第 2 章 线性表 (线性表的静态单链表存储结构(一个数组只生成一个静态链表)实现)
1. 背景说明
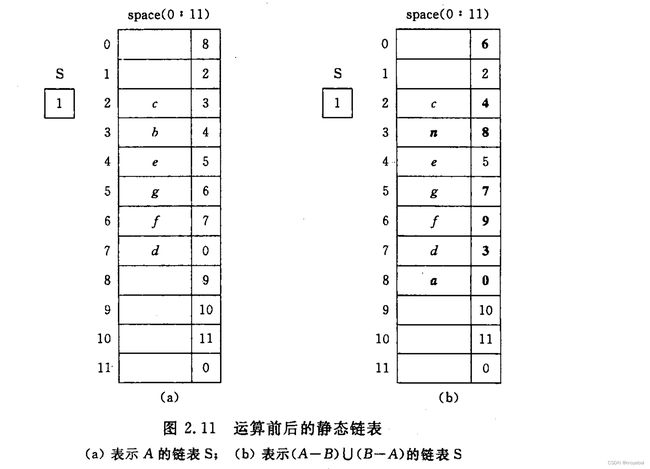
A = { c, b, e, g, f, d }
B = { a, b, n, f }2. 示例代码
1) status.h
/* DataStructure 预定义常量和类型头文件 */
#ifndef STATUS_H
#define STATUS_H
#define CHECK_RET(ret) if (ret != RET_OK) { \
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret); \
return ret; \
}
#define CHECK_VALUE(value, ERR_CODE) if (value) { \
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_CODE); \
return ERR_CODE; \
}
#define CHECK_FALSE(value, ERR_CODE) if (!(value)) { \
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_CODE); \
return FALSE; \
}
/* 函数结果状态码 */
#define TRUE 1 /* 返回值为真 */
#define FALSE 0 /* 返回值为假 */
#define RET_OK 0 /* 返回值正确 */
#define INFEASIABLE 2 /* 返回值未知 */
#define ERR_MEMORY 3 /* 访问内存错 */
#define ERR_NULL_PTR 4 /* 空指针错误 */
#define ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE 5 /* 内存分配错 */
#define ERR_NULL_STACK 6 /* 栈元素为空 */
#define ERR_PARA 7 /* 函数参数错 */
#define ERR_OPEN_FILE 8 /* 打开文件错 */
#define ERR_NULL_QUEUE 9 /* 队列为空错 */
#define ERR_FULL_QUEUE 10 /* 队列为满错 */
#define ERR_NOT_FOUND 11 /* 表项不存在 */
typedef int Status; /* Status 是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如 RET_OK 等 */
typedef int Bollean; /* Boolean 是布尔类型,其值是 TRUE 或 FALSE */
#endif // !STATUS_H
2) staticLinkListSingle.h
/* 静态链表(一个数组只生成一个静态链表)实现头文件 */
#ifndef STATICLINKLISTSINGLE_H
#define STATICLINKLISTSINGLE_H
#include "status.h"
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct {
ElemType data;
int curr;
} SLinkList[MAX_SIZE];
/* 若备用链表非空,则返回分配的结点下标(备用链表的第一个结点),否则返回 0 */
int Malloc(SLinkList space);
/* 将下标为 i 的空闲结点回收到备用链表(成为备用链表的第一个结点) */
void Free(SLinkList space, int i);
/* 静态数组无法被销毁 */
void DestroyList(void);
/* 构造一个空的链表,表头为 L 的最后一个单元 L[MAXSIZE - 1],其余单元链成
一个备用链表,表头为 L 的第一个单元 L[0],'0' 表示空指针 */
void InitList(SLinkList L);
/* 初始条件:线性表 L 已存在
操作结果:将 L 重置为空表 */
Status ClearList(SLinkList L);
/* 若 L 是空表,返回 TRUE;否则返回 FALSE */
Bollean ListEmpty(SLinkList L);
/* 返回 L 中数据元素个数 */
int ListLength(SLinkList L);
/* 用 e 返回 L 中第 i 个元素的值 */
Status GetElem(SLinkList L, int i, ElemType *e);
/* 算法 2.13, 在静态单链线性表 L 中查找第 1 个值为 e 的元素。若找到,则返回它
在 L 中的位序,否则返回 0 */
int LocateElem(SLinkList L, ElemType e);
/* 初始条件:线性表 L 已存在
操作结果:若 curr_e 是 L 的数据元素,且不是第一个,则用 pre_e返回它的前驱否
则操作失败,pre_e 无定义 */
Status PriorElem(SLinkList L, ElemType curr_e, ElemType *pre_e);
/* 初始条件:线性表 L 已存在
操作结果:若 curr_e 是 L 的数据元素,且不是最后一个,则用 next_e 返回它的后
继, 否则操作失败,next_e 无定义 */
Status NextElem(SLinkList L, ElemType curr_e, ElemType *next_e);
/* 在 L 中第 i 个元素之前插入新的数据元素 e */
Status ListInsert(SLinkList L, int i, ElemType e);
/* 删除在 L 中第 i 个数据元素 e,并返回其值 */
Status ListDelete(SLinkList L, int i, ElemType *e);
/* 初始条件: 线性表 L 已存在
操作结果: 依次对 L 的每个数据元素调用函数 vi()。一旦 vi() 失败, 则操作失败 */
Status ListTraverse(SLinkList L, void(*vi)(ElemType));
#endif3) staticLinkListSingle.c
/* 静态链表(一个数组只生成一个静态链表)实现源文件 */
