链表例题小总结:
链表:
第一种题型:双指针
力扣203:移除链表元素
力扣题目链接
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例 1: 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2: 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]
示例 3: 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
代码: 用的是双指针,而且是快慢指针算法。
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 因为删除可能涉及到头节点,所以设置dummy节点,统一操作
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
力扣206:反转链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
题意:反转一个单链表。
示例: 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
代码:思路依旧还是双指针,只是需要多加一个变量,来保存下一个指针。
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;// 保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return prev;
}
}
力扣19:删除链表的倒数第N个节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5] 示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1 输出:[] 示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1 输出:[1]
思路:还是双指针,依旧是快慢指针
代码:
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n){
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode fastIndex = dummyNode;
ListNode slowIndex = dummyNode;
//只要快慢指针相差 n 个结点即可
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
}
while (fastIndex.next != null){
fastIndex = fastIndex.next;
slowIndex = slowIndex.next;
}
//此时 slowIndex 的位置就是待删除元素的前一个位置。
//具体情况可自己画一个链表长度为 3 的图来模拟代码来理解
slowIndex.next = slowIndex.next.next;
return dummyNode.next;
}
第二种题型:哈希表
力扣02.07:链表相交
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
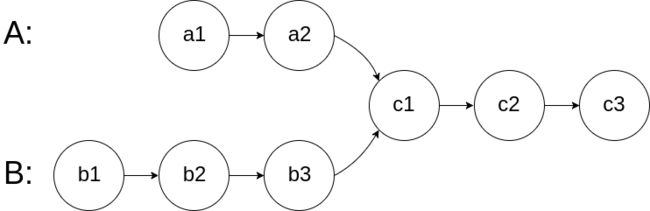
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交**:**
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
代码: 暴力循环即可
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
while(curA!=null){
while(curB!=null){
if(curB == curA){
return curB;
}
curB =curB.next;
}
curB = headB; //重置B节点
curA=curA.next;
}
return null;
}
}
哈希表的方式
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
while(curA!=null){
set.add(curA);
curA = curA.next;
}
while(curB!=null){
if(!set.add(curB)){
return curB;
}
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
力扣142:环形链表II
力扣题目链接
题意: 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
思路:这道题的思路就是哈希表 双指针的太麻烦了。
代码:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur!=null){
if(!set.add(cur)) return cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
}
第三种题型:递归
力扣24:两两交换链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
思路:递归最简单
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode t1 = head.next;
ListNode t2 = head.next.next;
t1.next = head;
head.next = swapPairs(t2);
return t1;
}