springboot监听器详解
上才艺:
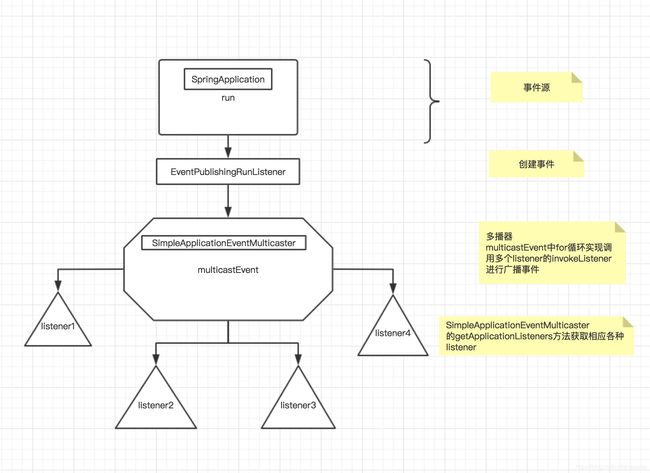
SpringApplication
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
//看这里
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
} SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);SpringApplicationRunListeners
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class mainApplicationClass) {
//看这里
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),
(step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
});
}EventPublishingRunListener
@Override
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
//看这里
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass()) ||
(event instanceof PayloadApplicationEvent &&
matchesClassCastMessage(msg, ((PayloadApplicationEvent) event).getPayload().getClass()))) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception.
Log loggerToUse = this.lazyLogger;
if (loggerToUse == null) {
loggerToUse = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
this.lazyLogger = loggerToUse;
}
if (loggerToUse.isTraceEnabled()) {
loggerToUse.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}源码结构
看不懂的继续看
透彻分析 设计模式----监听模式
整体感觉:
你得在某个地方(事件源),安装监听器,当发生(事件的时候),监听器会触发(其实就是调用监听器的方法)
如何实现所谓的“监听”:
调用监听器的方法
问你问题
1、你能把下边例子的代码对应到springboot源码上吗?
2、监听器为何要实现EventListener?固定格式:instantof判定该类和监听模式有关系
3、事件为何要继承EventObject?固定格式:instantof判定该类和监听模式有关系
4、具体哪个方法如何触发事件监听的动作?
/**
* 定义事件源
* @author administrator
*
*/
public class EventSource {
private List listeners = new ArrayList();
public EventSource() {
}
public void addDemoListener(DemoEventListener demoListener) {
listeners.add(demoListener);
}
public void notifyDemoEvent() {
for (DemoEventListener eventListener : listeners) {
DemoEvent demoEvent = new DemoEvent(this);
eventListener.processEvent(demoEvent);
}
}
} //事件
public class DemoEvent extends EventObject {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public DemoEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
}
}//监听器
public interface DemoEventListener extends EventListener {
public void processEvent(DemoEvent demoEvent);
}
public class FirstEventListener implements DemoEventListener {
@Override
public void processEvent(DemoEvent demoEvent) {
System.out.println("First event listener process event..."+demoEvent.getSource());
}
}
/**
* 测试监听器处理过程
* @author administrator
*
*/
public class DemoEventClient {
public static void main(String args[]) {
//定义事件源
EventSource eventSource = new EventSource();
//定义并向事件源中注册事件监听器
FirstEventListener firstEventListener = new FirstEventListener();
eventSource.addDemoListener(firstEventListener);
//定义并向事件源中注册事件监听器
SecondEventListener secondEventListener=new SecondEventListener();
eventSource.addDemoListener(secondEventListener);
//触发监听,事件通知
eventSource.notifyDemoEvent();
}
}