IDEA代码警告(warning)整理以及解决办法
背景
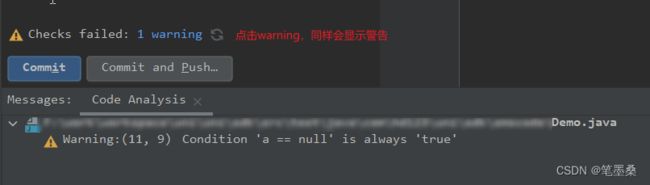
在日常开发中,IDEA可能会通过下方的problems窗口以及编辑窗口最右方的黄色标记提示给我们一些警告:
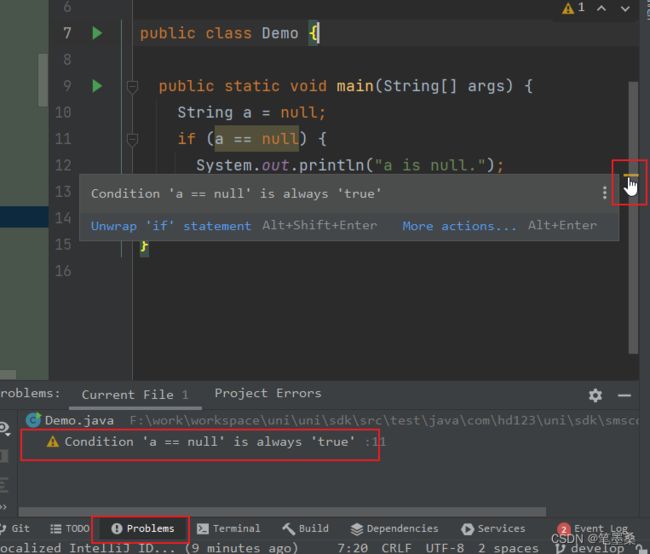
大多数情况下,无视这些警告并不会影响我们的程序结果,但却说明了我们的代码或多或少有一些问题,还有优化的空间,也有可能有潜在的风险,而且有强迫症同学同样也不想看到这些警告。这篇文章整理了我在平时开发中遇到的一些IDEA警告,以便后续碰到同样的问题可以作为参考。
注意:不是所有警告都需要处理,需要自行判断是否有处理的必要。(如我们对变量进行了缩写,而IDEA认为是一个错误的单词)。
如何检查代码
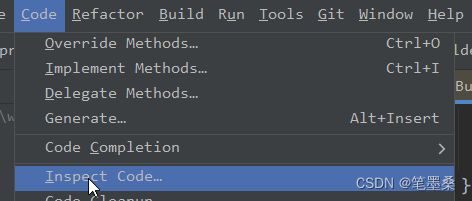
默认情况下,problems窗口的Current File页签中会展示的当前文件的错误以及警告等。如果想查看整个项目、某一模块或某个条件下的文件时,需要依次点击最上方菜单栏上的Code -> Inspect Code
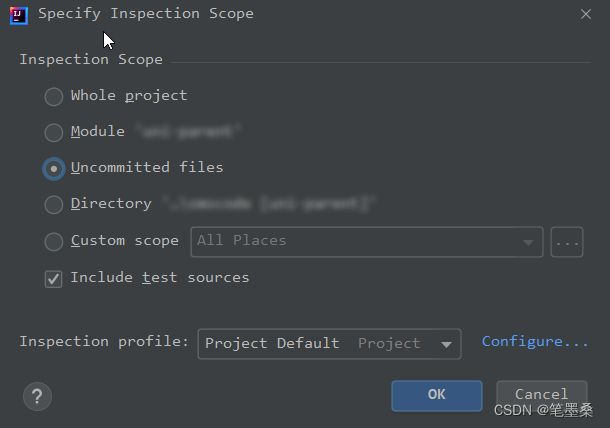
在弹出的窗口中可以选择检查哪些文件的代码,如整个项目,某个模块,未提交的文件等,也可以自己配置检查哪些项:
警告分析
X can be simplified to Y
原因:写法比较啰嗦,有简化写法。
public class Demo {
boolean result;
public boolean test() {
return result == true;
}
}
// 'result == true' can be simplified to 'result'
解决办法:
按照提示将X修改为Y即可。
public class Demo {
boolean result;
public boolean test() {
// 直接返回布尔值即可。
return result;
}
}
‘OptionalInt.getAsInt()’ without ‘isPresent()’ check
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^(" + name + "\\()(\\d+)(\\))$");
int max = apps.stream()
.mapToInt(app -> {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(app.getName());
if (matcher.find()) {
// 取第二部分表示版本号
String group = matcher.group(2);
// 正则表达式过滤都数字,不用担心转换异常
return Integer.parseInt(group);
}
return 1;
})
.max()
.getAsInt();
return max + 1;
示例代码中,apps为一个对象列表,经过一些列处理变为某个int值最后取最大值。提示的原因是因为map中有if的判断,所以有可能全部不匹配,此时max()可能返回一个类似Optional为空的一个东西,需要进行类似处理,将getAsInt改为orElse即可
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^(" + name + "\\()(\\d+)(\\))$");
int max = apps.stream()
.mapToInt(app -> {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(app.getName());
if (matcher.find()) {
// 取第二部分表示版本号
String group = matcher.group(2);
// 正则表达式过滤都数字,不用担心转换异常
return Integer.parseInt(group);
}
return 1;
})
.max()
// 给一个默认值
.orElse(1);
return max + 1;
Iteration can be replaced with bulk ‘Collection.addAll’ call
原因:采用循环一个一个向集合中添加,比较麻烦。
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList();
List<String> list2 = xxxx;
for (String str : list2) {
list1.add(str);
}
解决办法:使用addAll方法。
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList();
List<String> list2 = xxxx;
list1.addAll(list2);
More arguments provided (1) than placeholders specified (0)
为SLF4J日志功能的警告
...
