- C++ 设计模式:抽象工厂(Abstract Factory)
冀晓武
C++设计模式c++设计模式抽象工厂模式
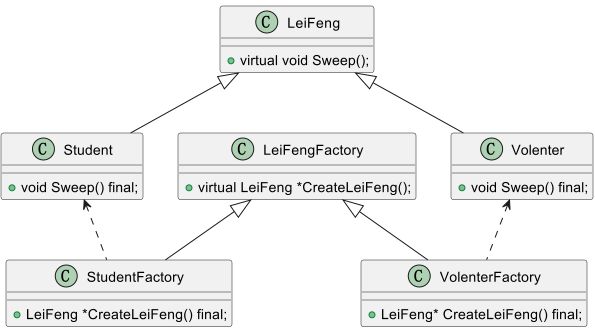
链接:C++设计模式链接:C++设计模式-工厂方法链接:C++设计模式-原型模式链接:C++设计模式-建造者模式抽象工厂(AbstractFactory)是一种创建型设计模式,它提供一个接口,用于创建一系列相关或相互依赖的对象,而无需指定它们的具体类。抽象工厂模式通常用于创建一组相关的产品对象,例如不同类型的机器人和它们的配件。1.问题分析在某些情况下,我们需要创建一组相关或相互依赖的对象,但我们
- C++设计模式:简单工厂、工厂方法、抽象工厂
起个别名
C++算法c++
1.工厂模式的特点在我们现实生活中,买馒头和自己蒸馒头、去饭店点一份大盘鸡和自己养鸡,杀鸡,做大盘鸡,这是全然不同的两种体验:自己做麻烦,而且有失败的风险,需要自己承担后果。买现成的,可以忽略制作细节,方便快捷并且无风险,得到的肯定是美味的食物。对于后者,就相当于是一个加工厂,通过这个工厂我们就可以得到想要的东西,在程序设计中,这种模式就叫做工厂模式,工厂生成出的产品就是某个类的实例,也就是对象。
- Java特性之设计模式【责任链模式】
Naijia_OvO
Java特性java设计模式责任链模式
一、责任链模式概述顾名思义,责任链模式(ChainofResponsibilityPattern)为请求创建了一个接收者对象的链。这种模式给予请求的类型,对请求的发送者和接收者进行解耦。这种类型的设计模式属于行为型模式在这种模式中,通常每个接收者都包含对另一个接收者的引用。如果一个对象不能处理该请求,那么它会把相同的请求传给下一个接收者,依此类推主要解决:职责链上的处理者负责处理请求,客户只需要将
- RocketMQ 基础教程-应用篇-死信队列
码炫课堂-码哥
rocketmq专题rocketmqjava
作者简介:大家好,我是smart哥,前中兴通讯、美团架构师,现某互联网公司CTO联系qq:184480602,加我进群,大家一起学习,一起进步,一起对抗互联网寒冬学习必须往深处挖,挖的越深,基础越扎实!阶段1、深入多线程阶段2、深入多线程设计模式阶段3、深入juc源码解析阶段4、深入jdk其余源码解析
- Java设计模式实战:高频场景解析与避坑指南
mckim_
笔记学习java设计模式
引言设计模式是软件开发的基石,但许多开发者面对23种模式时容易陷入“学完就忘”或“滥用模式”的困境。本文从工业级项目视角出发,精选10种高频设计模式,结合真实代码案例与主流框架应用,帮你建立模式思维,拒绝纸上谈兵。一、创建型模式:告别new的暴力美学1.工厂方法模式(FactoryMethod)核心痛点:对象创建逻辑散落各处,难以统一管理。场景案例:电商平台需要支持多种支付方式(支付宝、微信、银联
- OkHttp3源码解析--设计模式,android开发实习面试题
this.cache=builder.cache;}//构造者publicstaticfinalclassBuilder{Cachecache;…//构造cache属性值publicBuildercache(@NullableCachecache){this.cache=cache;returnthis;}//在build方法中真正创建OkHttpClient对象,并传入前面构造的属性值publi
- C# 设计模式(结构型模式):组合模式
硅谷调试员
玩转C#设计模式c#设计模式组合模式
C#设计模式(结构型模式):组合模式在软件设计中,有时我们需要处理的是一组对象,而这些对象既可以是单独的元素,也可以是由多个子元素组成的复合体。这时,组合模式(CompositePattern)便能提供帮助。它允许客户端将单个对象和对象集合统一对待,从而简化了树形结构的管理。1.组合模式的定义组合模式是一个结构型设计模式,主要用于将多个对象组合成树形结构,以表示“部分-整体”的层次关系。通过组合模
- OkHttp3源码解析--设计模式
2401_84413396
程序员设计模式
