算法通关村第十八关——回溯热门问题(白银)
算法通关村第十八关——回溯热门问题(白银)
-
- 1. 组合总问题
- 2. 分割回文串
- 3. 子集问题
- 4. 排列问题
- 5. 字母大小写全排列
- 6.单词搜索
1. 组合总问题
leetcode 39. 组合总和
这题跟青铜的最后一题一个意思,写题的方式还是那三步:
- 递归函数的返回值以及参数
- 回溯函数的终止条件
- 单层搜索的过程
仍然要注意的地方:撤销动作!!!!
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> resultArray = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
combinationList(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return result;
}
private void combinationList(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex){
if(sum > target){
return;
}
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(resultArray));
return;
}
for(int i=startIndex; i<candidates.length ;i++ ){
sum += candidates[i];
resultArray.add(candidates[i]);
combinationList(candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
resultArray.remove(resultArray.size() - 1);
}
}
}
当然,这里可以进行剪枝,自行理解:
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> resultArray = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
// 需要先对candidates数组排序,方便剪枝
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationList(candidates, target, 0, 0);
return result;
}
private void combinationList(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex){
if(sum > target){
return;
}
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(resultArray));
return;
}
for(int i=startIndex; i<candidates.length;i++ ){
// 剪枝:如果当前sum加上candidates[i]已经大于target,则结束本次循环
if (sum + candidates[i] > target) {
break;
}
sum += candidates[i];
resultArray.add(candidates[i]);
combinationList(candidates, target, sum, i);
sum -= candidates[i];
resultArray.remove(resultArray.size() - 1);
}
}
}
2. 分割回文串
leetcode 131. 分割回文串
同上,套路都是一样的,最难的部分就是索引的理解
class Solution {
private List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private List<String> currentList = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
partitionList(s, 0);
return result;
}
private void partitionList(String s, int startIndex){
if(startIndex == s.length()){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(currentList));
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){
String substring = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
if(isPalindrome(substring)){
currentList.add(substring);
partitionList(s, i + 1);
currentList.remove(currentList.size() - 1);
}
}
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s){
int left = 0;
int right = s.length() - 1;
while(left <= right){
if(s.charAt(left++) != s.charAt(right--)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
3. 子集问题
leetcode 78. 子集
跟之前的也算没差别,主要还是要索引的理解吧!!
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> currentList = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(currentList));
return result;
}
dfs(nums, 0);
return result;
}
private void dfs(int[] nums, int startIndex){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(currentList));
if(startIndex >= nums.length){
return;
}
for(int i = startIndex; i<nums.length; i++){
currentList.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, i+1);
currentList.remove(currentList.size() - 1);
}
}
}
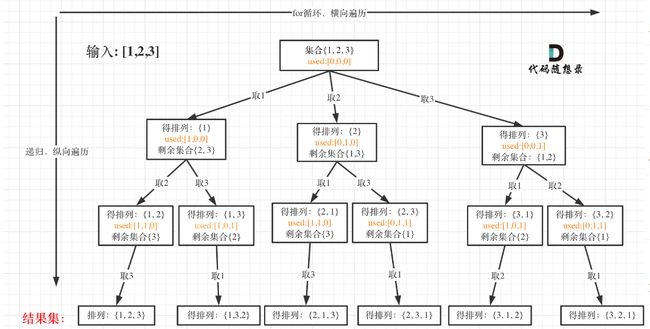
4. 排列问题
leetcode 46. 全排列
这题跟前面的题目就不一样了,前面需要使用startIndex定位位置,从哪里开始,这道题每个都是一样的长度
抽象成树,题目就是这样的啦
所以,我们需要有个方式来记录哪个数b以及被用过,如果没被用过就加进去,被用过就不准使用
则,可以使用boolean[]可以记录,用数组的方式,记录true,false(说实话,我也是第一次用。。。)
所以回溯三部曲第一,第二步就是这样啦!