LOGGER.error("user {0} is not found ", userId);
...
问题分析:
SL4FJ中占位符不像MessageFormat需要指定index,而是直接使用{}即可
解决办法:直接使用{}
...
LOGGER.error("user {} is not found ", userId);
...
Call to ‘asList()’ with only one argument
原因:使用Arrays.asList时只向其中添加了一个元素。
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a");
解决方法:使用Collections.singletonList代替
List<String> list = Collections.singletonList("a");
Raw use of parameterized class xx
原因:一般为没有指定泛型
例1:如有一个类定义为
public class ResponseDto<T> {
}
在实例化的时候按照如下所示
ResponseDto<String> response = new ResponseDto();
虽然引用加上了泛型,但是对象没有加泛型,此时就会出现警告
解决方法:在对象上也加上泛型,但是无需写全部,只需写<>即可,否则IDE会觉得多余并发出警告
![]()
// 无需写全
// ResponseDto response = new ResponseDto();
ResponseDto<String> response = new ResponseDto<>();
例2:在单元测试中使用mockito来虚拟一个feign客户端时,如果参数为list那么会按照如下方式虚拟
XXClient client = mock(XXClient.class);
when(client.listByIds(anyList())).thenAnswer(invocation -> {
// Do something
}
此时IDE会给予警告
![]()
因为我们的接口参数指定了list的泛型
List<XX> listByIds(List<Long> ids);
但是mock时调用的方法anyList的返回值并没有指定泛型
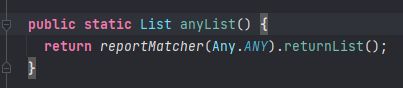
所以IDE给出警告
解决办法:调用mockito中提供的其他可以指定泛型的方法,如
when(client.listByIds(anyListOf(Long.class))).thenAnswer(invocation -> {
...
}
Passing a non-null argument to ‘Optional’
原因:向Optional.ofNullable传递一个非null对象。
User user = xxxx;
if (user != null) {
Optional.ofNullable(user).xxx;
}
解决办法,如果可以明确对象非null,则直接使用of。
User user = xxxx;
if (user != null) {
Optional.of(user).xxx;
}
Method ‘xx()’ recurses infinitely, and can only end by throwing an exception
原因:提示为无限递归,只能通过触发异常的方式结束。
public void method1() {
method1();
}
解决办法:
一般来说为错误的调用了自己(如想调用重载的其他方法,最后由于马虎又重新调用了自己),或是递归方法写的有问题,需要具体检查代码。
‘if’ statement replaceable with ‘switch’ statement
原因:为if…else…判断条件太多导致,IDEA认为应该替换为swtich语句
if (condition1) {
// Do something
} else if (condition2) {
// Do something
} else if (condition3) {
// Do something
} else if (condition4) {
// Do something
} else if (condition5) {
// Do something
} else if (condition6) {
// Do something
} else {
// Do something
}
解决办法:建议通过表驱动、多态、设计模式等方式消除这么多的判断,如果不得不进行判断,那么可以根据提示修改为switch。
switch(xxx) {
case condition1:
xxx;
break;
case condition2:
xxx;
break;
...
}
Result of ‘XX’ is ignored
原因:调用一个有返回值的方法,但是没有使用该返回值。
File folder = new File("xx");
if (!folder.exists()) {
folder.mkdir();
}
由于mkdir()方法会返回boolean类型的返回值,但是我们没有使用,所以编译器会报出警告。
解决办法:可以使用返回值输出一些日志等,如果实在不想使用返回值,那么可以在方法上标注以下注解来压制警告。
@SuppressWarnings("ResultOfMethodCallIgnored")
Statement lambda can be replaced with expression lambda
users.forEach(u -> {
u.setState(xxx);
})
当有以上写法时会有警告,可以看出lambda表达式方法体内只有一行代码,此时可以将花括号去掉进行简写
解决办法:去掉大括号
users.forEach(u -> u.setState(xxx))
Lambda can be replaced with method reference
names.stream().
map(n -> n.toUpperCase())
...
当有如上写法时会出现警告。
解决办法:可以替换为方法调用的简写形式
names.stream().
map(String::toUpperCase)
...
Condition ‘x != null’ covered by subsequent condition ‘x instanceof List’
原因:后面的判断条件包含了前面的判断条件
public boolean test(Object obj) {
if (obj != null && obj instanceof String) {
// Do sth...
}
}
上例中,如果obj为null,则自然obj instanceof String为false,所以不用重复判断
解决办法:去掉多余判断
public boolean test(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof String) {
// Do sth...
}
}
Actual value of parameter ‘xxx’ is always ‘yyy’
原因:调用某个方法时,某个参数的值目前来说一直是固定的一个值。
解决办法:
-
- 考虑是否一直是固定值,如果是,则将传参改为局部变量或常量等。
-
- 如果该参数确实需要传递,只不过目前来说是一个值,将来不确定,可以考虑将其压制
@SuppressWarnings("SameParameterValue")
Unchecked generics array creation for varargs parameter
解决办法:在方法上添加注解
@SafeVarargs
XXX is deprecated
原因:调用某个标记为@Deprecated方法或属性时,会报此警告。意为提示调用者这是个过时的方法或属性,再未来的某个版本有可能会消失,不应该调用该方法。
但是某种情况下我们确实需要调用过时的方法,比如我们开发工具类需要兼容老版本,或我们将一个方法标记了过时之后,单元测试依旧调用此方法。
解决办法:
-
- 如果可能的话,尝试使用替代方法。一般来说在此方法的Javadoc中指引出新的方法。
-
- 如果确实需要调用过时的方法或属性,可以考虑将其压制
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")