}//在创建OkHttpClient的时候OkHttpClientclient=newOkHttpClient.Builder().cache(/创建cache对象/).build();工厂模式====直接看代码:publicinterfaceCallextendsCloneable{Requestrequest();Responseexecute()throwsIOException;voide
- C#中的设计模式:构建更加优雅的代码
Envyᥫᩣᩚ
c#开发语言
C#在面向对象编程(OOP)方面的强大支持,我们可以探讨“C#中的设计模式”。这不仅有助于理解如何更好地组织代码,还能提高代码的可维护性和可扩展性。引言设计模式是软件工程中经过实践验证的解决方案模板,它们提供了一种标准化的方法来解决常见的开发问题。对于使用C#进行开发的程序员来说,理解和应用这些模式可以帮助创建结构良好、易于维护和扩展的应用程序。本文将介绍几种常用的设计模式,并展示如何用C#实现它
- 设计模式(行为型)-责任链模式
找了一圈尾巴
#设计模式设计模式责任链模式
定义责任链模式的核心定义是:使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系。将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止。这一模式的本质是建立一个灵活的处理流程,让请求在不同的处理器之间流转,每个处理器根据自身职责决定是否处理请求,或者将其传递给下一个处理器。从本质上来说,责任链模式模拟了现实生活中的“逐级上报”或“分工协作”机制。比如在公司中,一
- 开发高效的寝室卫生管理系统
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:寝室卫生管理系统是一款利用JavaWeb技术开发的软件,涉及JSP、MySQL数据库和Servlet等关键组件,旨在管理寝室卫生状况。系统提供了一个实用的学习平台,便于初学者掌握这些核心技术并理解JavaWeb架构。具体实现包括用户模块、寝室管理、卫生检查、评分系统、报表统计及权限控制,同时强调了MVC设计模式和安全性的重要性。1.JavaWeb技术与寝室卫生
- MVVMDemo:一款现代Android开发的最佳实践示例
MVVMDemo:一款现代Android开发的最佳实践示例本文将向您介绍项目,这是一个基于MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel)架构模式的Android应用实例,旨在帮助开发者更好地理解和应用这一流行的软件设计模式。项目概述MVVMDemo是由zhouxu88维护的一个开源项目,它展示了如何在Android平台上有效地实施MVVM架构。此项目包括了基本的数据绑定、LiveData观测
- Java设计模式之行为型模式(策略模式)介绍与说明
爪哇手记
#Java知识点java设计模式策略模式
一、策略模式简介策略模式(StrategyPattern)是一种行为型设计模式,它定义了一系列算法,并将每个算法封装起来,使它们可以相互替换,且算法的变化不会影响使用算法的客户。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而变化,属于对象行为型模式。其核心思想是将算法的定义与使用分离,通过接口或抽象类来定义算法族,具体算法实现由具体策略类完成,客户端可以根据需要选择合适的策略。二、策略模式的结构抽象策略(St
- 设计模式 — 行为型模式 — 责任链模式
范桂飓
架构师之路专栏python责任链模式开发语言
目录文章目录目录责任链模式应用场景代码示例责任链模式责任链模式,将多个处理方法连接成一条链条,请求将在这条链条上流动直到该链条中有一个节点可以处理该请求。通常这条链条是一个对象包含对另一个对象的引用而形成链条,每个节点有对请求的条件,当不满足条件将传递给下一个节点处理。责任链模式有几个要点:一个对象中含有另一个对象的引用以此类推形成链条。每个对象中应该有明确的责任划分,即处理请求的条件。链条的最后
- 【行为型模式】责任链模式
陈宝子
