- 数据结构:链表和二叉树的应用和算法设计
鱼弦
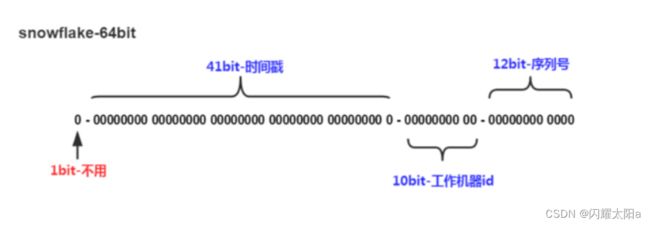
数据结构链表
鱼弦:CSDN内容合伙人、CSDN新星导师、全栈领域创作新星创作者、51CTO(Top红人+专家博主)、github开源爱好者(go-zero源码二次开发、游戏后端架构https://github.com/Peakchen)链表:链表是一种常见的线性数据结构,由一系列节点组成,每个节点包含数据和指向下一个节点的指针。链表的优势在于可以动态添加和删除元素,不需要预先分配固定大小的内存空间。链表常用于
- 双指针算法-day12(判断子序列)
拾零吖
力扣算法leetcode数据结构
1.判断子序列题目解析字符相等:双指针一起动,不相等:长字符串指针动;代码classSolution{public:boolisSubsequence(strings,stringt){//时间复杂度:O(m)//空间复杂度:O(1)intn=s.size(),m=t.size();inti=0,j=0;while(i&dictionary){stringans="";intn=ans.size(
- 算法-每日一题(DAY11)每日温度
浮灯Foden
数据结构与算法-每日一题算法c++开发语言数据结构面试leetcode
1.题目链接:739.每日温度-力扣(LeetCode)2.题目描述:给定一个整数数组temperatures,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组answer,其中answer[i]是指对于第i天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用0来代替。示例1:输入:temperatures=[73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]输出:[1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
- 快速排序的详解
分治策略:将大问题分解为小问题解决关键操作:选择基准(Pivot)并进行分区(Partition)递归处理:对分区后的子数组递归排序前言1.快速排序概述快速排序(QuickSort)是由英国计算机科学家TonyHoare于1960年提出的一种高效的分治排序算法。它在平均情况下的时间复杂度为O(nlogn),最坏情况下为O(n²)(但可通过优化避免),且是原地排序(不需要额外空间)。2.算法步骤详解
- python学智能算法(十六)|机器学习支持向量机简单示例
西猫雷婶
python学习笔记人工智能机器学习机器学习python支持向量机人工智能深度学习
【1】引言前序学习了逻辑回归等算法,相关文章链接包括且不限于:python学智能算法(十)|机器学习逻辑回归(Logistic回归)_逻辑回归算法python-CSDN博客python学智能算法(十一)|机器学习逻辑回归深入(Logistic回归)_np.random.logistic()-CSDN博客今天在此基础上更进一步,学习支持向量机,为实现较好地理解,先解读一个简单算例。【2】代码解读【2
- 算法-每日一题(DAY12)最长和谐子序列
浮灯Foden
数据结构与算法-每日一题算法数据结构leetcode哈希算法c++面试
1.题目链接:594.最长和谐子序列-力扣(LeetCode)2.题目描述:和谐数组是指一个数组里元素的最大值和最小值之间的差别正好是1。给你一个整数数组nums,请你在所有可能的子序列中找到最长的和谐子序列的长度。数组的子序列是一个由数组派生出来的序列,它可以通过删除一些元素或不删除元素、且不改变其余元素的顺序而得到。示例1:输入:nums=[1,3,2,2,5,2,3,7]输出:5解释:最长和
