01.Spring Framework 源码解析之启动容器
1. 环境搭建
代码已经上传至 https://github.com/masteryourself/spring-framework,工程是
tutorial-spring-start
2. 源码解析
详细的源码注释可参考 https://github.com/masteryourself/spring-framework
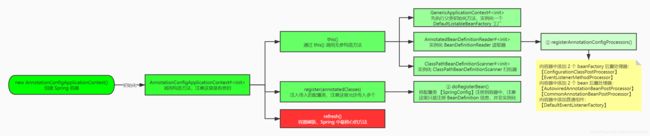
2.1 初始化流程
2.1.1 流程分析
2.1.2 核心代码剖析
1. org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils#registerAnnotationConfigProcessors
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
// 向 beanDefinitionMap 中注册【BeanFactoryPostProcessor】:【ConfigurationClassPostProcessor】
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// 向 beanDefinitionMap 中注册【BeanPostProcessor】:【AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor】
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
// 向 beanDefinitionMap 中注册【BeanPostProcessor】:【CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor】
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
// 向 beanDefinitionMap 中注册【BeanPostProcessor】:【PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor】,前提条件是在 jpa 环境下
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// 向 beanDefinitionMap 中注册【BeanFactoryPostProcessor】:【EventListenerMethodProcessor】
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// 向 beanDefinitionMap 中注册组件:【DefaultEventListenerFactory】
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
2. org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader#doRegisterBean
<T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> annotatedClass, @Nullable Supplier<T> instanceSupplier, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... definitionCustomizers) {
// 解析传入的配置类,实际上这个方法既可以解析配置类,也可以解析 Spring bean 对象
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(annotatedClass);
// 判断是否需要跳过,判断依据是此类上有没有 @Conditional 注解
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(instanceSupplier);
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
// 处理类上的通用注解
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
// 封装成一个 BeanDefinitionHolder
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : definitionCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
// 处理 scopedProxyMode
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
// 把 BeanDefinitionHolder 注册到 registry
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
2.2 refresh() 流程
2.2.1 流程分析
2.2.2 核心代码剖析
1. org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 1. 刷新前的预处理
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 2. 获取 beanFactory,即前面创建的【DefaultListableBeanFactory】
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 3. 预处理 beanFactory,向容器中添加一些组件
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 4. 子类通过重写这个方法可以在 BeanFactory 创建并与准备完成以后做进一步的设置
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 5. 执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 方法,beanFactory 后置处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 6. 注册 BeanPostProcessors,bean 后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 7. 初始化 MessageSource 组件(做国际化功能;消息绑定,消息解析)
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 8. 初始化事件派发器,在注册监听器时会用到
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 9. 留给子容器(子类),子类重写这个方法,在容器刷新的时候可以自定义逻辑,web 场景下会使用
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 10. 注册监听器,派发之前步骤产生的一些事件(可能没有)
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 11. 初始化所有的非单实例 bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 12. 发布容器刷新完成事件
finishRefresh();
}
...
}
}
2. org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#prepareBeanFactory
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 设置 classLoader
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
//设置 bean 表达式解析器
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 添加一个 BeanPostProcessor【ApplicationContextAwareProcessor】
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 设置忽略自动装配的接口,即不能通过注解自动注入
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 注册可以解析的自动装配类,即可以在任意组件中通过注解自动注入
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
// 添加一个 BeanPostProcessor【ApplicationListenerDetector】
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
// 添加编译时的 AspectJ
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
// 注册 environment 组件,类型是【ConfigurableEnvironment】
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
// 注册 systemProperties 组件,类型是【Map】
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
// 注册 systemEnvironment 组件,类型是【Map】
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
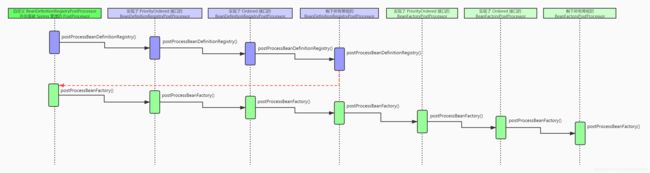
3. org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// beanFactoryPostProcessors 这个参数是指用户通过 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor() 方法手动传入的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,没有交给 spring 管理
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
// 代表执行过的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
// 常规后置处理器集合,即实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 注册后置处理器集合,即实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 处理自定义的 beanFactoryPostProcessors(指调用 context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor() 方法),一般这里都没有
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 调用 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
// 定义一个变量 currentRegistryProcessors,表示当前要处理的 BeanFactoryPostProcessors
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 首先,从容器中查找实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 类型,这里只会查找出一个【ConfigurationClassPostProcessor】
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 判断是否实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// 添加到 currentRegistryProcessors
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 添加到 processedBeans,表示已经处理过这个类了
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 设置排列顺序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
// 添加到 registry 中
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行 [postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry] 回调方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 将 currentRegistryProcessors 变量清空,下面会继续用到
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 接下来,从容器中查找实现了 Ordered 接口的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 类型,这里可能会查找出多个
// 因为【ConfigurationClassPostProcessor】已经完成了 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 方法,已经向容器中完成扫描工作,所以容器会有很多个组件
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 判断 processedBeans 是否处理过这个类,且是否实现 Ordered 接口
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 设置排列顺序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
// 添加到 registry 中
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行 [postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry] 回调方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 将 currentRegistryProcessors 变量清空,下面会继续用到
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
// 最后,从容器中查找剩余所有常规的 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 类型
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
// 根据类型从容器中查找
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 判断 processedBeans 是否处理过这个类
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// 添加到 currentRegistryProcessors
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 添加到 processedBeans,表示已经处理过这个类了
processedBeans.add(ppName);
// 将标识设置为 true,继续循环查找,可能随时因为防止下面调用了 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors() 方法引入新的后置处理器