设计模式java设计模式责任链模式
文章目录1、简介2、结构3、实现方式3.1、案例引入3.2、结构分析3.3、具体实现4、责任链优缺点5、应用场景1、简介责任链模式(ChainofResponsibility)是一种行为型设计模式,它允许对象在链上依次处理请求,用户只需要将请求发送到责任链上即可,无须关心请求的处理细节和请求的传递,从而避免了请求发送者和接收者之间的直接耦合。具体来说,当一个请求进入责任链时,每个对象都有机会对该请
- 抽象类与接口:Java面向对象设计的两大支柱
一、学习抽象类与接口的必要性在Java面向对象设计中,抽象类和接口是构建可扩展、可维护系统的基石:抽象类:实现代码复用与框架设计的核心工具接口:定义系统契约与实现多继承特性的关键机制模板方法模式:通过抽象类实现算法框架的经典设计模式掌握这些概念能帮助开发者:设计灵活可扩展的系统架构实现代码复用与多态的优雅结合适应Java版本演进带来的新特性二、抽象类详解2.1抽象类核心特性publicabstra
- UI自动化测试 - POM设计模式
什么鬼昵称
selenium自动化设计模式
一、介绍基于selenium的ui自动化测试核心上只要定位到元素,对元素执行相应的操作即可。例如下面的脚本代码:打开Chrome浏览器,在百度页面搜索自动化测试:fromseleniumimportwebdriverimporttimedriver=webdriver.chrome()driver.implicitly_wait(30)#打开浏览器,百度driver.get("http://www
- 23种设计模式
buyue__
设计模式
创建型模式1.单例模式(Singleton):确保有且只有一个对象被创建2.工厂方法模式(FactoryMethod):由子类决定要创建的具体类是哪一个3.抽象工厂模式(AbstractFactory):允许客户创建对象的家族,而无需指定他们的具体类4.原型模式(Prototype)5.建造者模式(Builder)结构型模式1.适配器模式(Adapter)2.装饰器模式(Decorator):包装
- 基于模板设计模式开发优惠券推送功能以及对过期优惠卷进行定时清理
Hellyc
设计模式java数据库rocketmq
1.模板设计模式:模板设计模式是一种常见的设计模式,主要作用是对具体操作的共有代码块进行提取,提升代码复用性。那么说道代码复用性,首先想到的是抽象类而不是接口。因为抽象类的本质就是为了代码复用,抽象类既可以包含抽象方法也可以包含具体方法。在模板设计模式中,我们将需要将原本共有的具体操作抽离并封装在抽象类的具体方法中。让抽象类的具体操作来实现需要被复用的逻辑。而其余的抽象方法是不同业务的个性,各个业
- 前端领域的前端设计模式技巧分享
前端视界
前端艺匠馆前端设计模式状态模式ai
前端领域的前端设计模式技巧分享关键词:前端设计模式、组件化开发、状态管理、性能优化、代码复用、可维护性、响应式设计摘要:本文深入探讨前端开发中的设计模式应用技巧,从基础概念到高级实践,全面解析如何通过设计模式提升前端代码质量。文章将详细介绍常见的前端设计模式如观察者模式、单例模式、工厂模式等,并结合React、Vue等现代框架展示实际应用场景。同时,我们还将探讨设计模式在状态管理、性能优化和组件复
- 前端UI逻辑复杂可以用什么设计模式
buyue__
设计设计模式ui设计模式
中介者模式当UI组件间存在复杂交互或多个组件需共享状态时,中介者模式能集中管理事件分发和状态更新,减少组件间的直接依赖,提升解耦性。vue实现中介者模式在Vue中实现中介者模式,你可以通过创建一个全局的事件中心(EventBus)或者使用一个专门的库如mitt、tiny-emitter等来实现。中介者模式主要用于减少组件之间的直接通信,通过一个中介者对象来处理不同组件之间的交互。下面,我将介绍如何
- 设计模式之中介者模式
缘来是庄
设计模式设计模式中介者模式java