- Linux-读者写者问题
“αβ”
Linuxlinux运维服务器c++多线程git云服务器
目录问题描述读写锁主要思想代码伪实现读者优先算法写者优先算法读者写者公平算法库函数的学习读写锁接口读写锁使用案例问题描述在编写多线程的时候,有一种情况是十分常见的。那就是,有些公共数据修改的机会比较少。相比较改写,它们读的机会反而高的多。通常而言,在读的过程中,往往伴随着查找的操作,中间耗时很长。给这种代码段加锁,会极大地降低我们程序的效率。这类问题就归结为读者写者问题。那么有没有一种方法,可以专
- Github 2024-11-01 开源项目月报 Top19
老孙正经胡说
github开源Github趋势分析开源项目PythonGolang
根据GithubTrendings的统计,本月(2024-11-01统计)共有19个项目上榜。根据开发语言中项目的数量,汇总情况如下:开发语言项目数量Python项目9TypeScript项目3JavaScript项目3Svelte项目1JupyterNotebook项目1Ruby项目1HTML项目1Rust项目1Java项目1C++项目1Go项目1Python中的算法实现集合创建周期:2831天
- Leetcode-423. Reconstruct Original Digits from English
K_W
算法javaleetcode算法
前言:为了后续的实习面试,开始疯狂刷题,非常欢迎志同道合的朋友一起交流。因为时间比较紧张,目前的规划是先过一遍,写出能想到的最优算法,第二遍再考虑最优或者较优的方法。如有错误欢迎指正。博主首发CSDN,mcf171专栏。博客链接:mcf171的博客——————————————————————————————Givenanon-emptystringcontaininganout-of-orderE
- JVM垃圾回收调优知识点整理
图灵农场
个人笔记jvm
目录1、JVM内存模型1.2、堆及垃圾回收1.3、JVM参数设置经验:1.4、对象逃逸分析:2、类加载2.1、类加载过程:2.2、类加载器分类:2.3、类加载机制:2.4、打破双亲委派机制:3、JVM内存分配机制4、如何判断对象可以被回收4.1、引用计数法4.2、可达性分析算法4.3、常见引用类型4.4、finalize()方法最终判定对象是否存活4.5、如何判断一个类是无用的类5、垃圾收集算法5
- 彻头彻尾搞定JVM系列之五:JVM垃圾回收算法
慕枫技术笔记
JVM从入门到精通jvm
引言做C++开发的同学特别羡慕Java开发的同学,因为Java开发的同学在开发过程中不用手动去申请内存以及释放内存,因为JVM虚拟机会帮助我们进行垃圾回收,虽然有时候它可能会崩掉,但是至少比手动进行内存申请以及释放幸福的多。本篇文章主要介绍JVM的垃圾回收机制。一、什么是垃圾在探讨垃圾回收机制之前,我们先来搞清楚Java中的垃圾指的是什么。既然叫做垃圾,那肯定是没用的东西,没用的东西就需要进行回收
- JVM垃圾回收(笔记)
Coder-thinking
Javajvm笔记
文章目录完全垃圾回收其他垃圾回收类型垃圾回收器1.Serial垃圾回收器2.ParNew垃圾回收器3.ParallelScavenge垃圾回收器4.CMS(ConcurrentMarkSweep)垃圾回收器5.G1(GarbageFirst)垃圾回收器6.ZGC(ZGarbageCollector)和Shenandoah垃圾回收器垃圾回收算法1.标记-清除(Mark-Sweep)算法2.复制(Co
- MCU、LIN收发器、LIN总线、节点,它们之间是如何协作的?