private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
private boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0){
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums){
if (path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
}
}
下面就是需要判断当前的nums[i]是否被用过,如果没有,那么就可以添加,添加完就变成true
回溯那一步,就是吧当前的数,变成false
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
private LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
private boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0){
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums){
if (path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (used[i]){
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
5. 字母大小写全排列
leetcode 784. 字母大小写全排列
这道题比较麻烦的是对字母的大小写转换
思路:
- 位运算
- ASCII表
讲解:
我们发现大写字符与其对应的小写字符的 ASCII 的差为 32,32 这个值如果敏感的话,它是 2^5,在编程语言中,可以表示为 1 << 5。
变换大小写这件事等价于:
- 如果字符是小写字符,减去 32 得到大写字符;
- 如果字符是大写字符,加上 32 得到小写字符。
而这两者合并起来,就是给这个字符做一次不进位的加法,即异或上 1 << 5。
class Solution {
private List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) {
dfs(s.toCharArray(), 0);
return result;
}
private void dfs(char[] arr, int startIndex){
if(startIndex == arr.length){
result.add(new String(arr));
return;
}
dfs(arr, startIndex + 1);
if(Character.isLetter(arr[startIndex])){
arr[startIndex] ^= 1 << 5;
dfs(arr, startIndex+1);
}
}
}
异或运算(^)是一种位运算符。在这段代码中,使用异或运算来实现大小写字母的翻转。
对于英文字母,它们的 ASCII 码中的第 6 位表示大小写信息,其中大写字母的第 6 位为 0,小写字母的第 6 位为 1。通过异或运算,可以将第 6 位取反,从而实现大小写字母的翻转。
具体来说,在这段代码中,通过
arr[startIndex] ^= 1 << 5这行代码,将当前字符的第 6 位进行异或操作。当字符是大写字母时,第 6 位为 0,异或操作会将其变为 1;当字符是小写字母时,第 6 位为 1,异或操作会将其变为 0。通过这种方式,我们可以在递归中生成所有可能的大小写组合。同时,由于异或运算是可逆的,所以在递归回溯时,再次对同一个字符进行异或操作,可以恢复原来的大小写形式。
6.单词搜索
leetcode 79. 单词搜索
注意:这题有点难,需要反复观看和理解!!!
首先,获取当前字符的位置
for(int i=0; i < board.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){
if(dfs(board, words, i, j, 0)){
return true;
}
}
}
-
外层循环
for(int i=0; i < board.length; i++)用于遍历字母矩阵的行。 -
内层循环
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++)用于遍历字母矩阵的列。
在每次循环迭代中,我们将当前字符的位置(i, j)作为参数传递给dfs方法进行搜索
下一步,递归,我们将目标单词转换为字符数组,以便于对每个字符进行处理。然后,我们遍历整个矩阵中的每个字符位置,调用一个名为dfs的递归函数进行搜索。
在dfs函数中,我们首先要检查一些边界条件:
- 如果当前位置超出了矩阵范围,即i大于等于矩阵行数或小于0,或者j大于等于矩阵列数或小于0,那么说明已经越界,返回false。
if(i >= board.length || i < 0 || j >= board[0].length || j <0){
return false;
}
- 如果当前位置的字符不匹配目标单词的第k个字符,那么也返回false。
if(board[i][j] != word[k]){
return false;
}
如果以上两个条件都不满足,我们继续判断一些其他情况:
- 如果k等于目标单词的长度减1,说明我们已经找到了完整的目标单词,因此返回true。
if(k == word.length - 1){
return true;
}
- 如果以上条件都没有满足,我们将当前位置的字符设为null(‘\0’)以表示已经访问过,并且继续递归地在上下左右四个方向上搜索下一个字符。
board[i][j] = '\0';
boolean res = dfs(board, word, i + 1, j, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
dfs(board, word, i, j + 1, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i, j - 1, k + 1);
- 如果有任何一个方向上的搜索结果为true,那么说明在这个方向上找到了目标单词,我们则返回true。
if(res){
return true;
}
- 最后,在递归结束之前,我们需要将当前位置的字符还原为目标单词的第k个字符(即将null还原为原来的字符),以便进行其他路径的搜索。
board[i][j] = word[k];
在主函数中,我们遍历整个矩阵中的每个字符位置,并调用dfs函数进行搜索。如果有任何一个位置能够找到完整的目标单词,那么返回true,否则返回false。
完整代码如下:
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
// 将目标单词转换为字符数组
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
// 遍历字母矩阵的每个字符位置
for(int i=0; i < board.length; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++){
// 调用dfs函数进行搜索
if(dfs(board, words, i, j, 0)){
// 如果找到完整的目标单词,则返回true
return true;
}
}
}
// 如果遍历完字母矩阵后仍然没有找到完整的目标单词,则返回false
return false;
}
private boolean dfs(char[][] board, char[] word, int i, int j, int k){
// 边界条件:越界或当前字符不匹配目标单词的第k个字符,返回false
if(i >= board.length || i < 0 || j >= board[0].length || j <0 || board[i][j] != word[k]){
return false;
}
// 如果k等于目标单词的长度减1,说明已经找到了完整的目标单词,返回true
if(k == word.length - 1){
return true;
}
// 将当前字符设为null以表示已访问过,并继续递归地在上下左右四个方向上搜索下一个字符
board[i][j] = '\0';
boolean res = dfs(board, word, i + 1, j, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
dfs(board, word, i, j + 1, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i, j - 1, k + 1);
// 在递归结束之前,将当前字符还原为目标单词的第k个字符,并返回搜索结果
board[i][j] = word[k];
return res;
}
}
over~~