C++从键盘输入多行数据
C++从键盘输入多行数据
- 1.cin
-
- cin>>
- cin.getline(数组名,长度,结束符)
- cin.get(数组名,长度,结束符)
- 关于cin、cin.get()、cin.get(ch)返回值的问题
- 2.std::getline
- 3.std::istringstream
- 4.istringstream、ostringstream、stringstream 类
- 5.练习题
1.cin
输入原理:
程序的输入都建有一个缓冲区,即输入缓冲区。一次输入过程是这样的,当一次键盘输入结束时会将输入的数据存入输入缓冲区,而cin函数直接从输入缓冲区中取数据。正因为cin函数是直接从缓冲区取数据的,所以有时候当缓冲区中有残留数据时,cin函数会直接取得这些残留数据而不会请求键盘输入
C++ 读取键盘输入(cin/cin.getline()/cin.get()/cin.clear())
cin>>
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/istream/istream/operator%3E%3E/
该操作符是根据后面变量的类型读取数据。
看一下cin>>支持读取的数据类型有哪些
//cin>>支持的类型,这里没有char&类型,但是实际上cin是可以一次读取一个字符的
//具体的可以看看的下面的链接
//https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/standard-library/istream-operators?view=vs-2019
istream& operator>> (bool& val);
istream& operator>> (short& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned short& val);
istream& operator>> (int& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned int& val);
istream& operator>> (long& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned long& val);
istream& operator>> (long long& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned long long& val);
istream& operator>> (float& val);
istream& operator>> (double& val);
istream& operator>> (long double& val);
//数组
istream& operator>> (void*& val);
//stream buffers
istream& operator>> (streambuf* sb );
//manipulators
istream& operator>> (istream& (*pf)(istream&));
istream& operator>> (ios& (*pf)(ios&));
istream& operator>> (ios_base& (*pf)(ios_base&));
输入结束条件 :遇到Enter、Space、Tab键。
对结束符的处理 :丢弃缓冲区中使得输入结束的结束符(Enter、Space、Tab)
使用cin读取键盘输入的字符串的实验:
#include cin通过使用空白(空格、制表符和换行符)来定字符串的界。这意味着cin在读取字符数组输入时只读取一个单词,读取该单词后,cin将该字符串放入数组中,并自动结尾添加’\0’字符。
另外,cin也没有很好的控制输入的字符数,即输入字符数大于数组大小的情况没有处理。
把上面的字符数组char [],换成string,cin>>也是可以工作的,只是和上面一样,在读取字符数组输入时只读取一个单词,遇到空白符(空格、制表符和换行符)就停止读入了。
下面看一下,怎样读取一个含空格的字符串,并将字符串整体保存在vector< string >中
#include
result.push_back(input);
if(ch!='\n')//未到结尾时,单词之间输出空格
//cout<<" ";
//不想保存空格的话,这里可以不需要
result.push_back(" ");
}
//输出result中的结果
for(auto& i:result)
cout<<i;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
cin.getline(数组名,长度,结束符)
cin.getline()函数读取整行,它使用通过回车键输入的换行符来确定输入结尾。
该函数有三个参数。第一个参数是用来存储输入行的数组的名称,第二个参数是要读取的字符数(包括空字符),第三个参数默认为ENTER,
cin.getline()成员函数在读取指定数目的字符或遇到换行符时停止读取。
cin.getline()的缺点在于:
必须传入一个固定大小的数组,用于保存输入的字符串,但是如果输入的字符串长度不确定呢?那这里cin.getline()就不好弄了,而且cin.getline()当输入超长时,会引起cin函数的错误,后面的cin操作将不再执行。
(由此看出cin.getline()并不好用,很多时候都不满足我们的需要)
#include 需要注意的是,cin.getline()丢弃了换行符。
当第一次输入没有超过数组规定的大小时,还能重新接收第二次输入

当第一次输入超过了数组规定的大小时,直接结束了,无法进行第二次输入

cin.get(数组名,长度,结束符)
其中结束符为可选参数,读入的字符个数最多为(长度-1)个,
结束符规定结束读取字符串的字符,默认为ENTER。
cin.get(数组名,长度,结束符) ,在读取指定数目的字符或遇到换行符时停止读取
读取字符的情况:
输入结束条件:Enter键
对结束符处理:不丢弃缓冲区中的Enter
cin.get()有无参,一个参数,两个参数,三个参数
若要读取字符,直接cin.get(char ch)或char ch; ch=cin.get()即可
get()(不带任何参数的变体)可以读取下一个字符(包括换行符)。
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/istream/istream/get/
//single character (1)
int get();//记住无参数的cin.get()返回的是int,想要得到字符的话得类型转换
istream& get (char& c);
//c-string (2)