#include "staticLinkListSingle.h"
#include
/* 若备用链表非空,则返回分配的结点下标(备用链表的第一个结点),否则返回 0 */
int Malloc(SLinkList space)
{
int i = space[0].curr;
if (i) {
space[0].curr = space[i].curr;
}
return i;
}
/* 将下标为 i 的空闲结点回收到备用链表(成为备用链表的第一个结点) */
void Free(SLinkList space, int i)
{
space[i].curr = space[0].curr;
space[0].curr = i;
}
/* 静态数组无法被销毁 */
void DestroyList(void)
{
printf("Static array do not need to free memory!\n");
}
/* 构造一个空的链表,表头为 L 的最后一个单元 L[MAXSIZE - 1],其余单元链成
一个备用链表,表头为 L 的第一个单元 L[0],'0' 表示空指针 */
void InitList(SLinkList L)
{
L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SIZE - 2; ++i) {
L[i].curr = i + 1;
}
L[MAX_SIZE - 2].curr = 0;
}
/* 初始条件:线性表 L 已存在
操作结果:将 L 重置为空表 */
Status ClearList(SLinkList L)
{
int i = L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr;
L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr = 0;
int k = L[0].curr;
L[0].curr = i;
int j;
while (i) {
j = i;
i = L[i].curr;
}
L[j].curr = k;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 若 L 是空表,返回 TRUE;否则返回 FALSE */
Bollean ListEmpty(SLinkList L)
{
return (L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr == 0) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
/* 返回 L 中数据元素个数 */
int ListLength(SLinkList L)
{
int length = 0;
int i = L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr;
while (i) {
i = L[i].curr;
++length;
}
return length;
}
/* 用 e 返回 L 中第 i 个元素的值 */
Status GetElem(SLinkList L, int i, ElemType *e)
{
CHECK_VALUE(((i < 1) || (i > ListLength(L))), ERR_PARA)
int head = MAX_SIZE - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
head = L[head].curr;
}
*e = L[head].data;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 算法 2.13, 在静态单链线性表 L 中查找第 1 个值为 e 的元素。若找到,则返回它
在 L 中的位序,否则返回 0 */
int LocateElem(SLinkList L, ElemType e)
{
int i = L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr;
while ((i) && (L[i].data != e)) {
i = L[i].curr;
}
return i;
}
/* 初始条件:线性表 L 已存在
操作结果:若 curr_e 是 L 的数据元素,且不是第一个,则用 pre_e返回它的前驱否
则操作失败,pre_e 无定义 */
Status PriorElem(SLinkList L, ElemType curr_e, ElemType *pre_e)
{
int i = L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr;
int j;
do {
j = i;
i = L[i].curr;
} while ((i) && (L[i].data != curr_e));
if (i) {
*pre_e = L[j].data;
return RET_OK;
}
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_NOT_FOUND);
return ERR_NOT_FOUND;
}
/* 初始条件:线性表 L 已存在
操作结果:若 curr_e 是 L 的数据元素,且不是最后一个,则用 next_e 返回它的后
继, 否则操作失败,next_e 无定义 */
Status NextElem(SLinkList L, ElemType curr_e, ElemType *next_e)
{
int i = LocateElem(L, curr_e);
int j;
if (i) {
j = L[i].curr;
if (j) {
*next_e = L[j].data;
return RET_OK;
}
}
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_NOT_FOUND);
return ERR_NOT_FOUND;
}
/* 在 L 中第 i 个元素之前插入新的数据元素 e */
Status ListInsert(SLinkList L, int i, ElemType e)
{
CHECK_VALUE((i < 1) || i > ListLength(L) + 1, ERR_PARA)
int j = Malloc(L);