Electron-er
汽车电子LIN总线通讯LIN总线单片机MCU
在LIN总线系统中,MCU(微控制器)、LIN收发器、LIN总线与节点通过分层协作实现数据通信。以下从硬件连接、通信流程、协议层级三方面解析它们的关系:一、硬件连接:从个体到网络的物理架构1.基础单元:节点的内部组成节点=MCU+LIN收发器+外围电路MCU:运行应用程序,处理数据逻辑(如传感器采样、控制算法)。LIN收发器(如TJA1020):实现TTL/CMOS电平与LIN总线电平的转换。外围
- 30、法律案例的关联检索:提升法律实践的信息处理能力
android
法律案例关联检索信息处理
法律案例的关联检索:提升法律实践的信息处理能力1.引言在当今信息爆炸的时代,法律从业者面临着前所未有的挑战。大量的法律案例、法规和判例使得信息检索变得复杂而耗时。为了提高工作效率和决策质量,法律从业者迫切需要一种高效的工具来发现和检索相互关联的法律案例。本文将探讨如何通过先进的信息检索技术和算法来实现这一点。2.关联模型关联模型是法律案例关联检索的核心。为了确定案例之间的关联性,通常采用以下几种模
- Halcon 初步了解
科学的发展-只不过是读大自然写的代码
图形编程c#视觉处理Halcon
1.Halcon概述Halcon是德国MVTec公司开发的一套完善的机器视觉算法包,也是一款功能强大的视觉处理软件,为工业自动化领域提供了全面的解决方案。它拥有应用广泛的机器视觉集成开发环境,提供了一套丰富的图像处理和机器视觉算法,可以在各种工业应用中进行图像分析、目标检测、测量、定位、识别等任务。Halcon的核心功能包括图像处理、特征提取与匹配、3D视觉、深度学习、条码识别、OCR识别以及视觉
- 边缘计算与 CDN 融合技术实践教程
快快网络-三七
云计算优化边缘计算人工智能
目录前言一、核心技术原理与架构设计1.1边缘计算与CDN协同架构1.2智能调度算法二、数据同步与一致性实现2.1边缘节点数据缓存机制2.2一致性哈希算法应用三、典型应用场景实践3.1实时视频直播优化3.2物联网数据处理四、部署与运维要点4.1容器化部署4.2监控与告警五、未来技术演进方向总结前言在互联网流量爆发式增长、低延迟应用场景不断涌现的背景下,边缘计算与CDN的融合已成为提升网络性能的核心技
- 基于MATLAB代码DWA算法的移动车路径规划
985计算机硕士
路径规划matlab算法android
基于MATLAB代码DWA算法的移动车路径规划,可实现动态避障和静态避障文章目录DWA(DynamicWindowApproach)是一种常用于移动机器人路径规划的局部路径规划算法。它通过在速度空间中采样,结合机器人的运动学约束和环境信息,选择最优的速度组合来实现避障和目标点导航。以下是一个基于DWA算法的MATLAB代码示例,用于实现移动车的路径规划:%DWA(DynamicWindowAppr
- 大学专业科普 | 计算机应用、视觉与算法
鸭鸭鸭进京赶烤
计算机应用
一、专业概述计算机应用专业是一门实践性很强的学科,专注于将计算机技术转化为实际应用,服务于各个行业和领域,为社会的数字化转型提供人才支撑。二、课程设置专业基础课程:包括计算机组成原理、操作系统、数据结构、计算机网络等,为学生构建坚实的理论基础。专业核心课程:聚焦于程序设计语言(如C、C++、Java、Python等)、数据库原理与应用、软件工程、Web前端开发等,使学生具备开发各类软件系统的能力。
- 【算法】动态规划 斐波那契类型: 740. 删除并获得点数
740.删除并获得点数中等题目给你一个整数数组nums,你可以对它进行一些操作。每次操作中,选择任意一个nums[i],删除它并获得nums[i]的点数。之后,你必须删除所有等于nums[i]-1和nums[i]+1的元素。开始你拥有0个点数。返回你能通过这些操作获得的最大点数。示例1:输入:nums=[3,4,2]输出:6解释:删除4获得4个点数,因此3也被删除。之后,删除2获得2个点数。总共获
- 【算法】动态规划 斐波那契类型: 198. 打家劫舍
等风来不如迎风去
算法/数据结构算法leetcode动态规划
198.打家劫舍中等你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警。给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你不触动警报装置的情况下,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。示例1:输入:[1,2,3,1]输出:4解释:偷窃1号房屋(金额=1),然后偷窃3号房屋(金
- 题解:二叉树的中序遍历(94.二叉树的中序遍历)
微白..