istream& get (char* s, streamsize n);
istream& get (char* s, streamsize n, char delim);
//stream buffer (3)
istream& get (streambuf& sb);
istream& get (streambuf& sb, char delim);
下面看一个示例,测试一下cin.get()有无参,一个参数,两个参数,三个参数的用法
#include 
另一个潜在的问题是,输入字符可能比分配的空间长。
如果输入行包含的字符数比指定的多,则get()和getline()将把余下的字符留在输入队列中,而getline()还会设置失效位,并关闭输入。
cin.get()当输入的字符串超长时,不会引起cin函数的错误,后面的cin操作会继续执行,只是直接从缓冲区中取数据。但是cin.getline()当输入超长时,会引起cin函数的错误,后面的cin操作将不再执行。
在看一个按字符读取文件内容的示例
// istream::get example
#include 关于cin、cin.get()、cin.get(ch)返回值的问题
关于cin、cin.get()、cin.get(ch)返回值的问题
详细参考
C++ get()函数读入一个字符
1.不带参数的get函数
//返回值为int,因为可能捕获的是EOF,而EOF一般是-1,并没有对应的字符,所以这里不是返回char类型
int get();
用来从指定的输入流中提取一个字符(包括空白字符),函数的返回值就是读入的字符。
若遇到输入流中的文件结束符EOF,Windows下为组合键Ctrl+Z, Unix/Linux下为组合键Ctrl+D,则函数值返回文件结束标志EOF(End Of File),一般以-1代表EOF,用-1而不用0或正值,是考虑到不与字符的ASCII代码混淆,但不同的C ++系统所用的EOF值有可能不同。
用get函数读入字符
#include - 有一个参数的get函数
istream& get (char& c);
其作用是从输入流中读取一个字符,赋给字符变量ch。如果读取成功则函数返回true(真),如失败(遇文件结束符) 则函数返回false(假)。
上面的程序可以改写如下:
#include 3)有2个参数的get函数
istream& get (char* s, streamsize n);
默认遇到’\n’,则终止输入。
4)有3个参数的get函数
其调用形式为
istream& get (char* s, streamsize n, char delim);
即
cin.get(字符数组, 字符个数n, 终止字符)
cin.get(字符指针, 字符个数n, 终止字符)
其作用是从输入流中读取n-1个字符,赋给指定的字符数组(或字符指针指向的数组),如果在读取n-1个字符之前遇到指定的终止字符,则提前结束读取。
如果读取成功则函数返回true(真),如失败(遇文件结束符) 则函数返回false(假)。
#include 
补充:
cin.getline(字符数组, 字符个数n, 终止字符)的返回值跟 cin.get(字符数组, 字符个数n, 终止字符)一样
如果读取成功则函数返回true(真),如失败(遇文件结束符) 则函数返回false(假)。
#include 2.std::getline
C++ getline函数用法详解
cin>>可以用于读取字符串,但是它会传递并忽略任何前导白色空格字符(空格、制表符或换行符)。一旦它接触到第一个非空格字符即开始阅读,当它读取到下一个空白字符时,它将停止读取。
cin.getline也可以用于读取字符串,但是需要传入固定大小的字符数组,所以一般不符合我们的需求。
这里可以使用std::getline,std::getline相比于cin.getline最大的优势在于不需要预先确定一行字符串的长度,一行字符串,你想输入多长,就输入多长。
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/getline/?kw=getline
头文件
<string>
函数声明
//可以看出getline支持string类作为参数
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);
istream& getline (istream&& is, string& str, char delim);
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);
istream& getline (istream&& is, string& str);
参数:
is :表示一个输入流,例如 cin。
str :string类型的引用,用来存储输入流中的流信息。
delim :char类型的变量,所设置的截断字符;在不自定义设置的情况下,遇到’\n’,则终止输入。
利用getline读取多行字符串的示例
#include 3.std::istringstream
std::istringstream
istringstream是一个比较有用的c++的输入输出控制类。
C++引入了ostringstream、istringstream、stringstream这三个类,要使用他们创建对象就必须包含< sstream >这个头文件。
- istringstream类用于执行C++风格的串流的输入操作。
- ostringstream类用于执行C++风格的字符串流的输出操作。
- strstream类同时可以支持C++风格的串流的输入输出操作。
<sstream>
常见的成员函数摘录几个,如下
Public member functions
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| (constructor) | Construct object (public member function ) |
| str | Get/set content (public member function ) |
| operator= | Move assignment (public member function ) |
| swap | Swap internals (public member function ) |
Public member functions inherited from istream
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| operator>> | Extract formatted input (public member function ) |
| gcount | Get character count (public member function ) |
