【代码随想录】DAY 4 链表Ⅱ(交换链表节点、删除链表节点、链表相交、环形链表)
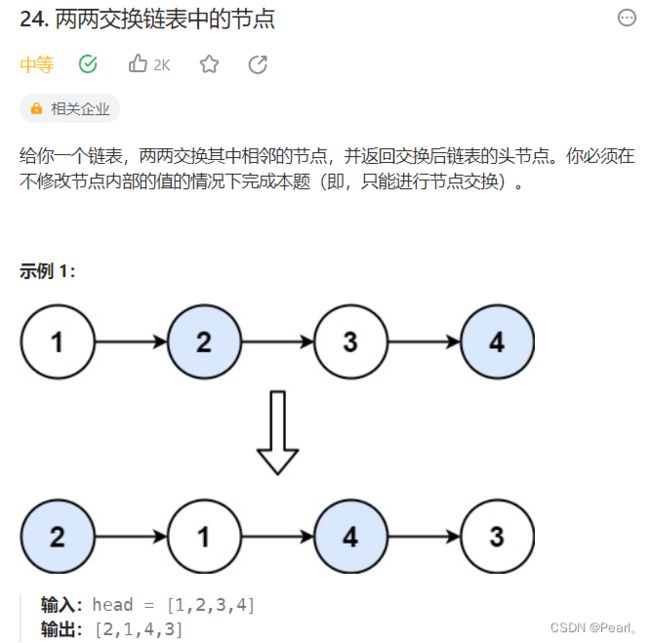
第一题
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
学习记录:
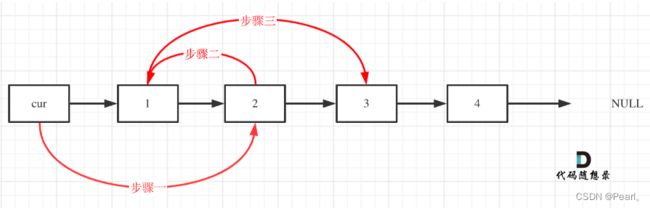
这个图非常重要,记住这两个图然后按照步骤1、2、3走就行了,其中cur每次循环移动两个节点,因为需要从前一次交换后的尾节点重新指向下一对要交换的节点,因此每次交换时cur都指向需要衔接上的那个节点。
此外猜测终止条件应该是看循环体内赋值符号右边的指针有哪些,不然会报错。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy_node = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur_node = dummy_node;
dummy_node->next = head;
while (cur_node->next != nullptr && cur_node->next->next !=nullptr) {
ListNode* temp = cur_node->next; //存节点1
ListNode* temp1 = cur_node->next->next->next; //存节点3
cur_node->next = cur_node->next->next; //步骤1
cur_node->next->next = temp; //步骤2
cur_node->next->next->next = temp1; //步骤3
cur_node = cur_node->next->next; //移动cur到该交换后的尾节点
}
return dummy_node->next;
}
};复习:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyNode = new ListNode();
dummyNode->next = head;
ListNode* curNode = dummyNode;
while (curNode->next != nullptr && curNode->next->next != nullptr) {
ListNode* temp1 = curNode->next; //记录节点1
ListNode* temp3 = temp1->next->next; //记录节点3
curNode->next = curNode->next->next; //dummy->2
curNode->next->next = temp1; //2->1
curNode->next->next->next = temp3; //1->3
curNode = curNode->next->next;
}
return dummyNode->next;
}
};第二题
力扣
我想的是先统计出整个链表的长度,然后再计算出从前往后数的索引值就行。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
int size = 0;
ListNode* dummy_node = new ListNode(0);
dummy_node->next = head;
ListNode* cur_node1 = dummy_node;
ListNode* cur_node2 = dummy_node;
while (cur_node1->next != nullptr) {
size++;
cur_node1 = cur_node1->next;
}
int diff = size-n;
while (diff--) {
cur_node2 = cur_node2->next;
}
cur_node2->next = cur_node2->next->next;
return dummy_node->next;
}
};已AC,第二道AC的......
