图解 LeetCode 算法汇总——回溯
本文首发公众号:小码A梦
回溯算法是一种常见的算法,常见用于解决排列组合、排列问题、搜索问题等算法,在一个搜索空间中寻找所有的可能的解。通过向分支不断尝试获取所有的解,然后找到合适的解,找完一个分支后再往回搜索。回溯算法通常使用递归的方式实现。
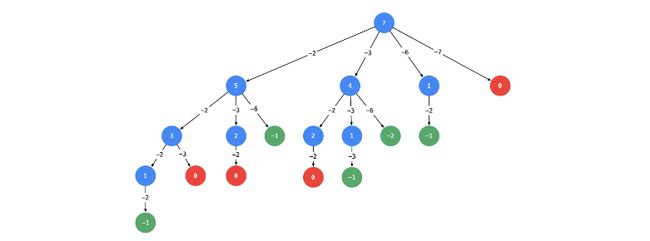
回溯本质是一种暴力搜索法,列出所有可能的解,然后找到合适的解。以 a、b、c的排列组合为例,画出全排列组合。
以上排列组合回溯步骤:
- 列出所有可能存在的组合。
- 分解组合,把问题分解多个阶段,每个阶段添加一个分叉。
- 走完一个分叉,或者遇到不符合期望条件的时,就退回到上一个分叉。继续走其它没走的路。直到走完所有的路。
- 回溯一半都是使用递归实现。
根据以上的步骤得出一个简单的回溯算法的模板:
public Solution {
List> result;
LinkedList path;
//记录那些元素被遍历过
boolean[] used;
private List> permute(int[] nums) {
result = new ArrayList<>();
path = new LinkedList<>();
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums) {
if (递归终止条件) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
//遍历各个元素
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
used[i] = true;
//选择元素
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
//移除元素
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
以上代码使用递归,递归一般要设置一个终止条件,然后遍历整个元素,通过链表选择元素和移除元素。
LeetCode 题解
上面所说的,回溯主要解决一些排列组合、排列问题、搜索问题等问题,LeetCode 有很多类似的问题,这里选取了几个比较常见的题目。
- 39 组合总和
- 40 组合总和 II
- 46 全排列
- 47 全排列 II
- 51 N皇后
39.组合总和(中等)
题目描述
解法
这是一个比较典型的排列组合问题,本题采用的是求总和,使用总和减去遍历的数据,最后得到结果为零,就是符合的组合。
- 为了减少遍历次数,数组需要先排序。总数减的数据如果小于零,就不会在该分支继续遍历了。
- 可以重复使用元素,每次都遍历一遍全部元素。
- 减去分支结果之后,以新的结果,再创建分支做减法。
- 递归遍历一直到结果为零和负数。
- 为零,符合条件,记录数据,对应的分支遍历终止,继续遍历下一个分支。
- 为负数,返回到上一个分支,继续遍历后面的分支。
最终代码:
class Solution {
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
int[] candidate;
public List> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
candidate = candidates;
recall(0,target,new LinkedList<>());
return list;
}
private void recall(int start, int target, LinkedList path) {
if (target == 0) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i recall 使用递归方法遍历分支,而使用链表的特性,记录遍历的节点,如果不符合要求就上一个分支回撤,同时链表移除最后一个结点。
40.组合总和II(中等)
解题思路
这题的解题思路和上面的组合总和是差不多的,唯一不同的是元素不能被重复遍历,使用一个变量记录遍历的起始值,遍历过的数据,下次往后一位开始遍历。
代码如下:
class Solution {
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
int[] candidate;
public List> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates);
candidate = candidates;
recall(0,target,new LinkedList<>());
return list;
}
private void recall(int start, int target, LinkedList path) {
if (target == 0) {
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = start; i start && candidate[i] == candidate[i-1]) {
continue;
}
int sub = target - candidate[i];
if (sub < 0) {
break;
}
path.add(candidate[i]);