算法数据结构leetcode
题目描述给定一个二叉树的根节点root,返回它的中序遍历。解题思路二叉树的中序遍历是一种常见的树遍历方法。它按照访问左子树——根节点——右子树的顺序进行。本文将介绍三种实现二叉树中序遍历的方法:递归、迭代和Morris遍历,并详细分析每种方法的复杂度。方法一:递归思路与算法递归是最直观的中序遍历实现方式。中序遍历的特点是先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树。因此,可以通过递归函数来实现这一
- java opencv 数字识别算法_[机器学习]基于OpenCV实现最简单的数字识别
后期小雨
javaopencv数字识别算法
本文将基于OpenCV实现简单的数字识别。这里以游戏AngryBirds为例,通过以下几个主要步骤对其中右上角的分数部分进行自动识别。1.学习分类器根据训练样本,选取模型训练产生数字分类器。这里的样本可以是通用的数字样本库(如NIST等),也可以是针对应用场景而制作的专门训练样本。前者优在泛化性,后者强在准确率,当然常用做法是将这两者结合,即在通用数字库基础上做修改。另外这里由于模式并不复杂,计算
- OpenCV CUDA模块设备层-----双曲正切函数tanh()
村北头的码农
OpenCVopencv人工智能计算机视觉
操作系统:ubuntu22.04OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9IDE:VisualStudioCode编程语言:C++11算法描述OpenCV的CUDA模块(cudev)中的一个设备函数,用于在GPU上对uchar4类型的向量(如RGBA像素)进行双曲正切(hyperbolictangent)运算,并返回一个float4类型的结果。函数原型__device____forceinline__f
- 双指针题解——反转字符串【LeetCode】
潮_
我的学习记录双指针篇_刷题笔记开发语言数据结构算法leetcodepython
344.反转字符串一、算法逻辑(逐步通顺讲解每一步思路)该题要求将字符数组s原地反转,即不能使用额外数组,直接在输入数组上进行修改。✅1️⃣初始化双指针指针left指向起始位置(索引0);指针right指向末尾位置(索引len(s)-1);✅2️⃣使用双指针交换字符每次将s[left]与s[right]对换;然后将left向右移动一位,right向左移动一位;重复此过程,直到两个指针相遇或交叉(即
- 二叉树题解——二叉树的中序遍历【LeetCode】统一写法版本
94.二叉树的中序遍历一、算法逻辑(逐步通顺地讲解)这段代码的目标是实现中序遍历,即按照顺序:左子树→当前节点→右子树遍历整个二叉树,并返回节点值的列表。与常见的递归或传统栈方法不同,这里使用的是一种“统一写法”技巧,将“节点值访问”与“节点展开”分开处理,流程如下:1️⃣初始化结构使用一个栈保存待处理元素(可能是TreeNode或int);初始栈中放入整棵树的根节点;结果数组rst用来保存最终遍
- 算法学习day6----双指针-最长不重复子序列
阴暗老鼠人
学习
Givenanintegersequenceoflengthn,pleasefindthelongestcontinuousintervalwithoutduplicatenumbersandoutputitslength.Thefirstlinecontainsanintegern.Thesecondlinecontainsnintegers(allwithintherangeof0to105)
- 刷题巩固-----DAY6(最长上升子序列和)
一颗铜豌豆
刷题巩固算法c++
题目链接活动-AcWing本课程系统讲解常用算法与数据结构的应用方式与技巧。https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1018/这道题是最后一道刷的lis题,下周开始刷背包九讲这道题的题目虽然有最长上升子序列,但是却不是用最长上升子序列的办法来做的,因为要求从一个上升子序列的和最大,感觉更像01背包的做法解题代码为#includeusingnamespacest
- OpenCV CUDA模块设备层-----二值化阈值操作函数thresh_binary_func()
操作系统:ubuntu22.04OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9IDE:VisualStudioCode编程语言:C++11算法描述OpenCV的CUDA模块(cudev)中的一个设备和主机通用函数(host/devicefunction),用于创建一个二值化阈值操作函数对象(functor)。这个函数返回一个仿函数(functor),用于在GPU上执行二值化阈值处理(ThresholdBin
- Keras环境复现代码(三)
yanyiche_