CHECK_VALUE(!j, ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE)
L[j].data = e;
int head = MAX_SIZE - 1;
for (int k = 0; k < i - 1; ++k) {
head = L[head].curr;
}
L[j].curr = L[head].curr;
L[head].curr = j;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 删除在 L 中第 i 个数据元素 e,并返回其值 */
Status ListDelete(SLinkList L, int i, ElemType *e)
{
CHECK_VALUE((i < 1) || i > ListLength(L), ERR_PARA)
int head = MAX_SIZE - 1;
int j;
for (j = 0; j < i - 1; ++j) {
head = L[head].curr;
}
j = L[head].curr;
L[head].curr = L[j].curr;
*e = L[j].data;
Free(L, j);
return RET_OK;
}
/* 初始条件: 线性表 L 已存在
操作结果: 依次对 L 的每个数据元素调用函数 vi()。一旦 vi() 失败, 则操作失败 */
Status ListTraverse(SLinkList L, void(*vi)(ElemType))
{
int i = L[MAX_SIZE - 1].curr;
while (i) {
vi(L[i].data);
i = L[i].curr;
}
return RET_OK;
} 4) main.c
#include "staticLinkListSingle.h"
#include
void Visit(ElemType e);
int main(void)
{
SLinkList L;
InitList(L);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
ListInsert(L, 1, i + 1);
}
printf("After insert 1 ~ 5 in head of L, L is: ");
ListTraverse(L, Visit);
putchar('\n');
printf("L is %s, the length of L is %d\n", ((ListEmpty(L) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty"),
ListLength(L));
ClearList(L);
printf("After clear L, L is: ");
ListTraverse(L, Visit);
putchar('\n');
printf("L is %s, the length of L is %d\n", ((ListEmpty(L) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty"),
ListLength(L));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
ListInsert(L, i + 1, i + 1);
}
printf("After insert 1 ~ 10 in tail of L, L is: ");
ListTraverse(L, Visit);
putchar('\n');
ElemType e;
GetElem(L, 5, &e);
printf("The %dth element of L is %d\n", 5, e);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
int pos = LocateElem(L, i);
if (pos) {
printf("The order of element %d in L is %d\n", i, pos);
} else {
printf("Element %d is not exist in L\n", i);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < 3; ++i) {
ElemType e, prior;
GetElem(L, i, &e);
Status ret = PriorElem(L, e, &prior);
if (ret == RET_OK) {
printf("The previous element of %d is %d\n", e, prior);
} else {
printf("The previous element of %d is not exist.\n", e);
}
}
for (int i = ListLength(L) - 1; i <= ListLength(L); ++i) {
ElemType e, next;
GetElem(L, i, &e);
Status ret = NextElem(L, e, &next);
if (ret == RET_OK) {
printf("The next element of %d is %d\n", e, next);
} else {
printf("The next element of %d is not exist.\n", e);
}
}
int length = ListLength(L);
for (int i = length + 1; i >= length; --i) {
ElemType e;
Status ret = ListDelete(L, i, &e);
if (ret == RET_OK) {
printf("The element deleted is %d\n", e);
} else {
printf("Delete %dth element failed!\n", i);
}
}
printf("Now, the element in L is: ");
ListTraverse(L, Visit);
putchar('\n');
DestroyList();
return 0;
}
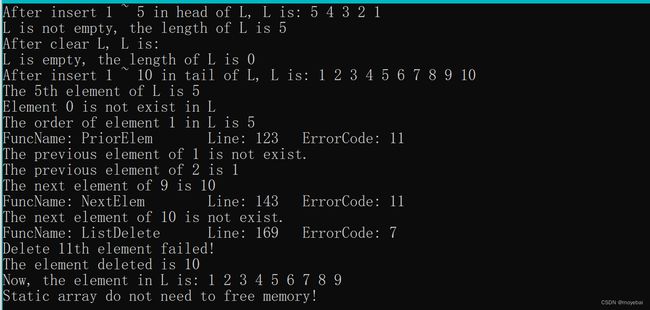
void Visit(ElemType e)
{
printf("%d ", e);
} 3. 运行示例