| get | Get characters (public member function ) |
| getline | Get line (public member function ) |
| ignore | Extract and discard characters (public member function ) |
| peek | Peek next character (public member function ) |
| tellg | Get position in input sequence (public member function ) |
| seekg | Set position in input sequence (public member function ) |
Public member functions inherited from ios
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| good | Check whether state of stream is good (public member function ) |
| eof | Check whether eofbit is set (public member function ) |
| fail | Check whether either failbit or badbit is set (public member function ) |
| bad | Check whether badbit is set (public member function ) |
| operator! | Evaluate stream (not) (public member function ) |
| operator bool | Evaluate stream (public member function ) |
| rdstate | Get error state flags (public member function ) |
| setstate | Set error state flag (public member function ) |
| clear | Set error state flags (public member function ) |
| rdbuf | Get/set stream buffer (public member function ) |
Public member functions inherited from ios_base
| 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| flags | Get/set format flags (public member function ) |
| precision | Get/Set floating-point decimal precision (public member function ) |
| getloc | Get current locale (public member function ) |
- istringstream的构造函数原形如下:
//默认构造函数
explicit istringstream (ios_base::openmode which = ios_base::in);
//传入string构造 ,它的作用是从string对象str中读取字符
explicit istringstream (const string& str,
ios_base::openmode which = ios_base::in);
//禁止复制构造
istringstream (const istringstream&) = delete;
//移动构造函数
istringstream (istringstream&& x);
- 成员函数str
//无参的str函数,返回流stream中的当前内容
string str() const;
//将流stream的内容设置为str,并丢弃任何先前的内容
void str (const string& s);
示例:
// istringstream::str
#include - seekg
设置要从输入流中提取的下一个字符的位置。
istream& seekg (streampos pos);
istream& seekg (streamoff off, ios_base::seekdir way);
参数:
pos
相对于流的开始位置的一个绝对位置,整型
off
相对于参数way指定的起点位置的偏移量,有符号的整型
way
为如下三个值,分别表示流的开始位置,当前位置,结尾位置
| way可取的值 | |
|---|---|
| ios_base::beg | beginning of the stream |
| ios_base::cur | current position in the stream |
| ios_base::end | end of the stream |
- 成员函数read
istream& read (char* s, streamsize n);
从流中提取n个字符并将它们存储在s指向的数组中。
此函数仅复制数据块,而不检查其内容或在末尾添加’\0’。
如果在成功读取n个字符之前到达文件末尾(即流中字符数量小于n个),则s指向的数组将包含直到该点之前读取的所有字符,并且eofbit和 为流设置了故障位标志。
示例
// read a file into memory
#include - 成员函数operator>>声明如下:
继承自std::istream
//cin>>支持的类型,这里没有char&类型,但是实际上cin是可以一次读取一个字符的
//具体的可以看看的下面的链接
//https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/standard-library/istream-operators?view=vs-2019
istream& operator>> (bool& val);
istream& operator>> (short& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned short& val);
istream& operator>> (int& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned int& val);
istream& operator>> (long& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned long& val);