keras深度学习人工智能
DQN雅达利Breakout强化学习实验要求明确实验目的:学习和实现深度Q学习(DQN),这是一种结合了Q学习和深度神经网络的强化学习算法,用于解决复杂的决策问题。清楚实验原理:1、深度Q学习(DeepQ-Network)将卷积神经网络与Q学习结合,解决高维视觉输入的强化学习问题:2、经验回放:将状态转换存储到缓冲区,打破数据相关性,稳定训练。3、目标网络:定期更新目标Q值计算网络,减少训练中的目
- Keras环境复现代码(二)
yanyiche_
Keras机器学习人工智能
PPOCartPole控制算法实践实验要求明确实验目的:学习和实现PPO算法,这是一种改进的策略梯度方法,通过限制策略更新的幅度来提高训练的稳定性。清楚实验原理:PPO算法是一种基于策略梯度的强化学习算法,它旨在解决传统策略梯度方法(如REINFORCE算法)在训练过程中可能出现的策略更新不稳定问题。PPO算法通过引入一种新的策略更新机制,限制每次更新的幅度,从而提高训练的稳定性和效率。PPO算法
- windows下源码安装golang
616050468
golang安装golang环境windows
系统: 64位win7, 开发环境:sublime text 2, go版本: 1.4.1
1. 安装前准备(gcc, gdb, git)
golang在64位系
- redis批量删除带空格的key
bylijinnan
redis
redis批量删除的通常做法:
redis-cli keys "blacklist*" | xargs redis-cli del
上面的命令在key的前后没有空格时是可以的,但有空格就不行了:
$redis-cli keys "blacklist*"
1) "blacklist:12:
[email protected]
- oracle正则表达式的用法
0624chenhong
oracle正则表达式
方括号表达示
方括号表达式
描述
[[:alnum:]]
字母和数字混合的字符
[[:alpha:]]
字母字符
[[:cntrl:]]
控制字符
[[:digit:]]
数字字符
[[:graph:]]
图像字符
[[:lower:]]
小写字母字符
[[:print:]]
打印字符
[[:punct:]]
标点符号字符
[[:space:]]
- 2048源码(核心算法有,缺少几个anctionbar,以后补上)
不懂事的小屁孩
2048
2048游戏基本上有四部分组成,
1:主activity,包含游戏块的16个方格,上面统计分数的模块
2:底下的gridview,监听上下左右的滑动,进行事件处理,
3:每一个卡片,里面的内容很简单,只有一个text,记录显示的数字
4:Actionbar,是游戏用重新开始,设置等功能(这个在底下可以下载的代码里面还没有实现)
写代码的流程
1:设计游戏的布局,基本是两块,上面是分
- jquery内部链式调用机理
换个号韩国红果果
JavaScriptjquery
只需要在调用该对象合适(比如下列的setStyles)的方法后让该方法返回该对象(通过this 因为一旦一个函数称为一个对象方法的话那么在这个方法内部this(结合下面的setStyles)指向这个对象)
function create(type){
var element=document.createElement(type);
//this=element;
- 你订酒店时的每一次点击 背后都是NoSQL和云计算
蓝儿唯美
NoSQL
全球最大的在线旅游公司Expedia旗下的酒店预订公司,它运营着89个网站,跨越68个国家,三年前开始实验公有云,以求让客户在预订网站上查询假期酒店时得到更快的信息获取体验。
云端本身是用于驱动网站的部分小功能的,如搜索框的自动推荐功能,还能保证处理Hotels.com服务的季节性需求高峰整体储能。
Hotels.com的首席技术官Thierry Bedos上个月在伦敦参加“2015 Clou
- java笔记1
a-john
java
1,面向对象程序设计(Object-oriented Propramming,OOP):java就是一种面向对象程序设计。
2,对象:我们将问题空间中的元素及其在解空间中的表示称为“对象”。简单来说,对象是某个类型的实例。比如狗是一个类型,哈士奇可以是狗的一个实例,也就是对象。
3,面向对象程序设计方式的特性:
3.1 万物皆为对象。
- C语言 sizeof和strlen之间的那些事 C/C++软件开发求职面试题 必备考点(一)
aijuans
C/C++求职面试必备考点
找工作在即,以后决定每天至少写一个知识点,主要是记录,逼迫自己动手、总结加深印象。当然如果能有一言半语让他人收益,后学幸运之至也。如有错误,还希望大家帮忙指出来。感激不尽。
后学保证每个写出来的结果都是自己在电脑上亲自跑过的,咱人笨,以前学的也半吊子。很多时候只能靠运行出来的结果再反过来
- 程序员写代码时就不要管需求了吗?
