C++ vector模拟实现
目录
-
- 使用insert时迭代器失效
- 使用erase时迭代器失效
- 使用memcpy浅拷贝的问题
- 调用最匹配的函数可能出现的问题
- 模拟实现vector
使用insert时迭代器失效
在模拟vector插入的时候会遇到扩容后pos失效的问题,需要更新pos
vector()
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{}
void insert(iterator pos, const T& value = T())
{
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
if (size() == capacity())
{
//pos位置的空间可能在扩容的时候被delete,要记录相对位置更新pos
int len = pos - _start;
reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : 2 * capacity());
pos = _start + len;
}
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
*(end + 1) = *end;
end--;
}
*pos = value;
_finish++;
}
void test2()
{
vector<int> v;
v.insert(v.begin(), 1);
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
v.insert(it, 2);
v.insert(it, 3);
v.insert(it, 4);
v.insert(it, 5);//这句代码之后it就失效了
v.insert(it, 6);//报错,因为it传给pos的位置已经被销毁了
}
insert插入后it就失效了,我们不知道什么时候扩容
给pos加引用的话,v.insert(v.begin(), 1);是不行的,因为begin返回的是临时变量的拷贝不可以修改
如果再给pos加const,那pos不能更改了
所以insert之后it失效,尽量不要再使用
库里的insert会返回新插入元素所在位置的迭代器
void test_vector9()
{
std::vector<int> v3;
v3.push_back(10);
v3.push_back(20);
v3.push_back(30);
v3.push_back(40);
for (auto e : v3)
{
cout << e << " ";//结果是10 20 30 40
}
cout << endl;
std::vector<int>::iterator it = v3.begin()+3;
int n = 6;
while (n--)
{
it = v3.insert(it, n);
}
for (auto e : v3)
{
cout << e << " ";//结果是10 20 30 0 1 2 3 4 5 40
}
cout << endl;
}
使用erase时迭代器失效
iterator erase(iterator pos)//返回被删位置的下一个位置
{
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
iterator it = pos + 1;
while (it < _finish)
{
*(it - 1) = *it;
it++;
}
_finish--;
return pos;
}
void test4()
{
// 1 2 3 4 5
// 1 2 3 4 5 6
// 2 2 3 4 5
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(6);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
v.erase(it);
}
++it;
}
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
不仅会漏检查,删最后一个的时候会出现 it 比_finish大的情况


vs2019会进行强制检查,erase以后认为it失效了,不能访问,我们模拟实现的跟g++下运行结果一样
erase返回被删位置的下一个位置
void test5()
{
//std::vector v;
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(6);
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
it = v.erase(it);
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
使用memcpy浅拷贝的问题
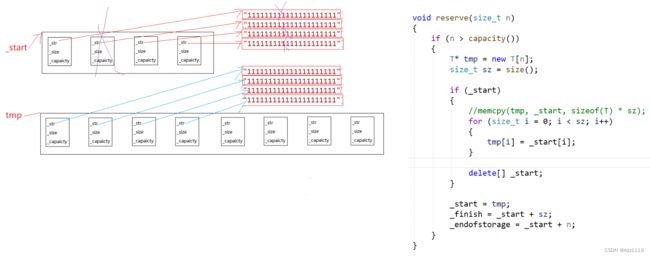
模拟实现的vector中的reserve接口中,使用memcpy进行的拷贝会出现问题
memcpy会将一段内存空间中内容拷贝到另外一段内存空间中,这种拷贝是浅拷贝,如果T是内置类型不会有问题,但如果是自定义类型就会出错
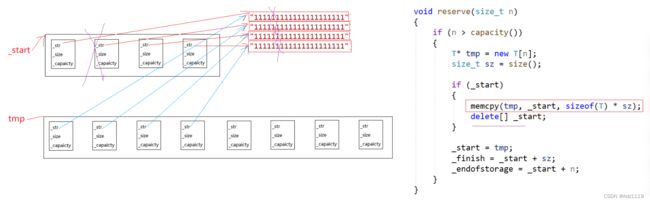
delete的时候如果是自定义的数据类型,会去调用这个对象的析构函数,释放的空间置成随机值,查编码表之后可能就是我们不认识的字
tmp中string对象的_str和_start中string对象的_str是一样的,所以_start中string对象的_str变了,tmp中的也会变
调string的赋值的时候,是深拷贝,就可以解决问题了,引用计数的浅拷贝也可以解决
库里面实现是拷贝构造的,因为库里的T[]是内存池来的(就像malloc来的没有初始化),要初始化就用定位new调拷贝构造。
所以自定义类型拷贝数据不能用memcpy
调用最匹配的函数可能出现的问题
会找最匹配的去调用
上面的是int和int
下面的是unsigned int 和int
上面的更匹配所以会调用模板
如果都是int,那么有更匹配的就不会去实例化模板:
vector(int n, const T& val = T())
{
reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
模拟实现vector
#include