贝塞尔曲线的一些资料收集
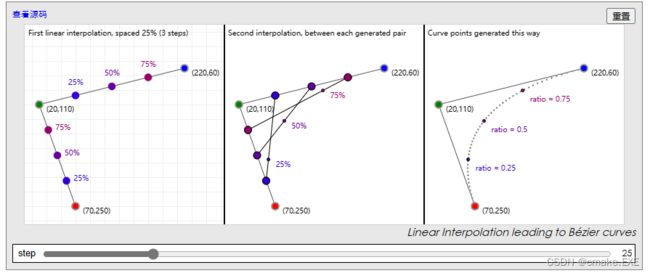
一本免费的在线书籍,供你在非常需要了解如何处理贝塞尔相关的事情。
https://pomax.github.io/bezierinfo/zh-CN/index.html
An algorithm to find bounding box of closed bezier curves? - Stack Overflow
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2587751/an-algorithm-to-find-bounding-box-of-closed-bezier-curves
前端动画之贝塞尔曲线推导及应用-CSDN博客
https://blog.csdn.net/frontend_frank/article/details/123437040
贝塞尔曲线在线绘制
https://www.bezier-curve.com/
Calculating / Computing the Bounding Box of Cubic Bezier https://floris.briolas.nl/floris/2009/10/bounding-box-of-cubic-bezier/
获取三阶贝塞尔曲线的最小包围盒
c# https://floris.briolas.nl/floris/2009/10/bounding-box-of-cubic-bezier/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Drawing;
namespace BoundingBoxTestProject
{
public static class BezierOp
{
public delegate TResult Func<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, TResult>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3, T4 arg4, T5 arg5);
//cubic polinomal
//x = At^3 + Bt^2 + Ct + D
//where A,B,C,D:
//A = p3 -3 * p2 + 3 * p1 - p0
//B = 3 * p2 - 6 * p1 +3 * p0
//C = 3 * p1 - 3 * p0
//D = p0
public static Func<double, double, double, double, double, double> bezierSpline = (p0, p1, p2, p3, t) =>
(p3 - 3 * p2 + 3 * p1 - p0) * Math.Pow(t, 3)
+ (3 * p2 - 6 * p1 + 3 * p0) * Math.Pow(t, 2)
+ (3 * p1 - 3 * p0) * t
+ (p0);
//X = At^3 + Bt^2 + Ct + D
//where A,B,C,D:
//A = (p3 -3 * p2 + 3 * p1 - p0)
//B = (3 * p2 - 6 * p1 +3 * p0)
//C = (3 * p1 - 3 * p0)
//D = (p0)
//We would like to know the values of t where X = 0
//X = (p3-3*p2+3*p1-p0)t^3 + (3*p2-6*p1+3*p0)t^2 + (3*p1-3*p0)t + (p0)
//Derivetive :
//X' = 3(p3-3*p2+3*p1-p0)t^(3-1) + 2(6*p2-12*p1+6*p0)t^(2-1) + 1(3*p1-3*p0)t^(1-1) [f(x)=aX^n => f'(x)=a*n*X^(n-1) remember?]
//simplified:
//X' = (3*p3-9*p2+9*p1-3*p0)t^2 + (6*p2-12*p1+6*p0)t + (3*p1-3*p0)
//**!!reusing a,b,and c!!!***
//taken as aX^2 + bX + c a,b and c are:
public static Func<double, double, double, double, double> A = (p0, p1, p2, p3) => 3 * p3 - 9 * p2 + 9 * p1 - 3 * p0;
//ommitting power 2 for now
public static Func<double, double, double, double> B = (p0, p1, p2) => 6 * p2 - 12 * p1 + 6 * p0;
public static Func<double, double, double> C = (p0, p1) => 3 * p1 - 3 * p0;
//b^2 - 4ac = Determinant
public static Func<double, double, double, double> Determinant = (a, b, c) => Math.Pow(b, 2) - 4d * a * c;
public static Func<double, double, double, double[]> Solve = (a, b, c) =>
{
Func<double, double, double, bool, double> _Solve =
(a_, b_, c_, s) =>
(-b_ +
(Math.Sqrt((b_ * b_) - (4d * a_ * c_)) *
((s) ? 1d : -1d))) / (2d * a_);
double d = Determinant(a, b, c);
if (d < 0)
return new double[] { };
if (a == 0)
//aX^2 + bX + c well then then this is a simple line
//x= -c / b
return new double[] { -c / b };
if (d == 0)
{
return new double[] { _Solve(a, b, c, true) };
}
else
return new double[]
{
_Solve(a, b, c, true),
_Solve(a, b, c, false)
};
};
public static RectangleF GetRect(PointF p1, PointF c1, PointF c2, PointF p2)
{
double aX = A(p1.X, c1.X, c2.X, p2.X);
double bX = B(p1.X, c1.X, c2.X);
double cX = C(p1.X, c1.X);
double aY = A(p1.Y, c1.Y, c2.Y, p2.Y);
double bY = B(p1.Y, c1.Y, c2.Y);
double cY = C(p1.Y, c1.Y);
var resX = Solve(aX, bX, cX).Where(t => (t >= 0) && (t <= 1)); //solve for t ==0 & filter
var resY = Solve(aY, bY, cY).Where(t => (t >= 0) && (t <= 1)); //solve for t ==0 & filter
//Draw min and max;
List<PointF> _BBox = new List<PointF>();
_BBox.Add(p1); //Add Begin and end point not the control points!
_BBox.Add(p2);
foreach (var e in resX.Union(resY))
{
double x = bezierSpline(p1.X, c1.X, c2.X, p2.X, e);
double y = bezierSpline(p1.Y, c1.Y, c2.Y, p2.Y, e);
PointF p = new PointF((float)x, (float)y);
_BBox.Add(p);
}
float minX = float.MaxValue;
float minY = float.MaxValue;
float maxX = float.MinValue;
float maxY = float.MinValue;
foreach (var e in _BBox) //find the bounding box.
{
minX = Math.Min(e.X, minX);
minY = Math.Min(e.Y, minY);
maxX = Math.Max(e.X, maxX);
maxY = Math.Max(e.Y, maxY);
}
return new RectangleF(minX, minY, maxX - minX, maxY - minY);
}
}
}
c++ 由上述c#代码改写而来,未做优化
#include