elasticsearch基础篇
目录
1.mysql与elasticsearch
2.索引库操作
2.1.mapping映射属性
2.2.索引库的CRUD
2.2.1.创建索引库和映射
2.2.2.查询索引库
2.2.3.修改索引库
2.2.4.删除索引库
2.2.5.总结
3.文档操作
3.1.新增文档
3.2.查询文档
3.3.删除文档
3.4.修改文档
3.4.1.全量修改
3.4.2.增量修改
3.5.总结
4.RestAPI
4.0.1.导入数据
4.0.2.导入项目
4.0.3.mapping映射分析
4.0.4.初始化RestClient
4.1.创建索引库
4.1.2.完整示例
4.2.删除索引库
4.3.判断索引库是否存在
4.4.总结
5.RestClient操作文档
5.1.新增文档
5.1.1.索引库实体类
5.1.2.语法说明
5.1.3.完整代码
5.2.查询文档
5.2.1.语法说明
5.3.删除文档
5.4.修改文档
5.4.1.语法说明
5.4.2.完整代码
5.5.批量导入文档
5.5.1.语法说明
5.5.2.完整代码
5.6.小结
1.mysql与elasticsearch
我们统一的把mysql与elasticsearch的概念做一下对比:
| MySQL |
Elasticsearch |
说明 |
| Table |
Index |
索引(index),就是文档的集合,类似数据库的表(table) |
| Row |
Document |
文档(Document),就是一条条的数据,类似数据库中的行(Row),文档都是JSON格式 |
| Column |
Field |
字段(Field),就是JSON文档中的字段,类似数据库中的列(Column) |
| Schema |
Mapping |
Mapping(映射)是索引中文档的约束,例如字段类型约束。类似数据库的表结构(Schema) |
| SQL |
DSL |
DSL是elasticsearch提供的JSON风格的请求语句,用来操作elasticsearch,实现CRUD |
是不是说,我们学习了elasticsearch就不再需要mysql了呢?
并不是如此,两者各自有自己的擅长支出:
- Mysql:擅长事务类型操作,可以确保数据的安全和一致性
- Elasticsearch:擅长海量数据的搜索、分析、计算
因此在企业中,往往是两者结合使用:
- 对安全性要求较高的写操作,使用mysql实现
- 对查询性能要求较高的搜索需求,使用elasticsearch实现
- 两者再基于某种方式,实现数据的同步,保证一致性
2.索引库操作
2.1.mapping映射属性
mapping是对索引库中文档的约束,常见的mapping属性包括:
- type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:
- 字符串:text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip地址)
- 数值:long、integer、short、byte、double、float、
- 布尔:boolean
- 日期:date
- 对象:object
- index:是否创建索引,默认为true
- analyzer:使用哪种分词器
- properties:该字段的子字段
例如下面的json文档:
{
"age": 21,
"weight": 52.1,
"isMarried": false,
"info": "黑马程序员Java讲师",
"email": "[email protected]",
"score": [99.1, 99.5, 98.9],
"name": {
"firstName": "云",
"lastName": "赵"
}
}对应的每个字段映射(mapping):
- age:类型为 integer;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- weight:类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- isMarried:类型为boolean;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- info:类型为字符串,需要分词,因此是text;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;分词器可以用ik_smart
- email:类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;不参与搜索,因此需要index为false;无需分词器
- score:虽然是数组,但是我们只看元素的类型,类型为float;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- name:类型为object,需要定义多个子属性
- name.firstName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
- name.lastName;类型为字符串,但是不需要分词,因此是keyword;参与搜索,因此需要index为true;无需分词器
2.2.索引库的CRUD
这里我们统一使用Kibana编写DSL的方式来演示。
2.2.1.创建索引库和映射
基本语法:
- 请求方式:PUT
- 请求路径:/索引库名,可以自定义
- 请求参数:mapping映射
格式:
PUT /heima
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"info":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"email": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"name": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"firstName": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"lastName": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}2.2.2.查询索引库
基本语法:
- 请求方式:GET
- 请求路径:/索引库名
- 请求参数:无
格式:
GET /索引库名
示例:GET /heima
2.2.3.修改索引库
倒排索引结构虽然不复杂,但是一旦数据结构改变(比如改变了分词器),就需要重新创建倒排索引,这简直是灾难。因此索引库一旦创建,无法修改mapping。
虽然无法修改mapping中已有的字段,但是却允许添加新的字段到mapping中,因为不会对倒排索引产生影响。
语法说明:
PUT /索引库名/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"新字段名":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}2.2.4.删除索引库
语法:
- 请求方式:DELETE
- 请求路径:/索引库名
- 请求参数:无
格式:
DELETE /索引库名
在kibana中测试:
2.2.5.总结
索引库操作有哪些?