asia007
程序员不能一味跟需求走
编程也有2年了,刚开始不懂的什么都跟需求走,需求是怎样就用代码实现就行,也不管这个需求是否合理,是否为较好的用户体验。当然刚开始编程都会这样,但是如果有了2年以上的工作经验的程序员只知道一味写代码,而不在写的过程中思考一下这个需求是否合理,那么,我想这个程序员就只能一辈写敲敲代码了。
我的技术不是很好,但是就不代
- Activity的四种启动模式
百合不是茶
android栈模式启动Activity的标准模式启动栈顶模式启动单例模式启动
android界面的操作就是很多个activity之间的切换,启动模式决定启动的activity的生命周期 ;
启动模式xml中配置
<activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:launchMode="standard&quo
- Spring中@Autowired标签与@Resource标签的区别
bijian1013
javaspring@Resource@Autowired@Qualifier
Spring不但支持自己定义的@Autowired注解,还支持由JSR-250规范定义的几个注解,如:@Resource、 @PostConstruct及@PreDestroy。
1. @Autowired @Autowired是Spring 提供的,需导入 Package:org.springframewo
- Changes Between SOAP 1.1 and SOAP 1.2
sunjing
ChangesEnableSOAP 1.1SOAP 1.2
JAX-WS
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 0: Primer (Second Edition)
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 1: Messaging Framework (Second Edition)
SOAP Version 1.2 Part 2: Adjuncts (Second Edition)
Which style of WSDL
- 【Hadoop二】Hadoop常用命令
bit1129
hadoop
以Hadoop运行Hadoop自带的wordcount为例,
hadoop脚本位于/home/hadoop/hadoop-2.5.2/bin/hadoop,需要说明的是,这些命令的使用必须在Hadoop已经运行的情况下才能执行
Hadoop HDFS相关命令
hadoop fs -ls
列出HDFS文件系统的第一级文件和第一级
- java异常处理(初级)
白糖_
javaDAOspring虚拟机Ajax
从学习到现在从事java开发一年多了,个人觉得对java只了解皮毛,很多东西都是用到再去慢慢学习,编程真的是一项艺术,要完成一段好的代码,需要懂得很多。
最近项目经理让我负责一个组件开发,框架都由自己搭建,最让我头疼的是异常处理,我看了一些网上的源码,发现他们对异常的处理不是很重视,研究了很久都没有找到很好的解决方案。后来有幸看到一个200W美元的项目部分源码,通过他们对异常处理的解决方案,我终
- 记录整理-工作问题
braveCS
工作
1)那位同学还是CSV文件默认Excel打开看不到全部结果。以为是没写进去。同学甲说文件应该不分大小。后来log一下原来是有写进去。只是Excel有行数限制。那位同学进步好快啊。
2)今天同学说写文件的时候提示jvm的内存溢出。我马上反应说那就改一下jvm的内存大小。同学说改用分批处理了。果然想问题还是有局限性。改jvm内存大小只能暂时地解决问题,以后要是写更大的文件还是得改内存。想问题要长远啊
- org.apache.tools.zip实现文件的压缩和解压,支持中文
bylijinnan
apache
刚开始用java.util.Zip,发现不支持中文(网上有修改的方法,但比较麻烦)
后改用org.apache.tools.zip
org.apache.tools.zip的使用网上有更简单的例子
下面的程序根据实际需求,实现了压缩指定目录下指定文件的方法
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWrit
- 读书笔记-4
chengxuyuancsdn
读书笔记
1、JSTL 核心标签库标签
2、避免SQL注入
3、字符串逆转方法
4、字符串比较compareTo
5、字符串替换replace
6、分拆字符串
1、JSTL 核心标签库标签共有13个,
学习资料:http://www.cnblogs.com/lihuiyy/archive/2012/02/24/2366806.html
功能上分为4类:
(1)表达式控制标签:out
- [物理与电子]半导体教材的一个小问题
comsci
问题
各种模拟电子和数字电子教材中都有这个词汇-空穴
书中对这个词汇的解释是; 当电子脱离共价键的束缚成为自由电子之后,共价键中就留下一个空位,这个空位叫做空穴
我现在回过头翻大学时候的教材,觉得这个
- Flashback Database --闪回数据库
daizj
oracle闪回数据库
