02_Flutter自定义Sliver组件实现分组列表吸顶效果
02_Flutter自定义Sliver组件实现分组列表吸顶效果
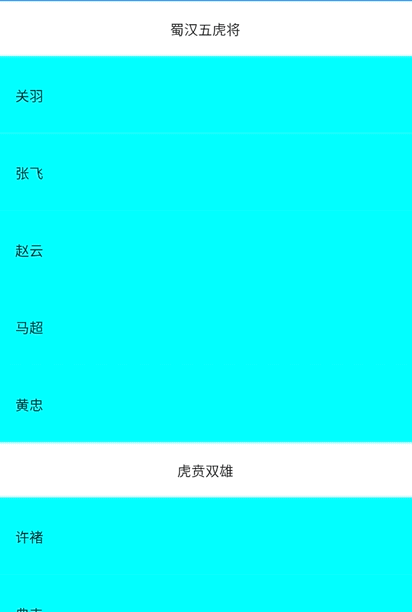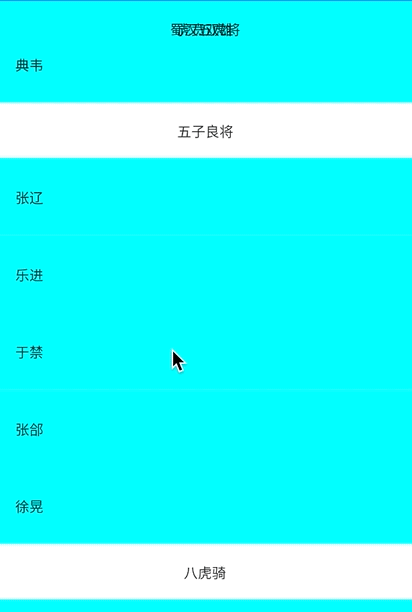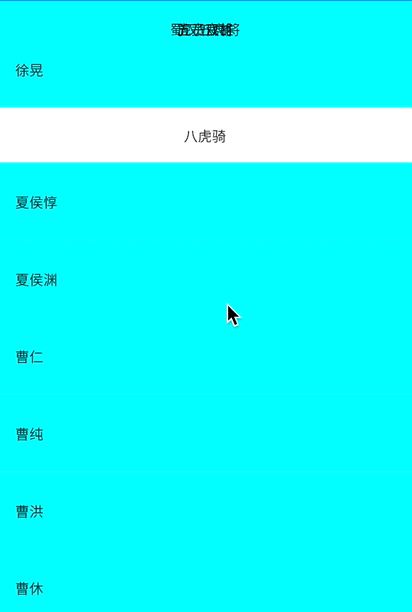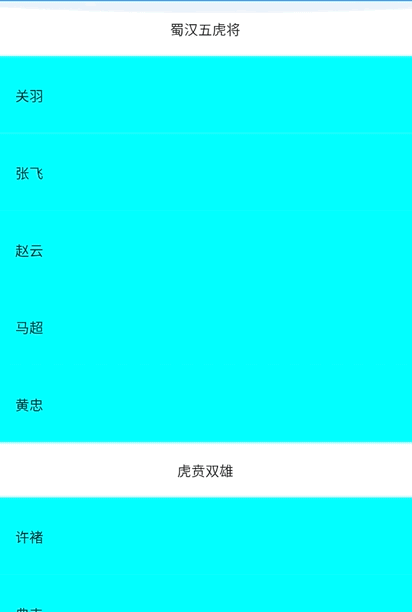
一.先上效果图
二.列表布局实现
比较简单,直接上代码,主要使用CustomScrollView和SliverToBoxAdapter实现
_buildSection(String title) {
return SliverToBoxAdapter(
child: RepaintBoundary(
child: Container(
height: 50,
color: Colors.brown,
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text(title),
),
)
);
}
_buildItem(String title) {
return SliverToBoxAdapter(
child: RepaintBoundary(
child: Container(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 15),
height: 70,
color: Colors.cyanAccent,
alignment: Alignment.centerLeft,
child: Text(title),
),
)
);
}
CustomScrollView(
slivers: [
_buildSection("蜀汉五虎将"),
_buildItem("关羽"),
_buildItem("张飞"),
_buildItem("赵云"),
_buildItem("马超"),
_buildItem("黄忠"),
_buildSection("虎贲双雄"),
_buildItem("许褚"),
_buildItem("典韦"),
_buildSection("五子良将"),
_buildItem("张辽"),
_buildItem("乐进"),
_buildItem("于禁"),
_buildItem("张郃"),
_buildItem("徐晃"),
_buildSection("八虎骑"),
_buildItem("夏侯惇"),
_buildItem("夏侯渊"),
_buildItem("曹仁"),
_buildItem("曹纯"),
_buildItem("曹洪"),
_buildItem("曹休"),
_buildItem("夏侯尚"),
_buildItem("曹真")
],
)
三.SliverToBoxAdapter和SliverPersistentHeader
可以使用Flutter提供的SliverPersistentHeader组件实现,在使用SliverPersistentHeader时要求我们明确指定子控件的高度,不支持吸顶上推效果,使用起来不够灵活,所以我们参考并结合SliverToBoxAdapter和SliverPersistentHeader源码,自己实现一个自适应高度的吸顶Sliver组件,并在此基础上一步步实现吸顶上推效果。
- 编写StickySliverToBoxAdapter类,继承自SingleChildRenderObjectWidget
class StickySliverToBoxAdapter extends SingleChildRenderObjectWidget {
const StickySliverToBoxAdapter({
super.key,
super.child
});
RenderObject createRenderObject(BuildContext context) => _StickyRenderSliverToBoxAdapter();
}
SingleChildRenderObjectWidget类要求我们自己实现createRenderObject方法,返回一个RenderObject对象,而对于一个S liver组件而言,这个RenderObject必须是RenderSilver的子类。