- 创建索引库:PUT /索引库名
- 查询索引库:GET /索引库名
- 删除索引库:DELETE /索引库名
- 添加字段:PUT /索引库名/_mapping
3.文档操作
3.1.新增文档
语法:
POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
"字段3": {
"子属性1": "值3",
"子属性2": "值4"
},
// ...
}示例:
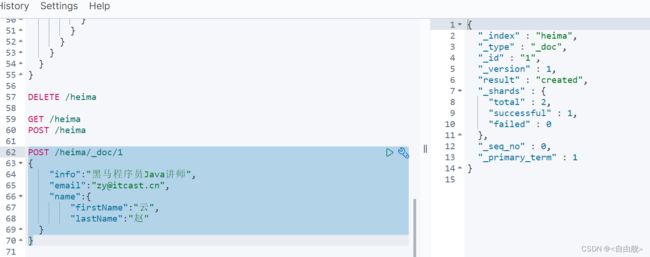
POST /heima/_doc/1
{
"info":"黑马程序员Java讲师",
"email":"[email protected]",
"name":{
"firstName":"云",
"lastName":"赵"
}
}3.2.查询文档
根据rest风格,新增是post,查询应该是get,不过查询一般都需要条件,这里我们把文档id带上。
语法:
GET /{索引库名称}/_doc/{id}
通过kibana查看数据:
GET /heima/_doc/13.3.删除文档
删除使用DELETE请求,同样,需要根据id进行删除:
语法:
DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/id值
示例:
# 根据id删除数据 DELETE /heima/_doc/1
3.4.修改文档
修改有两种方式:
- 全量修改:直接覆盖原来的文档
- 增量修改:修改文档中的部分字段
3.4.1.全量修改
全量修改是覆盖原来的文档,其本质是:
- 根据指定的id删除文档
- 新增一个相同id的文档
注意:如果根据id删除时,id不存在,第二步的新增也会执行,也就从修改变成了新增操作了。
语法:
PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
{
"字段1": "值1",
"字段2": "值2",
// ... 略
}示例:
PUT /heima/_doc/1
{
"info": "黑马程序员高级Java讲师",
"email": "[email protected]",
"name": {
"firstName": "云",
"lastName": "赵"
}
}3.4.2.增量修改
增量修改是只修改指定id匹配的文档中的部分字段。
语法:
POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id
{
"doc": {
"字段名": "新的值",
}
}示例:
POST /heima/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"email": "[email protected]"
}
}3.5.总结
文档操作有哪些?
- 创建文档:POST /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id { json文档 }
- 查询文档:GET /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
- 删除文档:DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
- 修改文档:
- 全量修改:PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id { json文档 }
- 增量修改:POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id { "doc": {字段}}
4.RestAPI
ES官方提供了各种不同语言的客户端,用来操作ES。这些客户端的本质就是组装DSL语句,通过http请求发送给ES。官方文档地址:Elasticsearch Clients | Elastic
其中的Java Rest Client又包括两种:
- Java Low Level Rest Client
- Java High Level Rest Client
4.0.1.导入数据
hotel_demo: ES-RestAPI学习Demo
首先导入课前资料提供的数据库数据:
数据结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `tb_hotel` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店id',
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店名称;例:7天酒店',
`address` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店地址;例:航头路',
`price` int(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店价格;例:329',
`score` int(2) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店评分;例:45,就是4.5分',
`brand` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '酒店品牌;例:如家',
`city` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '所在城市;例:上海',
`star_name` varchar(16) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '酒店星级,从低到高分别是:1星到5星,1钻到5钻',
`business` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商圈;例:虹桥',
`latitude` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '纬度;例:31.2497',
`longitude` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT '经度;例:120.3925',
`pic` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '酒店图片;例:/img/1.jpg',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;4.0.2.导入项目
然后导入课前资料提供的项目:
4.0.3.mapping映射分析
创建索引库,最关键的是mapping映射,而mapping映射要考虑的信息包括:
- 字段名
- 字段数据类型
- 是否参与搜索
- 是否需要分词
- 如果分词,分词器是什么?
