Flutter开发之数据存储-2-文件存储(33)
数据存储部分在移动开发中是非常重要的部分,无论是一些
轻量级的数据(如用户信息、APP配置信息等)还是把需要长期存储的数据写入本地文件或者Sqlite3。都离不开数据存储,上一篇SharedPreferences的使用,今天就练习一下文件存储-写入本地文件。
文件存储
这三种存储方式Flutter本身都没有内置,不过好在官方提供了第三方库,操作文件同样我们也需要像SharedPreferences一样,需要在pubspec.yaml引入。在 Flutter 里实现文件读写,需要使用 path_provider 和 dart 的 io 模块。path_provider 负责查找 iOS/Android 的目录文件,IO 模块负责对文件进行读写。
官方文档:https://pub.dev/packages/path_provider#-installing-tab-
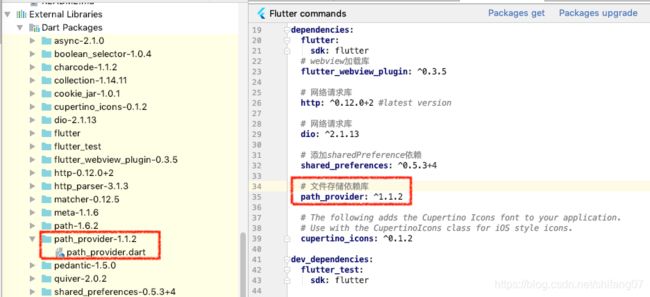
# 文件存储依赖库
path_provider: ^1.1.2
然后命令行执行flutter packages get 完成后如下:
数据存取示例
测试的地方导入
import 'package:path_provider/path_provider.dart';
import 'dart:io';
整个操作演示逻辑跟SharedPreferences一样,关于文件存储的三个获取文件路径的方法我这里说明一下。
在path_provider中有三个获取文件路径的方法:
getTemporaryDirectory()//获取应用缓存目录,等同IOS的NSTemporaryDirectory()和Android的getCacheDir() 方法
getApplicationDocumentsDirectory()获取应用文件目录类似于Ios的NSDocumentDirectory和Android上的 AppData目录
getExternalStorageDirectory()//这个是存储卡,仅仅在Android平台可以使用
来看下操作文件的效果图:
借用了SharedPreferences存储的逻辑,只是把存储的代码放在了file.text中,代码里有详尽的注释,我就不多做解释说明了,读者可自行尝试对比跟SharedPreferences的差别
样例代码
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:path_provider/path_provider.dart';
import 'dart:io';
class FileSaveTest extends StatefulWidget {
FileSaveTest({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
createState() => new _FileSaveTestState();
}
class _FileSaveTestState extends State {
var _textFieldController = new TextEditingController();
var _storageString = '';
final STORAGE_KEY_FILE = 'storage_key';
/**
* 利用文件存储数据
*/
saveString() async {
final file = await getFile('file.text');
//写入字符串
file.writeAsString(_textFieldController.value.text.toString());
}
/**
* 获取存在文件中的数据
*/
Future getString() async {
final file = await getFile('file.text');
var filePath = file.path;
setState(() {
file.readAsString().then((String value) {
_storageString = value +'\n文件存储路径:'+filePath;
});
});
}
/**
* 初始化文件路径
*/
Future getFile(String fileName) async {
//获取应用文件目录类似于Ios的NSDocumentDirectory和Android上的 AppData目录
final fileDirectory = await getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
//获取存储路径
final filePath = fileDirectory.path;
//或者file对象(操作文件记得导入import 'dart:io')
return new File(filePath + "/"+fileName);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new Scaffold(
appBar: new AppBar(
title: new Text('文件存储'),
),
body: new Column(
children: [
SizedBox(height: 5,),
Text("文件存储", textAlign: TextAlign.center,style: TextStyle(fontSize: 24,color: Colors.deepOrange),),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10),
height: 58,
child: TextField(
controller: _textFieldController,
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28),
),
),
MaterialButton(
onPressed: saveString,
child: new Text("存储",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white,fontSize: 22),),
color: Colors.lightBlueAccent,
),
MaterialButton(
onPressed: getString,
child: new Text("获取",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white,fontSize: 22),),
color: Colors.lightGreen,
),
SizedBox(height: 15,),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
height: 180,
child: Text('存储的值为:$_storageString',style: TextStyle(fontSize: 22,color: Colors.deepOrange)
),
),
],
),
);
}
}
部分摘自
[Flutter入门进阶之旅(十二)Flutter 数据存储](https://blog.csdn.net/xieluoxixi/article/details/8665501