- 编写_StickyRenderSliverToBoxAdapter,继承RenderSliverSingleBoxAdapter
class _StickyRenderSliverToBoxAdapter extends RenderSliverSingleBoxAdapter {
void performLayout() {
// TODO: implement performLayout
}
}
RenderSliverSingleBoxAdapter要求子类实现performLayout方法,performLayout会对widegt的布局和绘制做控制,实现吸顶效果的关键就在于performLayout方法的实现。先依次看下SliverToBoxAdapter和SliverPersistentHeader对应RenderObject的performLayout相关方法的实现。
- RenderSliverToBoxAdapter#performLayout
void performLayout() {
if (child == null) {
geometry = SliverGeometry.zero;
return;
}
final SliverConstraints constraints = this.constraints;
//摆放子View,并把constraints传递给子View
child!.layout(constraints.asBoxConstraints(), parentUsesSize: true);
//获取子View在滑动主轴方向的尺寸
final double childExtent;
switch (constraints.axis) {
case Axis.horizontal:
childExtent = child!.size.width;
case Axis.vertical:
childExtent = child!.size.height;
}
final double paintedChildSize = calculatePaintOffset(constraints, from: 0.0, to: childExtent);
final double cacheExtent = calculateCacheOffset(constraints, from: 0.0, to: childExtent);
assert(paintedChildSize.isFinite);
assert(paintedChildSize >= 0.0);
//更新SliverGeometry
geometry = SliverGeometry(
scrollExtent: childExtent,
paintExtent: paintedChildSize,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
maxPaintExtent: childExtent,
hitTestExtent: paintedChildSize,
hasVisualOverflow: childExtent > constraints.remainingPaintExtent || constraints.scrollOffset > 0.0,
);
//更新paintOffset,由滑动偏移量constraints.scrollOffset决定
setChildParentData(child!, constraints, geometry!);
}
- RenderSliverFloatingPersistentHeader#performLayout
SliverPersistentHeader的performLayout方法中调用了updateGeometry方法去更新geometry,而吸顶的关键就在updateGeometry方法中,也就是paintOrigin的值。constraints.overlap的值代表前一个Sliver和当前Sliver被覆盖部分的高度。
double updateGeometry() {
final double minExtent = this.minExtent;
final double minAllowedExtent = constraints.remainingPaintExtent > minExtent ?