reiterate = true;
}
}
// 设置排列顺序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
// 添加到 registry 中
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 执行 [postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry] 回调方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
// 将 currentRegistryProcessors 变量清空,因为下一次循环可能会用到
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
// 现在执行 registryProcessors 的 [postProcessBeanFactory] 回调方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行 regularPostProcessors 的 [postProcessBeanFactory] 回调方法,也包含用户手动调用 addBeanFactoryPostProcessor() 方法添加的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// 从容器中查找实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的类
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 表示实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 表示实现了 Ordered 接口的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 表示剩下来的常规的 BeanFactoryPostProcessors
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 判断是否已经处理过,因为 postProcessorNames 其实包含了上面步骤处理过的 BeanDefinitionRegistry 类型
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
// 判断是否实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 判断是否实现了 Ordered 接口
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
// 剩下所有常规的
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 先将 priorityOrderedPostProcessors 集合排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行 priorityOrderedPostProcessors 的 [postProcessBeanFactory] 回调方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 接下来,把 orderedPostProcessorNames 转成 orderedPostProcessors 集合
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 将 orderedPostProcessors 集合排序
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行 orderedPostProcessors 的 [postProcessBeanFactory] 回调方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
// 最后把 nonOrderedPostProcessorNames 转成 nonOrderedPostProcessors 集合,这里只有一个,myBeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 执行 nonOrderedPostProcessors 的 [postProcessBeanFactory] 回调方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
// 清除缓存
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
4. org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 从容器中获取 BeanPostProcessor 类型
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
// 向容器中添加【BeanPostProcessorChecker】,主要是用来检查是不是有 bean 已经初始化完成了,
// 如果没有执行所有的 beanPostProcessor(用数量来判断),如果有就会打印一行 info 日志
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 存放实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口的 BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 存放 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 类型的 BeanPostProcessor
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 存放实现了 Ordered 接口的 BeanPostProcessor 的 name
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 存放剩下来普通的 BeanPostProcessor 的 name
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 从 beanFactory 中查找 postProcessorNames 里的 bean,然后放到对应的集合中
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 判断有无实现 PriorityOrdered 接口
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
// 如果实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口,且属于 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
// 把 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 类型的添加到 internalPostProcessors 集合中
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
// 给 priorityOrderedPostProcessors 排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 先注册实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口的 beanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
// 从 beanFactory 中查找 orderedPostProcessorNames 里的 bean,然后放到对应的集合中
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 给 orderedPostProcessors 排序
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 再注册实现了 Ordered 接口的 beanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
// 再注册常规的 beanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
// 排序 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 这种类型的 beanPostProcessor
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 最后注册 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 类型的 beanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
// 给容器中添加【ApplicationListenerDetector】 beanPostProcessor,判断是不是监听器,如果是就把 bean 放到容器中保存起来
// 此时容器中默认会有 6 个内置的 beanPostProcessor
// 0 = {ApplicationContextAwareProcessor@1632}
// 1 = {ConfigurationClassPostProcessor$ImportAwareBeanPostProcessor@1633}
// 2 = {PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker@1634}
// 3 = {CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor@1635}
// 4 = {AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor@1636}
// 5 = {ApplicationListenerDetector@1637}
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
5. org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#initApplicationEventMulticaster
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
// 获取 beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
// 看看容器中是否有自定义的 applicationEventMulticaster
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
// 有就从容器中获取赋值
this.applicationEventMulticaster =
beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]");
}
}
else {
// 没有,就创建一个 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
// 将创建的 ApplicationEventMulticaster 添加到 BeanFactory 中, 其他组件就可以自动注入了
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +
"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");
}
}
}
6. org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#registerListeners
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
// 获取之前步骤中保存的 ApplicationListener
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
// getApplicationEventMulticaster() 就是获取之前步骤初始化的 applicationEventMulticaster
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
// 从容器中获取所有的 ApplicationListener
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
// 派发之前步骤产生的 application events
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
7. org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 获取容器中的所有 beanDefinitionName
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 循环进行初始化和创建对象
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 获取 RootBeanDefinition,它表示自己的 BeanDefinition 和可能存在父类的 BeanDefinition 合并后的对象
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 如果是非抽象的,且单实例,非懒加载
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 如果是 factoryBean,利用下面这种方法创建对象
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 如果是 factoryBean,则 加上 &,先创建工厂 bean
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 不是工厂 bean,用这种方法创建对象
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 检查所有的 bean 是否是 SmartInitializingSingleton 接口
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 回调 afterSingletonsInstantiated() 方法,可以在回调中做一些事情
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
8. org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#finishRefresh
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
// 清理缓存
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
// 初始化和生命周期有关的后置处理器
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
// 拿到前面定义的生命周期处理器【LifecycleProcessor】回调 onRefresh() 方法
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
// 发布容器刷新完成事件
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}