目录定义结构适用场景使用示例定义中介者模式通过引入中介对象封装多个对象间的交互,使对象间无需直接引用,从而降低耦合度。各对象仅与中介者通信,交互逻辑集中管理,符合迪米特法则(最少知识原则)。结构适用场景1)复杂网状依赖对象间存在大量直接引用,导致系统混乱(如用户-角色-权限循环依赖)。2)需集中管控的交互GUI组件联动(按钮点击触发输入框禁用)。3)聊天系统中用户消息广播。多玩家游戏的
- JavaScript 常见的设计模式
YuLong~W
JavaScriptjavascriptjava设计模式开发语言前端
文章目录设计模式工厂模式简单工厂抽象工厂单例模式装饰器模式代理模式观察者模式(发布-订阅模式)设计模式设计模式:设计模式是解决某个特定场景下对某种问题的解决方案。因此,当我们遇到合适的场景时,可能会条件反射一样自然而然想到符合这种场景的设计模式。为什么要学习设计模式:设计模式来源众多专家的经验和智慧,它们是从许多优秀的软件系统中总结出的成功的、能够实现可维护性、复用的设计方案,使用这些方案将可以让
- 基于odoo17的设计模式详解---构建模式
大家好,我是你的Odoo技术伙伴。在Odoo开发中,创建一个简单的记录可能只需要一行self.env['res.partner'].create({'name':'NewPartner'})。但如果我们要创建一个复杂的对象,比如一个包含了特定上下文、具有多个可选配置、并且需要执行一系列关联操作的销售订单,传统的create()方法可能会变得非常臃肿和难以阅读。为了解决这个问题,软件设计领域提出了构
- 设计模式的六大设计原则
WISHMELUCK1'
八股文设计模式里氏替换原则依赖倒置原则单一职责原则接口隔离原则迪米特法则合成复用原则
一、什么是设计模式设计模式是一套被反复使用、被多数人知晓的、代码设计经验的总结,它可以让代码更容易理解、提升代码可靠性以及更能够被复用。二、设计模式的六大原则单一原则“应该有且只有一个原因引起类的变更”,通俗来讲,一个类或接口尽可能只做一件事。如此,有以下好处:类和接口的复杂性降低,职责明确可读性好可维护性提高变更引起的风险降低,这也使开闭原则更容易实现开闭原则“可拓展,不修改(少修改)”子类替换
- c++高级工程师掌握的基本知识
作为一名C++高级工程师,通常需要掌握以下知识和技能体系,涵盖语言深度、库使用、性能优化、多线程、设计模式等多个方面。下面我帮你罗列一个全面的知识清单,方便你做自我评估或者准备面试。1.C++语言核心熟练掌握C++11/14/17/20及最新标准的特性自动类型推导(auto、decltype)智能指针(std::unique_ptr,std::shared_ptr,std::weak_ptr)La
- iOS Widget 开发-7:TimelineProvider 机制全解析:构建未来时间线
技术拾光
iOSWidget技术手册iosswiftwidget
在WidgetKit中,TimelineProvider是小组件生命周期的核心机制之一。它控制着数据获取时机、展示内容与刷新策略,是实现时间驱动内容更新的基础。本文将介绍TimelineProvider的工作原理、设计模式、常见场景与高级用法,帮助大家构建智能、节能且灵活的iOS小组件。一、什么是TimelineProvider?TimelineProvider是WidgetKit提供的协议,用于
- 前端学习 vben 之 axios interceptors
aha-凯心
vbenadmin启航前端学习
前端学习vben之axiosinterceptorsinterceptor拦截器,是一种软件设计模式,核心思想就是在程序执行的特定阶段(如请求发送前,响应返回后,方法调用前后等)自动插入自定义逻辑。实现对核心流程的“拦截”和增强。它本质上是一种面向切面编程(AOP)的具体实现,用于解耦横跨多个模块的通用功能(如日志、认证、错误处理)。axios中的interceptoraxios中实现了inter
- 设计模式六大原则:依赖倒置原则、为什么、多例子、分析例子、总结
赴梦、
设计模式杂谈设计模式抽象类接口
1.依赖倒置原则的定义高层模块不应该依赖低层模块,二者都应该依赖其抽象抽象不应该依赖细节,细节应该依赖抽象依赖倒转的中心思想是面向接口编程依赖倒转原则是基于这样的设计理念:相对于细节的多变性,抽象的东西要稳定的多,以抽象为基础搭建的框架比以细节的框架要稳定的多。在JAVA、C#中,抽象指的是接口或者抽象类,细节就是具体的实现类。使用接口或抽象类的目的是指定好的规范,而不涉及任何的具体操作,把展现细