minExtent :
constraints.remainingPaintExtent;
final double maxExtent = this.maxExtent;
final double paintExtent = maxExtent - _effectiveScrollOffset!;
final double clampedPaintExtent = clampDouble(paintExtent,
minAllowedExtent,
constraints.remainingPaintExtent,
);
final double layoutExtent = maxExtent - constraints.scrollOffset;
final double stretchOffset = stretchConfiguration != null ?
constraints.overlap.abs() :
0.0;
geometry = SliverGeometry(
scrollExtent: maxExtent,
paintOrigin: math.min(constraints.overlap, 0.0),
paintExtent: clampedPaintExtent,
layoutExtent: clampDouble(layoutExtent, 0.0, clampedPaintExtent),
maxPaintExtent: maxExtent + stretchOffset,
maxScrollObstructionExtent: minExtent,
hasVisualOverflow: true, // Conservatively say we do have overflow to avoid complexity.
);
return 0.0;
}
四.吸顶效果实现
直接把上面updateGeometry中设置SliverGeometry的代码拷贝到_StickyRenderSliverToBoxAdapter#performLayout实现中,maxExtent和minExtent这两个值是由SliverPersistentHeader传入的SliverPersistentHeaderDelegate对象提供的。这里可以自己去看SliverPersistentHeaderDelegate的源码,就不多废话了。我们只需要把maxExtent和minExtent这两个值都改为子控件在主轴方向的尺寸大小即可。
_buildSection(String title) {
return StickySliverToBoxAdapter(
child: RepaintBoundary(
child: Container(
height: 50,
color: Colors.brown,
alignment: Alignment.center,
child: Text(title),
),
)
);
}
class _StickyRenderSliverToBoxAdapter extends RenderSliverSingleBoxAdapter {
void performLayout() {
if (child == null) {
geometry = SliverGeometry.zero;
return;
}
final SliverConstraints constraints = this.constraints;
//摆放子View,并把constraints传递给子View
child!.layout(constraints.asBoxConstraints(), parentUsesSize: true);
//获取子View在滑动主轴方向的尺寸
final double childExtent;
switch (constraints.axis) {
case Axis.horizontal:
childExtent = child!.size.width;
case Axis.vertical:
childExtent = child!.size.height;
}
final double minExtent = childExtent;
final double minAllowedExtent = constraints.remainingPaintExtent > minExtent ?
minExtent : constraints.remainingPaintExtent;
final double maxExtent = childExtent;
final double paintExtent = maxExtent;
final double clampedPaintExtent = clampDouble(paintExtent,
minAllowedExtent,
constraints.remainingPaintExtent,
);
final double layoutExtent = maxExtent - constraints.scrollOffset;
geometry = SliverGeometry(
scrollExtent: maxExtent,
paintOrigin: min(constraints.overlap, 0.0),
paintExtent: clampedPaintExtent,
layoutExtent: clampDouble(layoutExtent, 0.0, clampedPaintExtent),
maxPaintExtent: maxExtent,
maxScrollObstructionExtent: minExtent,
hasVisualOverflow: true, // Conservatively say we do have overflow to avoid complexity.