istream& operator>> (long long& val);
istream& operator>> (unsigned long long& val);
istream& operator>> (float& val);
istream& operator>> (double& val);
istream& operator>> (long double& val);
//数组
istream& operator>> (void*& val);
//stream buffers (2)
istream& operator>> (streambuf* sb );
//manipulators (3)
istream& operator>> (istream& (*pf)(istream&));
istream& operator>> (ios& (*pf)(ios&));
istream& operator>> (ios_base& (*pf)(ios_base&));
关于operator>>的返回值,
1.返回值为(*this)
2.内部状态错误时,会设置标志位
| 标志 | 错误 |
|---|---|
| eofbit | 输入序列中没有更多可用字符(到达文件末尾)。 |
| failbit | 没有提取任何字符,或者提取的字符不能解释为适当类型的有效值。 |
| badbit | 流上的错误(例如,当此函数捕获内部操作引发的异常时)。 |
- ignore:提取并丢弃字符
从输入序列中提取字符并丢弃它们,直到提取出n个字符或一个等于delim的终止字符为止。
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/istream/istream/ignore/
istream& ignore (streamsize n = 1, int delim = EOF);
参数:需要提取并丢弃字符串的最大长度,终止字符delim
#include- 成员函数operator bool声明如下:
主要是为了能够根据上下文转换为bool类型,使其能够作为判断条件
explicit operator bool() const;
功能:评估stream
返回值:
false:设置了错误标志(failbit或badbit)
true:没有设置错误标志
- clear:设置error state 标志
为流的内部error state 标志设置一个新值(类似于发生错误,设置错误标志位后,clear能起到复位的功能,清除被置位的error state 标志)
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/ios/ios/clear/
void clear (iostate state = goodbit);
这里看一个示例(关于stringtream的使用看下一章节,这里用看看clear()的用法)
stringtream最常用于string与各种内置数据类型的转换
#include
sstr.clear();
//cout<
string name = "string1";
char cname[200];
sstr<<name;
sstr>>cname;
cout<<cname;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
关于istringstream对象输出字符串时,类比cin>>的行为
通过使用空白(空格、制表符和换行符)来定字符串的界。这意味着在读取输入时只读取一个单词,读取该单词后,将该字符串放入string或字符数组(自动结尾添加’\0’字符)。
具体看下面的实例
#include4.istringstream、ostringstream、stringstream 类
关于istringstream、ostringstream、stringstream 类介绍 的其他介绍,直接看这篇博文
istringstream、ostringstream、stringstream 类介绍
摘录几个示例如下:
示例1:把一行字符串放入流中,单词以空格隔开。之后把一个个单词从流中依次读取到字符串
#include
while(istr >> str)//每次读取一个单词(以空格为界),存入str中
{
cout<<str<<endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
示例2:用 stream.str("") 清除一下缓冲
由于stringstream构造函数会特别消耗内存,似乎不打算主动释放内存(或许是为了提高效率),但如果你要在程序中用同一个流,反复读写大量的数据,将会造成大量的内存消耗,因些这时候,需要适时地清除一下缓冲 (用 stream.str("") )。
另外不要企图用 stream.str().resize(0),或 stream.str().clear() 来清除缓冲,使用它们似乎可以让stringstream的内存消耗不要增长得那么快,但仍然不能达到清除stringstream缓冲的效果,内存的消耗还在缓慢的增长!,至于stream.flush(),则根本就起不到任何作用。
#include 5.练习题
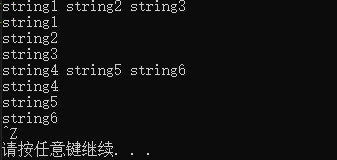
- 从键盘读入多行数据,并保存到容器中
利用上面的getline和istringstream即可完成
#include- LeetCode:557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
给定一个字符串,你需要反转字符串中每个单词的字符顺序,同时仍保留空格和单词的初始顺序。
class Solution {
public:
//1.直观的思路:双指针,找到空格,则反转两个指针之间的字符串
//2.利用strtok或者istringstream分割字符串,然后反转每一个单词即可
string reverseWords(string s) {
if(s=="") return "";
istringstream istr(s);
string res,temp;
while(istr>>temp){
reverse(temp.begin(),temp.end());
res+=temp;
res+=" ";
}
//删除尾部多余的一个空格
res.pop_back();
return res;
}
};
- 分割字符串
给定一个字符串,例如"12,14,#,#,13,43,2324,#,#,#,232,#,432,#,#"
去掉其中所有的逗号,分割后的字符串保存到vector< string >中
方法一:利用istringstream和getline
#include![]()
方法二:利用strtok函数
#include![]()