b, h = recurrent.size()
t_rec = recurrent.view(T * b, h)
output = self.embedding(t_rec) # [T * b, nOut]
output = output.view(T, b, -1)
return output
class CRNN_Head(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,use_conv=False,
use_attention=False,
use_lstm=True,
lstm_num=2,
inchannel=512,
hiddenchannel=128,
classes=1000):
super(CRNN_Head,self).__init__()
self.use_lstm = use_lstm
self.lstm_num = lstm_num
self.use_conv = use_conv
if use_attention:
self.attention = SeModule(inchannel)
self.use_attention = use_attention
if(use_lstm):
assert lstm_num>0 ,Exception('lstm_num need to more than 0 if use_lstm = True')
for i in range(lstm_num):
if(i==0):
if(lstm_num==1):
setattr(self, 'lstm_{}'.format(i + 1), BLSTM(inchannel, hiddenchannel,classes))
else:
setattr(self, 'lstm_{}'.format(i + 1), BLSTM(inchannel,hiddenchannel,hiddenchannel))
elif(i==lstm_num-1):
setattr(self, 'lstm_{}'.format(i + 1), BLSTM(hiddenchannel, hiddenchannel, classes))
else:
setattr(self, 'lstm_{}'.format(i + 1), BLSTM(hiddenchannel, hiddenchannel, hiddenchannel))
elif(use_conv):
self.out = nn.Conv2d(inchannel, classes, kernel_size=1, padding=0)
else:
self.out = nn.Linear(inchannel,classes)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
assert h == 1, "the height of conv must be 1"
x = x.squeeze(2)
x = x.permute(2, 0, 1) # [w, b, c]
if self.use_lstm:
for i in range(self.lstm_num):
x = getattr(self, 'lstm_{}'.format(i + 1))(x)
else:
x = self.out(x)
return x
- CTC Loss
from warpctc_pytorch import CTCLoss as PytorchCTCLoss
import torch.nn as nn
from .basical_loss import focal_ctc_loss
class CTCLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,config):
super(CTCLoss,self).__init__()
self.criterion = PytorchCTCLoss()
self.config = config
def forward(self,preds, labels, preds_size, labels_len):
loss = self.criterion(preds, labels, preds_size, labels_len)
if self.config['loss']['reduction']=='none':
loss = focal_ctc_loss(loss)
return loss/self.config['trainload']['batch_size']
criterion = CTCLoss()
loss = criterion(preds, labels, preds_size, labels_len)
# preds:网络输出,(70, 2, 90),即(T(特征步长), Bs(批次数), C(字符总数))
# labels: [14, 23, 54, 54, 72, 83, 74, 26, 58, 6, 50],即同一批次内合并所以的标签的对应词库id
# preds_size:[70, 70],即网络输出的结果,步长
# labels_len:[8, 3],即同一批次内每张图片对应的标签个数
- 预测阶段的解码
网络输出为 (32, 90 ), 解码先取每个位置的最大概率的字符index, index转str时,如果两个相同的index连续,那么合并为一个
例: 假设输出为: [1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 3, 0, 7, 7, 7, 0, 3, 3] , 由于后边全为0,只取前18位. 0 对应的字符是 ‘-’, 对于相邻的非0字符, 看做一个字符, 因此该例子为 [1,0,0,1,0,0,2,0,3,0,7,0,3], 再将0对应的blank 去掉, 则为实际的字符index为 [1,1,2,3,7,3]
参考:一文读懂CRNN+CTC文字识别
参考:pytorch-crnn实践以及内置ctc_loss使用小结
有想要代码的小伙伴请留言~