- C/C++ 知识总结
灿烂阳光g
后端
目录C/C++STL数据结构算法Problems操作系统计算机网络网络编程数据库设计模式链接装载库海量数据处理音视频其他书籍复习刷题网站招聘时间岗位面试题目经验C/C++const作用修饰变量,说明该变量不可以被改变;修饰指针,分为指向常量的指针和指针常量;常量引用,经常用于形参类型,即避免了拷贝,又避免了函数对值的修改;修饰成员函数,说明该成员函数内不能修改成员变量。使用const使用stati
- linux系统服务器下jsp传参数乱码
3213213333332132
javajsplinuxwindowsxml
在一次解决乱码问题中, 发现jsp在windows下用js原生的方法进行编码没有问题,但是到了linux下就有问题, escape,encodeURI,encodeURIComponent等都解决不了问题
但是我想了下既然原生的方法不行,我用el标签的方式对中文参数进行加密解密总该可以吧。于是用了java的java.net.URLDecoder,结果还是乱码,最后在绝望之际,用了下面的方法解决了
- Spring 注解区别以及应用
BlueSkator
spring
1. @Autowired
@Autowired是根据类型进行自动装配的。如果当Spring上下文中存在不止一个UserDao类型的bean,或者不存在UserDao类型的bean,会抛出 BeanCreationException异常,这时可以通过在该属性上再加一个@Qualifier注解来声明唯一的id解决问题。
2. @Qualifier
当spring中存在至少一个匹
- printf和sprintf的应用
dcj3sjt126com
PHPsprintfprintf
<?php
printf('b: %b <br>c: %c <br>d: %d <bf>f: %f', 80,80, 80, 80);
echo '<br />';
printf('%0.2f <br>%+d <br>%0.2f <br>', 8, 8, 1235.456);
printf('th
- config.getInitParameter
171815164
parameter
web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>servlet1</servlet-name>
<jsp-file>/index.jsp</jsp-file>
<init-param>
<param-name>str</param-name>
- Ant标签详解--基础操作
g21121
ant
Ant的一些核心概念:
build.xml:构建文件是以XML 文件来描述的,默认构建文件名为build.xml。 project:每个构建文
- [简单]代码片段_数据合并
53873039oycg
代码
合并规则:删除家长phone为空的记录,若一个家长对应多个孩子,保留一条家长记录,家长id修改为phone,对应关系也要修改。
代码如下:
- java 通信技术
云端月影
Java 远程通信技术
在分布式服务框架中,一个最基础的问题就是远程服务是怎么通讯的,在Java领域中有很多可实现远程通讯的技术,例如:RMI、MINA、ESB、Burlap、Hessian、SOAP、EJB和JMS等,这些名词之间到底是些什么关系呢,它们背后到底是基于什么原理实现的呢,了解这些是实现分布式服务框架的基础知识,而如果在性能上有高的要求的话,那深入了解这些技术背后的机制就是必须的了,在这篇blog中我们将来
- string与StringBuilder 性能差距到底有多大
aijuans
之前也看过一些对string与StringBuilder的性能分析,总感觉这个应该对整体性能不会产生多大的影响,所以就一直没有关注这块!
由于学程序初期最先接触的string拼接,所以就一直没改变过自己的习惯!