recall(i + 1,sub,path);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
start 记录遍历的起始值,其他解题方法和上面的组合求和是类似的。题目还有一个要求是不能出现重复的组合,就需要判断 candidate[i] == candidate[i-1] 就忽略该数据,往后继续遍历。
46.全排列
解题思路
- 每个元素都需要遍历一遍。
- 遍历元素的时,遍历完第一数,继续遍历未遍历的数据。
- 遍历结束后,返回上一个分叉。
代码整理如下:
class Solution {
List> result = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList path = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] used;
public List> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (used[i]) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
使用 used 记录哪些数据遍历过,遍历过的数据不会遍历,其他也是使用递归搜索。
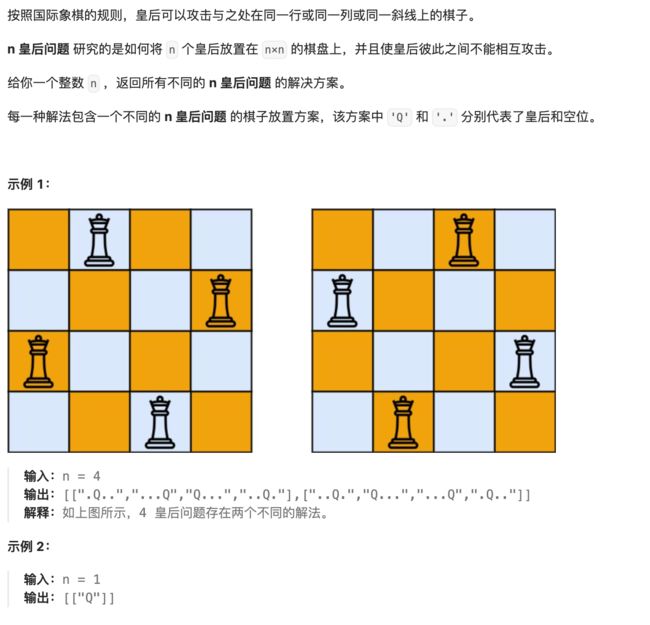
51.N皇后
题目描述
解题思路
N 皇后问题是一个经典的回溯算法问题,是面试比较常见的问题。在一个 n * n 的棋盘上,每个格子放入的元素后,查看是够有同行、同列、左上方以及右上方是否冲突,冲突就回溯,不冲突就继续往下遍历。
- 初始化数组,默认初始值。
- 每一行只能放一个 Q,不冲突后,再遍历下一列的数据(因为同一行不能冲突)。
- 因为每一行只放一个 Q,所以不存在同行冲突。判断冲突就潘丹同一列、左上方以及右上方是否有冲突。
- 遍历到最后一行时,记录符合条件的数据。
class Solution {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List> solveNQueens(int n) {
// 初始化棋盘 "." 表示空,"Q"表示皇后,
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (char[] c : board) {
Arrays.fill(c, '.');
}
backtrack(board, 0);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(char[][] board, int row) {
//终止条件
if (row == board.length) {
res.add(charToList(board));
return;
}
//每一行列数(也就是长度)
int n = board[row].length;
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
//排除相互攻击的格子
if (!isValid(board,row,col)) {
continue;
}
//放入Q
board[row][col] = 'Q';
//进入下一行放皇后
backtrack(board,row + 1);
//撤销Q
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
private boolean isValid(char[][] board, int row, int col) {
int n = board.length;
//检查列是否有皇后冲突
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (board[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
//检查右上方是否有皇后冲突
for (int i = row - 1,j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--,j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
//检查左上方是否有皇后冲突
for (int i = row - 1,j = col - 1; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--,j--) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public List charToList(char[][] board) {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
list.add(String.copyValueOf(board[i]));
}
return list;
}
}
总结
回溯算法尝试在问题的解空间中搜索可能的解,并在搜索过程中进行选择、撤销选择和终止搜索,直到找到解或确定无解为止。
- 通常通过递归函数来实现回溯算法。
- 在每一步,需要做出选择(选择一个分支)然后递归地探索该选择的结果。
- 在递归返回后,需要撤销之前的选择,以便继续探索其他分支。
- 使用条件语句或循环来控制选择的范围和条件。