MySQL数据库——多表查询(4)-实例练习、多表查询总结
目录
练习1
练习2
总结
1.多表关系
2.多表查询
进行案例练习之前,需要先增加一个表格
create table salgrade(
grade int,
losal int, -- 对应等级的最低薪资
hisal int -- 对应等级的最高薪资
) comment '薪资等级表';
insert into salgrade values (1,0,3000);
insert into salgrade values (2,3001,5000);
insert into salgrade values (3,5001,8000);
insert into salgrade values (4,8001,10000);
insert into salgrade values (5,10001,15000);
insert into salgrade values (6,15001,20000);
insert into salgrade values (7,20001,25000);
insert into salgrade values (8,25001,30000);练习1
- 查询员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息 (隐式内连接)
- 查询年龄小于30岁的员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(显式内连接)
- 查询拥有员工的部门ID、部门名称
- 查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工, 及其归属的部门名称; 如果员工没有分配部门, 也需要展示出来
- 查询所有员工的工资等级
1-1
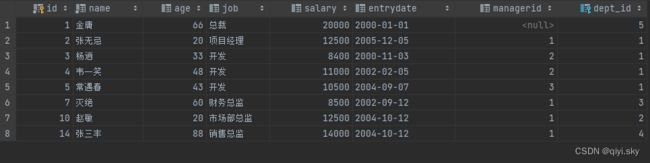
-- 查询员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息 (隐式内连接)
select e.name '姓名',e.age '年龄',e.job '职位',d.name '部门信息'
from emp e,dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;查询结果:
1-2
-- 查询年龄小于30岁的员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(显式内连接)
select e.name '姓名',e.age '年龄',e.job '职位',d.name '部门信息'
from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age < 30;查询结果:
1-3
-- 查询拥有员工的部门ID、部门名称
-- 要点:自连接,去重关键字
select distinct d.id,d.name from emp e,dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;查询结果:
1-4
-- 查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工, 及其归属的部门名称; 如果员工没有分配部门, 也需要展示出来
-- 要点:左外连接
select e.name '姓名',d.name '部门名称'
from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where age > 40;查询结果:
1-5
-- 查询所有员工的工资等级
-- 要点:表结构为emp和salgrade,搞清楚两张表的连接条件
select e.name '姓名',s.grade '工资等级'
from emp e left join salgrade s on e.salary >= s.losal and e.salary <= s.hisal;
-- 另一种写法
select e.name '姓名',s.grade '工资等级'
from emp e left join salgrade s on e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal;查询结果:
练习2
- 查询 "研发部" 所有员工的信息及 工资等级
- 查询 "研发部" 员工的平均工资
- 查询工资比 "灭绝" 高的员工信息。
- 查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
- 查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
- 查询所有的部门信息, 并统计部门的员工人数
- 查询所有学生的选课情况, 展示出学生名称, 学号, 课程名称
2-1
-- 查询 "研发部" 所有员工的信息及 工资等级
-- 要点:搞清楚连接条件和查询条件
-- 连接条件:
(e.dept_id = d.id)
(e.salary between losal and hisal)
-- 查询条件 (d.name = '研发部')
select e.*,s.grade
from emp e,
dept d,
salgrade s
where (e.dept_id = d.id)
and (e.salary between losal and hisal)
and (d.name = '研发部');查询结果:
2-2
-- 查询 "研发部" 员工的平均工资
-- 要点:函数avg()
select avg(e.salary)
from emp e,
dept d
where e.dept_id = d.id
and d.name = '研发部';查询结果:
2-3
-- 查询工资比 "灭绝" 高的员工信息。
select *
from emp
where salary > (select salary from emp where name = '灭绝');查询结果:
2-4
-- 查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
select *
from emp
where salary > (select avg(salary) from emp);查询结果:
2-5
-- 查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
-- 要点:查询出每个部门的平均工资
select *, (select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = e2.dept_id) '所在部门平均工资'
from emp e2
where e2.salary < (select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = e2.dept_id);查询结果:
2-6
-- 查询所有的部门信息, 并统计部门的员工人数
先查询所有部门的部门信息:
select * from dept;再统计单个部门的员工人数:
select count(*) from emp where dept_id = 1;整合起来:
select d.*, (select count(*) from emp e where e.dept_id = d.id) '员工人数'
from dept d;查询结果:
2-7
-- 查询所有学生的选课情况, 展示出学生名称, 学号, 课程名称
涉及另外的三个表,是多对多的关系
理清楚三个表的连接关系就可以查询出来
select s.name '学生名称', s.no '学号', c.name '课程名称'
from student s,
course c,
student_course sc
where (s.id = sc.studentid)
and (c.id = sc.courseid);查询结果:
总结
1.多表关系
一对多:在多的一方设置外键,关联一的一方的主键
多对多:建立中间表,中间表包含两个外键,关联两张表的主键
一对一:用于表结构拆分,在其中任何一方设置外键(UNIQUE),关联另一方的主键
2.多表查询
自连接
隐式:SELECT...FROM 表A,表B WHERE 条件...
显式:SELECT...FROM 表A INNER JOIN 表B ON 条件...
外连接:
左外:SELECT...FROM 表A LEFT JOIN 表B ON 条件...
右外:SELECT...FROM 表A RIGHT JOIN 表B ON 条件...
自连接:SELECT ... FROM 表A 别名1,表A 别名2 WHERE 条件...
子查询:标量子查询、列子查询、行子查询、表子查询
end
学习自:黑马程序员——MySQL数据库课程