- 今天碰到 java.util.ConcurrentModificationException 异常
antonyup_2006
java多线程工作IBM
今天改bug,其中有个实现是要对map进行循环,然后有删除操作,代码如下:
Iterator<ListItem> iter = ItemMap.keySet.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
ListItem it = iter.next();
//...一些逻辑操作
ItemMap.remove(it);
}
结果运行报Con
- PL/SQL的类型和JDBC操作数据库
百合不是茶
PL/SQL表标量类型游标PL/SQL记录
PL/SQL的标量类型:
字符,数字,时间,布尔,%type五中类型的
--标量:数据库中预定义类型的变量
--定义一个变长字符串
v_ename varchar2(10);
--定义一个小数,范围 -9999.99~9999.99
v_sal number(6,2);
--定义一个小数并给一个初始值为5.4 :=是pl/sql的赋值号
- Mockito:一个强大的用于 Java 开发的模拟测试框架实例
bijian1013
mockito单元测试
Mockito框架:
Mockito是一个基于MIT协议的开源java测试框架。 Mockito区别于其他模拟框架的地方主要是允许开发者在没有建立“预期”时验证被测系统的行为。对于mock对象的一个评价是测试系统的测
- 精通Oracle10编程SQL(10)处理例外
bijian1013
oracle数据库plsql
/*
*处理例外
*/
--例外简介
--处理例外-传递例外
declare
v_ename emp.ename%TYPE;
begin
SELECT ename INTO v_ename FROM emp
where empno=&no;
dbms_output.put_line('雇员名:'||v_ename);
exceptio
- 【Java】Java执行远程机器上Linux命令
bit1129
linux命令
Java使用ethz通过ssh2执行远程机器Linux上命令,
封装定义Linux机器的环境信息
package com.tom;
import java.io.File;
public class Env {
private String hostaddr; //Linux机器的IP地址
private Integer po
- java通信之Socket通信基础
白糖_
javasocket网络协议
正处于网络环境下的两个程序,它们之间通过一个交互的连接来实现数据通信。每一个连接的通信端叫做一个Socket。一个完整的Socket通信程序应该包含以下几个步骤:
①创建Socket;
②打开连接到Socket的输入输出流;
④按照一定的协议对Socket进行读写操作;
④关闭Socket。
Socket通信分两部分:服务器端和客户端。服务器端必须优先启动,然后等待soc
- angular.bind
boyitech
AngularJSangular.bindAngularJS APIbind
angular.bind 描述: 上下文,函数以及参数动态绑定,返回值为绑定之后的函数. 其中args是可选的动态参数,self在fn中使用this调用。 使用方法: angular.bind(se
- java-13个坏人和13个好人站成一圈,数到7就从圈里面踢出一个来,要求把所有坏人都给踢出来,所有好人都留在圈里。请找出初始时坏人站的位置。
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class KickOutBadGuys {
/**
* 题目:13个坏人和13个好人站成一圈,数到7就从圈里面踢出一个来,要求把所有坏人都给踢出来,所有好人都留在圈里。请找出初始时坏人站的位置。
* Maybe you can find out
- Redis.conf配置文件及相关项说明(自查备用)
Kai_Ge
redis
Redis.conf配置文件及相关项说明
# Redis configuration file example
# Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specifiy
# it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth:
#
- [强人工智能]实现大规模拓扑分析是实现强人工智能的前奏
comsci
人工智能
真不好意思,各位朋友...博客再次更新...
节点数量太少,网络的分析和处理能力肯定不足,在面对机器人控制的需求方面,显得力不从心....
但是,节点数太多,对拓扑数据处理的要求又很高,设计目标也很高,实现起来难度颇大...