Flashback 技术是以Undo segment中的内容为基础的, 因此受限于UNDO_RETENTON参数。要使用flashback 的特性,必须启用自动撤销管理表空间。
在Oracle 10g中, Flash back家族分为以下成员: Flashback Database, Flashback Drop,Flashback Query(分Flashback Query,Flashbac
- 简单排序:插入排序
dieslrae
插入排序
public void insertSort(int[] array){
int temp;
for(int i=1;i<array.length;i++){
temp = array[i];
for(int k=i-1;k>=0;k--)
- C语言学习六指针小示例、一维数组名含义,定义一个函数输出数组的内容
dcj3sjt126com
c
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int * p; //等价于 int *p 也等价于 int* p;
int i = 5;
char ch = 'A';
//p = 5; //error
//p = &ch; //error
//p = ch; //error
p = &i; //
- centos下php redis扩展的安装配置3种方法
dcj3sjt126com
redis
方法一
1.下载php redis扩展包 代码如下 复制代码
#wget http://redis.googlecode.com/files/redis-2.4.4.tar.gz
2 tar -zxvf 解压压缩包,cd /扩展包 (进入扩展包然后 运行phpize 一下是我环境中phpize的目录,/usr/local/php/bin/phpize (一定要
- 线程池(Executors)
shuizhaosi888
线程池
在java类库中,任务执行的主要抽象不是Thread,而是Executor,将任务的提交过程和执行过程解耦
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
public class RunMain implements Executor{
@Override
pub
- openstack 快速安装笔记
haoningabc
openstack
前提是要配置好yum源
版本icehouse,操作系统redhat6.5
最简化安装,不要cinder和swift
三个节点
172 control节点keystone glance horizon
173 compute节点nova
173 network节点neutron
control
/etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward =
- 从c面向对象的实现理解c++的对象(二)
jimmee
C++面向对象虚函数
1. 类就可以看作一个struct,类的方法,可以理解为通过函数指针的方式实现的,类对象分配内存时,只分配成员变量的,函数指针并不需要分配额外的内存保存地址。
2. c++中类的构造函数,就是进行内存分配(malloc),调用构造函数
3. c++中类的析构函数,就时回收内存(free)
4. c++是基于栈和全局数据分配内存的,如果是一个方法内创建的对象,就直接在栈上分配内存了。
专门在
- 如何让那个一个div可以拖动
lingfeng520240
html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml
- 第10章 高级事件(中)
onestopweb
事件
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- 计算两个经纬度之间的距离
roadrunners
计算纬度LBS经度距离
要解决这个问题的时候,到网上查了很多方案,最后计算出来的都与百度计算出来的有出入。下面这个公式计算出来的距离和百度计算出来的距离是一致的。
/**
*
* @param longitudeA
* 经度A点
* @param latitudeA
* 纬度A点
* @param longitudeB
*
- 最具争议的10个Java话题
tomcat_oracle
java
1、Java8已经到来。什么!? Java8 支持lambda。哇哦,RIP Scala! 随着Java8 的发布,出现很多关于新发布的Java8是否有潜力干掉Scala的争论,最终的结论是远远没有那么简单。Java8可能已经在Scala的lambda的包围中突围,但Java并非是函数式编程王位的真正觊觎者。
2、Java 9 即将到来
Oracle早在8月份就发布
- zoj 3826 Hierarchical Notation(模拟)
阿尔萨斯
rar
题目链接:zoj 3826 Hierarchical Notation
题目大意:给定一些结构体,结构体有value值和key值,Q次询问,输出每个key值对应的value值。
解题思路:思路很简单,写个类词法的递归函数,每次将key值映射成一个hash值,用map映射每个key的value起始终止位置,预处理完了查询就很简单了。 这题是最后10分钟出的,因为没有考虑value为{}的情