学习记录:
快慢指针法:定义两个指针,俩指针相差n个节点,当快指针指向尾节点时,慢指针也就指向了待删除节点的前一个,就可以进行删除操作了(有点像固定窗口长度的滑动窗口)。
看了题解以后写的:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy_node = new ListNode(0);
dummy_node->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummy_node;
ListNode* slow = dummy_node;
while (n--) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast->next != nullptr){
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return dummy_node->next;
}
};复习:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode();
dummy->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummy;
ListNode* slow = dummy;
while (n--) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast->next != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
};第三题
力扣(LeetCode)官网 - 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台
思路就是将短的链表和长的链表从尾端对齐,因为如果两个链表从某个点开始相交,则表示后面的一整串都相交,那么尾端对齐后再比较前一个节点的next指向是否一致就行了。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* dummy_node1 = new ListNode(0);
dummy_node1->next = headA;
ListNode* dummy_node2 = new ListNode(0);
dummy_node2->next = headB;
ListNode* cur_node1 = dummy_node1;
ListNode* cur_node2 = dummy_node2;
ListNode* size_node1 = dummy_node1;
ListNode* size_node2 = dummy_node2;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
while (size_node1->next != nullptr) {
lenA++;
size_node1 = size_node1->next;
}
while (size_node2->next != nullptr) {
lenB++;
size_node2 = size_node2->next;
}
if (lenA >= lenB) {
int diff = lenA - lenB;
while (diff--) {
cur_node1 = cur_node1->next;
}
while (lenB--) {
if (cur_node1->next == cur_node2->next) {
return cur_node2->next;
}
cur_node1 = cur_node1->next;
cur_node2 = cur_node2->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
else if (lenA < lenB) {
int diff = lenB - lenA;
while (diff--) {
cur_node2 = cur_node2->next;
}
while (lenA--) {
if (cur_node1->next == cur_node2->next) {
return cur_node1->next;
}
cur_node1 = cur_node1->next;
cur_node2 = cur_node2->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
return nullptr;
}
};复习:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
if (headA == nullptr || headB == nullptr) return nullptr;
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != nullptr) {
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while (curB != nullptr) {
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if (lenA > lenB) { //B为长链表,A为短链表
swap(curA, curB);
swap(lenA, lenB);
}
int diff = lenB - lenA;
while (diff--) {
curB = curB->next;
}
while (curA != nullptr) {
if (curA == curB) break;
else {
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
}
return curA;
}
};第四题
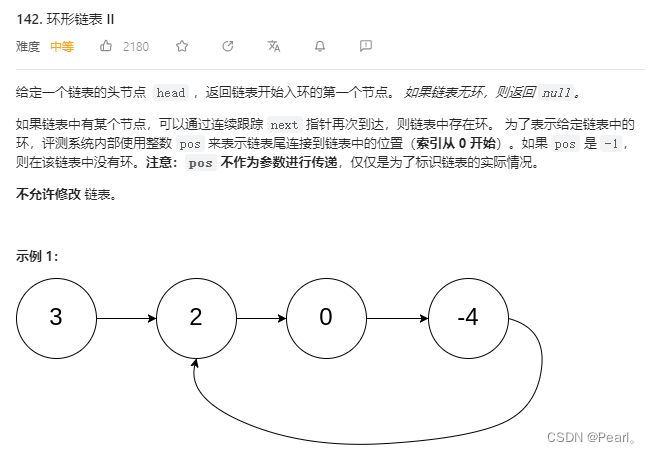
力扣
想到了判断有环和找入环节点两步走,但是实际写起来一脸蒙。。。
学习记录:
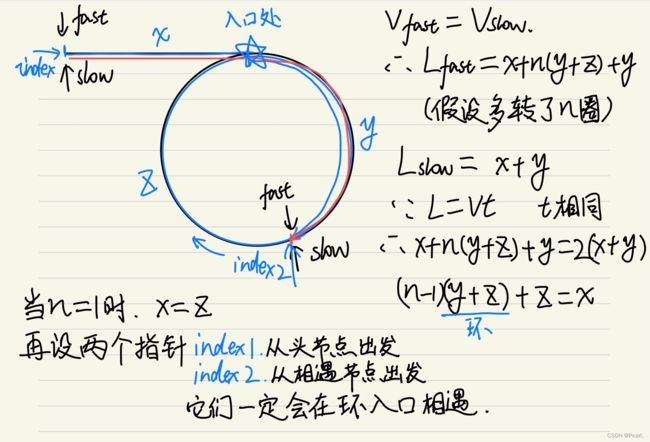
1、判断是否有环:快慢指针,快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,那么在有环的情况下快慢指针一定能相遇。如果快指针走三步,可能会跳过去。
2、找到环的入口:因为快指针走的比慢指针快,所以俩指针相遇一定是在环里,且慢指针是被快指针“套圈”,且一定是没走满第一圈的时候就被快指针第一次追上(因为快指针的速度是慢指针的两倍),具体思路如下图:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) { //这里貌似是一个固定写法
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode* index2 = fast;
ListNode* index1 = head;
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};复习:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) {
ListNode* index1 = head;
ListNode* index2 = slow;
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};