- 记录一些常用的函数
dai_lm
java
public static String convertInputStreamToString(InputStream is) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
if (is != null)
try {
InputStreamReader inputReader = new InputStreamRead
- Hadoop中小规模集群的并行计算缺陷
datamachine
mapreducehadoop并行计算
注:写这篇文章的初衷是因为Hadoop炒得有点太热,很多用户现有数据规模并不适用于Hadoop,但迫于扩容压力和去IOE(Hadoop的廉价扩展的确非常有吸引力)而尝试。尝试永远是件正确的事儿,但有时候不用太突进,可以调优或调需求,发挥现有系统的最大效用为上策。
-----------------------------------------------------------------
- 小学4年级英语单词背诵第二课
dcj3sjt126com
englishword
egg 蛋
twenty 二十
any 任何
well 健康的,好
twelve 十二
farm 农场
every 每一个
back 向后,回
fast 快速的
whose 谁的
much 许多
flower 花
watch 手表
very 非常,很
sport 运动
Chinese 中国的
- 自己实践了github的webhooks, linux上面的权限需要注意
dcj3sjt126com
githubwebhook
环境, 阿里云服务器
1. 本地创建项目, push到github服务器上面
2. 生成www用户的密钥
sudo -u www ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "
[email protected]"
3. 将密钥添加到github帐号的SSH_KEYS里面
3. 用www用户执行克隆, 源使
- Java冒泡排序
蕃薯耀
冒泡排序Java冒泡排序Java排序
冒泡排序
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
蕃薯耀 2015年6月23日 10:40:14 星期二
http://fanshuyao.iteye.com/
- Excle读取数据转换为实体List【基于apache-poi】
hanqunfeng
apache
1.依赖apache-poi
2.支持xls和xlsx
3.支持按属性名称绑定数据值
4.支持从指定行、列开始读取
5.支持同时读取多个sheet
6.具体使用方式参见org.cpframework.utils.excelreader.CP_ExcelReaderUtilTest.java
比如:
Str
- 3个处于草稿阶段的Javascript API介绍
jackyrong
JavaScript
原文:
http://www.sitepoint.com/3-new-javascript-apis-may-want-follow/?utm_source=html5weekly&utm_medium=email
本文中,介绍3个仍然处于草稿阶段,但应该值得关注的Javascript API.
1) Web Alarm API
&
- 6个创建Web应用程序的高效PHP框架
lampcy
Web框架PHP
以下是创建Web应用程序的PHP框架,有coder bay网站整理推荐:
1. CakePHP
CakePHP是一个PHP快速开发框架,它提供了一个用于开发、维护和部署应用程序的可扩展体系。CakePHP使用了众所周知的设计模式,如MVC和ORM,降低了开发成本,并减少了开发人员写代码的工作量。
2. CodeIgniter
CodeIgniter是一个非常小且功能强大的PHP框架,适合需
- 评"救市后中国股市新乱象泛起"谣言
nannan408
首先来看百度百家一位易姓作者的新闻:
三个多星期来股市持续暴跌,跌得投资者及上市公司都处于极度的恐慌和焦虑中,都要寻找自保及规避风险的方式。面对股市之危机,政府突然进入市场救市,希望以此来重建市场信心,以此来扭转股市持续暴跌的预期。而政府进入市场后,由于市场运作方式发生了巨大变化,投资者及上市公司为了自保及为了应对这种变化,中国股市新的乱象也自然产生。
首先,中国股市这两天
- 页面全屏遮罩的实现 方式
Rainbow702
htmlcss遮罩mask
之前做了一个页面,在点击了某个按钮之后,要求页面出现一个全屏遮罩,一开始使用了position:absolute来实现的。当时因为画面大小是固定的,不可以resize的,所以,没有发现问题。
最近用了同样的做法做了一个遮罩,但是画面是可以进行resize的,所以就发现了一个问题,当画面被reisze到浏览器出现了滚动条的时候,就发现,用absolute 的做法是有问题的。后来改成fixed定位就
- 关于angularjs的点滴
tntxia
AngularJS
angular是一个新兴的JS框架,和以往的框架不同的事,Angularjs更注重于js的建模,管理,同时也提供大量的组件帮助用户组建商业化程序,是一种值得研究的JS框架。
Angularjs使我们可以使用MVC的模式来写JS。Angularjs现在由谷歌来维护。
这里我们来简单的探讨一下它的应用。
首先使用Angularjs我
- Nutz--->>反复新建ioc容器的后果
xiaoxiao1992428
DAOmvcIOCnutz
问题:
public class DaoZ {
public static Dao dao() { // 每当需要使用dao的时候就取一次
Ioc ioc = new NutIoc(new JsonLoader("dao.js"));
return ioc.get(