其中:
- 字段名、字段数据类型,可以参考数据表结构的名称和类型
- 是否参与搜索要分析业务来判断,例如图片地址,就无需参与搜索
- 是否分词呢要看内容,内容如果是一个整体就无需分词,反之则要分词
- 分词器,我们可以统一使用ik_max_word
来看下酒店数据的索引库结构:
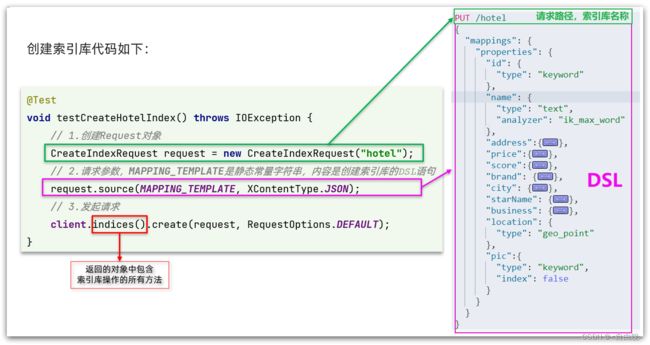
PUT /hotel
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"score":{
"type": "integer"
},
"brand":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"city":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"starName":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"business":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"location":{
"type": "geo_point"
},
"pic":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"all":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}几个特殊字段说明:
- location:地理坐标,里面包含精度、纬度
- all:一个组合字段,其目的是将多字段的值 利用copy_to合并,提供给用户搜索
copy_to说明:
4.0.4.初始化RestClient
在elasticsearch提供的API中,与elasticsearch一切交互都封装在一个名为RestHighLevelClient的类中,必须先完成这个对象的初始化,建立与elasticsearch的连接。
分为三步:
1)引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖:
org.elasticsearch.client
elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client
2)因为SpringBoot默认的ES版本是7.6.2,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本:
1.8
7.12.1
3)初始化RestHighLevelClient:
初始化的代码如下:
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));这里为了单元测试方便,我们创建一个测试类HotelIndexTest,然后将初始化的代码编写在@BeforeEach方法中:
package cn.itcast.hotel;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HotelIndexTest {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
this.client.close();
}
}4.1.创建索引库
4.1.1.代码解读
代码分为三步:
- 1)创建Request对象。因为是创建索引库的操作,因此Request是CreateIndexRequest。
- 2)添加请求参数,其实就是DSL的JSON参数部分。因为json字符串很长,这里是定义了静态字符串常量MAPPING_TEMPLATE,让代码看起来更加优雅。
- 3)发送请求,client.indices()方法的返回值是IndicesClient类型,封装了所有与索引库操作有关的方法。
4.1.2.完整示例
在hotel-demo的cn.itcast.hotel.constants包下,创建一个类,定义mapping映射的JSON字符串常量:
package cn.itcast.hotel.constants;
public class HotelConstants {
public static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"id\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"address\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"score\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"brand\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"city\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"starName\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"business\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"location\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"geo_point\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"pic\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
}在hotel-demo中的HotelIndexTest测试类中,编写单元测试,实现创建索引:
@Test
void createHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求的参数:DSL语句
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}4.2.删除索引库
删除索引库的DSL语句非常简单:
DELETE /hotel
与创建索引库相比:
- 请求方式从PUT变为DELTE
- 请求路径不变
- 无请求参数
所以代码的差异,注意体现在Request对象上。依然是三步走:
- 1)创建Request对象。这次是DeleteIndexRequest对象
- 2)准备参数。这里是无参
- 3)发送请求。改用delete方法
在hotel-demo中的HotelIndexTest测试类中,编写单元测试,实现删除索引:
@Test
void testDeleteHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发送请求
client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}4.3.判断索引库是否存在
判断索引库是否存在,本质就是查询,对应的DSL是:
GET /hotel