);
}
}
仔细看上面的效果,貌似只有第一个Sliver吸顶了,我们把分组item的背景改成透明的,再来看看效果,就知道怎么回事了。
可以看到,所有的分组section都已经吸顶了,只不过吸顶位置都是0,并且前一个section把后一个section覆盖了,我们下一步实现上推功能后,这个问题自热而然的就解决了。
五.实现上推效果
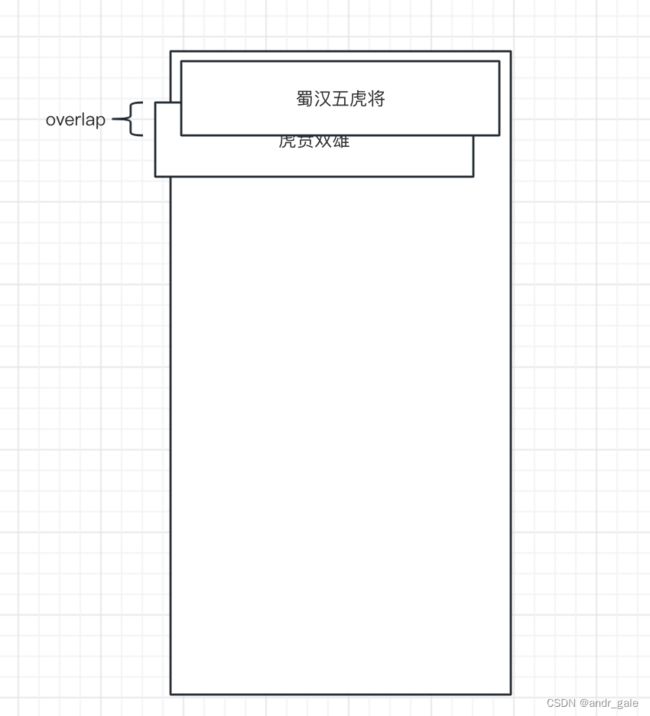
如图,当前section与前一个section重合了多少,前一个section就往上移动多少,也就是移动constraints.overlap即可,往下滑动也是同样的道理。
//查找前一个吸顶的section
RenderSliver? _prev() {
if(parent is RenderViewportBase) {
RenderSliver? current = this;
while(current != null) {
current = (parent as RenderViewportBase).childBefore(current);
if(current is _StickyRenderSliverToBoxAdapter && current.geometry != null) {
return current;
}
}
}
return null;
}
void performLayout() {
if (child == null) {
geometry = SliverGeometry.zero;
return;
}
final SliverConstraints constraints = this.constraints;
//摆放子View,并把constraints传递给子View
child!.layout(constraints.asBoxConstraints(), parentUsesSize: true);
//获取子View在滑动主轴方向的尺寸
final double childExtent;
switch (constraints.axis) {
case Axis.horizontal:
childExtent = child!.size.width;
case Axis.vertical:
childExtent = child!.size.height;
}
final double minExtent = childExtent;
final double minAllowedExtent = constraints.remainingPaintExtent > minExtent ?
minExtent : constraints.remainingPaintExtent;
final double maxExtent = childExtent;
final double paintExtent = maxExtent;
final double clampedPaintExtent = clampDouble(paintExtent,
minAllowedExtent,
constraints.remainingPaintExtent,
);
final double layoutExtent = maxExtent - constraints.scrollOffset;
geometry = SliverGeometry(
scrollExtent: maxExtent,
paintOrigin: min(constraints.overlap, 0.0),
paintExtent: clampedPaintExtent,
layoutExtent: clampDouble(layoutExtent, 0.0, clampedPaintExtent),
maxPaintExtent: maxExtent,
maxScrollObstructionExtent: minExtent,
hasVisualOverflow: true, // Conservatively say we do have overflow to avoid complexity.
);
//上推关键代码: 当前吸顶的Sliver被覆盖了多少,前一个吸顶的Sliver就移动多少
RenderSliver? prev = _prev();
if(prev != null && constraints.overlap > 0) {
setChildParentData(_prev()!, constraints.copyWith(scrollOffset: constraints.overlap), _prev()!.geometry!);
}
}
搞定,可以洗洗睡了,嘿嘿。
六.Fixed: 吸顶section点击事件失效
重写childMainAxisPosition方法返回0即可
class _StickyRenderSliverToBoxAdapter extends RenderSliverSingleBoxAdapter {
...
// 必须重写,否则点击事件失效。
double childMainAxisPosition(covariant RenderBox child) => 0.0;
}