因此与删除的Java代码流程是类似的。依然是三步走:
- 1)创建Request对象。这次是GetIndexRequest对象
- 2)准备参数。这里是无参
- 3)发送请求。改用exists方法
@Test
void testExistsHotelIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.发送请求
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.输出
System.err.println(exists ? "索引库已经存在!" : "索引库不存在!");
}4.4.总结
JavaRestClient操作elasticsearch的流程基本类似。核心是client.indices()方法来获取索引库的操作对象。
索引库操作的基本步骤:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxIndexRequest。XXX是Create、Get、Delete
- 准备DSL( Create时需要,其它是无参)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#indices().xxx()方法,xxx是create、exists、delete
5.RestClient操作文档
为了与索引库操作分离,我们再次参加一个测试类,做两件事情:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 我们的酒店数据在数据库,需要利用IHotelService去查询,所以注入这个接口
package cn.itcast.hotel;
import cn.itcast.hotel.pojo.Hotel;
import cn.itcast.hotel.service.IHotelService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class HotelDocumentTest {
@Autowired
private IHotelService hotelService;
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
this.client.close();
}
}
5.1.新增文档
我们要将数据库的酒店数据查询出来,写入elasticsearch中。
5.1.1.索引库实体类
数据库查询后的结果是一个Hotel类型的对象。结构如下:
@Data
@TableName("tb_hotel")
public class Hotel {
@TableId(type = IdType.INPUT)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String longitude;
private String latitude;
private String pic;
}与我们的索引库结构存在差异:
- longitude和latitude需要合并为location
因此,我们需要定义一个新的类型,与索引库结构吻合:
package cn.itcast.hotel.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class HotelDoc {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String location;
private String pic;
public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) {
this.id = hotel.getId();
this.name = hotel.getName();
this.address = hotel.getAddress();
this.price = hotel.getPrice();
this.score = hotel.getScore();
this.brand = hotel.getBrand();
this.city = hotel.getCity();
this.starName = hotel.getStarName();
this.business = hotel.getBusiness();
this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude();
this.pic = hotel.getPic();
}
}
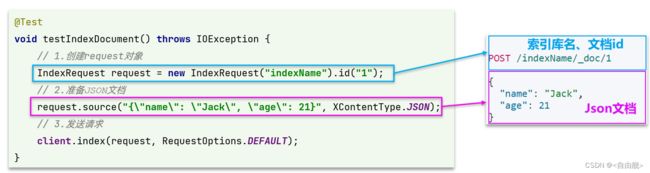
5.1.2.语法说明
新增文档的DSL语句如下:
POST /{索引库名}/_doc/1
{
"name": "Jack",
"age": 21
}可以看到与创建索引库类似,同样是三步走:
- 1)创建Request对象
- 2)准备请求参数,也就是DSL中的JSON文档
- 3)发送请求
变化的地方在于,这里直接使用client.xxx()的API,不再需要client.indices()了。
5.1.3.完整代码
我们导入酒店数据,基本流程一致,但是需要考虑几点变化:
- 酒店数据来自于数据库,我们需要先查询出来,得到hotel对象
- hotel对象需要转为HotelDoc对象
- HotelDoc需要序列化为json格式
因此,代码整体步骤如下:
- 1)根据id查询酒店数据Hotel
- 2)将Hotel封装为HotelDoc
- 3)将HotelDoc序列化为JSON
- 4)创建IndexRequest,指定索引库名和id
- 5)准备请求参数,也就是JSON文档
- 6)发送请求
在hotel-demo的HotelDocumentTest测试类中,编写单元测试:
@Test
void testAddDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.根据id查询酒店数据
Hotel hotel = hotelService.getById(61083L);
// 2.转换为文档类型
HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);
// 3.将HotelDoc转json
String json = JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc);
// 1.准备Request对象
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString());
// 2.准备Json文档
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}5.2.查询文档
5.2.1.语法说明
查询的DSL语句如下:
GET /hotel/_doc/{id}
非常简单,因此代码大概分两步:
- 准备Request对象
- 发送请求
不过查询的目的是得到结果,解析为HotelDoc,因此难点是结果的解析。完整代码如下:
可以看到,结果是一个JSON,其中文档放在一个_source属性中,因此解析就是拿到_source,反序列化为Java对象即可。
与之前类似,也是三步走:
- 1)准备Request对象。这次是查询,所以是GetRequest
- 2)发送请求,得到结果。因为是查询,这里调用client.get()方法
- 3)解析结果,就是对JSON做反序列化
5.2.2.完整代码
在hotel-demo的HotelDocumentTest测试类中,编写单元测试:
@Test
void testGetDocumentById() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("hotel", "61082");
// 2.发送请求,得到响应
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.解析响应结果
String json = response.getSourceAsString();
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
System.out.println(hotelDoc);
}5.3.删除文档
删除的DSL为是这样的:
DELETE /hotel/_doc/{id}
与查询相比,仅仅是请求方式从DELETE变成GET,可以想象Java代码应该依然是三步走:
- 1)准备Request对象,因为是删除,这次是DeleteRequest对象。要指定索引库名和id
- 2)准备参数,无参
- 3)发送请求。因为是删除,所以是client.delete()方法
在hotel-demo的HotelDocumentTest测试类中,编写单元测试:
@Test
void testDeleteDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.发送请求
client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}5.4.修改文档
5.4.1.语法说明
修改我们讲过两种方式:
- 全量修改:本质是先根据id删除,再新增
- 增量修改:修改文档中的指定字段值
在RestClient的API中,全量修改与新增的API完全一致,判断依据是ID:
- 如果新增时,ID已经存在,则修改
- 如果新增时,ID不存在,则新增
这里不再赘述,我们主要关注增量修改。
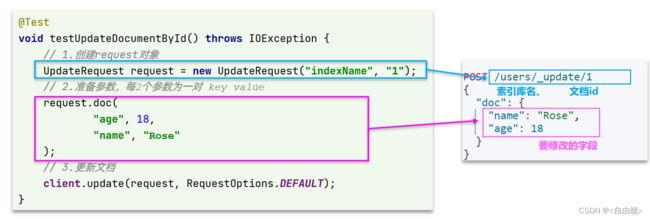
与之前类似,也是三步走:
- 1)准备Request对象。这次是修改,所以是UpdateRequest
- 2)准备参数。也就是JSON文档,里面包含要修改的字段
- 3)更新文档。这里调用client.update()方法
5.4.2.完整代码
在hotel-demo的HotelDocumentTest测试类中,编写单元测试:
@Test
void testUpdateDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.准备请求参数
request.doc(
"price", "952",
"starName", "四钻"
);
// 3.发送请求
client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}这里也可以传Map
@Test
void testUpdateDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.准备请求参数
Map docMap = new HashMap<>();
docMap.put("price", "952");
docMap.put("starName", "四钻");
request.doc(docMap);
client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} 5.5.批量导入文档
案例需求:利用BulkRequest批量将数据库数据导入到索引库中。
步骤如下:
- 利用mybatis-plus查询酒店数据
- 将查询到的酒店数据(Hotel)转换为文档类型数据(HotelDoc)
- 利用JavaRestClient中的BulkRequest批处理,实现批量新增文档
5.5.1.语法说明
批量处理BulkRequest,其本质就是将多个普通的CRUD请求组合在一起发送。
可以看到,能添加的请求包括:
- IndexRequest,也就是新增
- UpdateRequest,也就是修改
- DeleteRequest,也就是删除
因此Bulk中添加了多个IndexRequest,就是批量新增功能了。示例: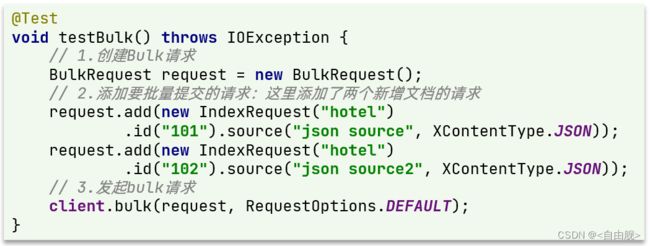
其实还是三步走:
- 1)创建Request对象。这里是BulkRequest
- 2)准备参数。批处理的参数,就是其它Request对象,这里就是多个IndexRequest
- 3)发起请求。这里是批处理,调用的方法为client.bulk()方法
我们在导入酒店数据时,将上述代码改造成for循环处理即可。
5.5.2.完整代码
在hotel-demo的HotelDocumentTest测试类中,编写单元测试:
@Test
void testBulkRequest() throws IOException {
// 批量查询酒店数据
List hotels = hotelService.list();
// 1.创建Request
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
// 2.准备参数,添加多个新增的Request
for (Hotel hotel : hotels) {
// 2.1.转换为文档类型HotelDoc
HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);
// 2.2.创建新增文档的Request对象
request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel")
.id(hotelDoc.getId().toString())
.source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON));
}
// 3.发送请求
client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} 5.6.小结
文档操作的基本步骤:
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxRequest。XXX是Index、Get、Update、Delete、Bulk
- 准备参数(Index、Update、Bulk时需要)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#.xxx()方法,xxx是index、get、update、delete、bulk
- 解析结果(Get时需要)