Flutter快速入门学习(一)
目录
前言
新建项目
项目入口
Dart的入口(项目的入口)
布局
视图组件
Container(容器)
Text(文本)
Image(图片)
Row(水平布局)和Column(垂直布局)
ListView(列表视图)
GridView(网格视图)
Stack(层叠布局)
Card(卡片)
AppBar(应用栏)
FloatingActionButton(浮动操作按钮)
TextField(文本输入框)
Button(按钮)
Checkbox(复选框)
Radio(单选框)
Switch(开关)
Slider(滑块)
ProgressIndicator(进度指示器)
AlertDialog(对话框)
前言
前面搭建环境,创建项目什么的,都太过简单
废话不多讲~开整~我们直接上代码~开始学习
新建项目
新建了项目是不是有点蒙不知道在哪里开始写我们的hello world?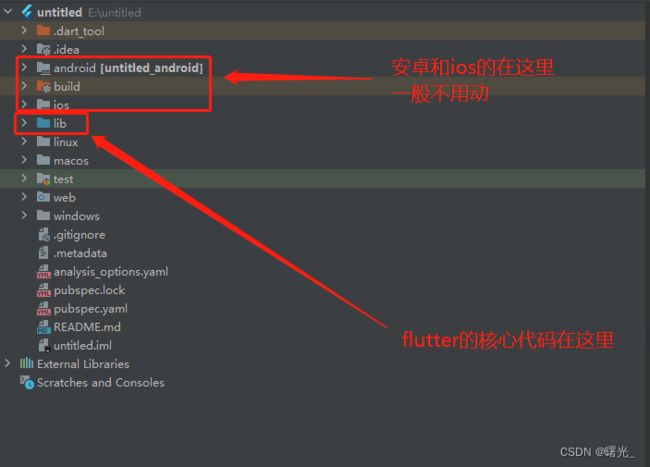
新建了一个项目android和ios两个包,按我个人的理解就是,都预制加载了Dart写好的好的界面
一般有特殊需求需要在对应项目里添加需求需要的配置项
这里我们入门学习,所以这一块就不多讲了
文档
Dart文档指南Learn to use the Dart language and libraries.![]() https://dart.dev/guides
https://dart.dev/guides
项目入口
Dart的入口(项目的入口)
main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed(seedColor: Colors.deepPurple),
useMaterial3: true,
),
home: const MyHomePage(title: '阿斯顿'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
final String title;
@override
State createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.inversePrimary,
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
const Text(
'You have pushed the button this many times:',
),
Text(
'$_counter',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
), // This trailing comma makes auto-formatting nicer for build methods.
);
}
}
布局
在这个例子中,我们使用了Stack来创建一个层层叠加的布局。在Stack中,我们使用了Positioned来实现绝对布局,Align来实现相对布局,以及Positioned.fill来实现权重布局。
每个Positioned和Align都有top、left、right、bottom等属性,用于指定子部件的位置。Positioned.fill会将子部件填充满整个父部件。
通过这种层层叠加的布局方式,我们可以实现复杂的界面布局。
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
body: Stack( // 使用绝对布局
children: [
Positioned( // 使用相对布局
top: 50,
left: 50,
child: Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.red,
),
),
Positioned(
top: 100,
left: 100,
child: Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.blue,
),
),
Align( // 使用相对布局
alignment: Alignment.bottomCenter,
child: Container(
width: 200,
height: 200,
color: Colors.green,
),
),
Positioned(
top: 200,
left: 200,
child: Container(
width: 100,
height: 100,
color: Colors.yellow,
),
),
Positioned.fill( // 使用权重布局
child: Container(
color: Colors.orange,
child: Center(
child: Text(
'Hello World',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
),
),
),
],
),
),
);
}
}视图组件
Container(容器)
用于创建一个矩形的容器,可以设置背景颜色、边框、内边距等属性。
- alignment:设置Container内部子组件的对齐方式。
- padding:设置Container内部子组件的内边距。
- color:设置Container的背景颜色。
- width:设置Container的宽度。
- height:设置Container的高度。
- margin:设置Container与其父组件之间的外边距。
- decoration:设置Container的装饰,可以包括背景图片、边框等。
- child:设置Container的子组件。
以下是一个使用注释说明的例子:
Container(
// 设置Container的宽度为200
width: 200,
// 设置Container的高度为100
height: 100,
// 设置Container的背景颜色为红色
color: Colors.red,
// 设置Container与其父组件之间的外边距为10
margin: EdgeInsets.all(10),
// 设置Container内部子组件的对齐方式为居中
alignment: Alignment.center,
// 设置Container内部子组件的内边距为20
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
// 设置Container的装饰,包括背景图片和边框
decoration: BoxDecoration(
image: DecorationImage(
image: AssetImage('assets/images/background.png'),
fit: BoxFit.cover,
),
border: Border.all(
color: Colors.black,
width: 2,
),
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10),
),
// 设置Container的子组件为一个文本组件
child: Text('Hello World'),
)Text(文本)
用于显示文本内容,可以设置字体样式、颜色、对齐方式等属性。
- data:设置Text显示的文本内容。
- style:设置Text的样式,包括字体、大小、颜色等。
- textAlign:设置Text的对齐方式。
- maxLines:设置Text显示的最大行数。
- overflow:设置Text超出最大行数时的处理方式。
- textDirection:设置Text的文本方向。
- softWrap:设置Text是否自动换行。
- textScaleFactor:设置Text的缩放比例
以下是一个使用注释说明的例子:
Text(
// 设置Text显示的文本内容为Hello World
data: 'Hello World',
// 设置Text的样式,包括字体、大小、颜色等
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.blue,
),
// 设置Text的对齐方式为居中
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
// 设置Text显示的最大行数为2
maxLines: 2,
// 设置Text超出最大行数时的处理方式为省略号
overflow: TextOverflow.ellipsis,
// 设置Text的文本方向为从左到右
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
// 设置Text是否自动换行为true
softWrap: true,
// 设置Text的缩放比例为1.5
textScaleFactor: 1.5,
)Image(图片)
用于显示图片,可以从本地或网络加载图片。
-
image:指定要显示的图片,可以是本地图片、网络图片或者内存图片。可以使用AssetImage、NetworkImage或者MemoryImage来创建ImageProvider对象。
-
width:指定图片的宽度,可以是具体数值或者是一个占位符,如:double.infinity表示宽度填充父容器。
-
height:指定图片的高度,可以是具体数值或者是一个占位符,如:double.infinity表示高度填充父容器。
-
fit:指定图片的适应方式,可以是BoxFit.contain(保持图片的宽高比,将图片完整地显示在容器内)、BoxFit.cover(保持图片的宽高比,将图片完整地显示在容器内并裁剪超出部分)、BoxFit.fill(拉伸图片以填充容器)、BoxFit.fitWidth(保持图片的宽高比,将图片宽度填充容器)、BoxFit.fitHeight(保持图片的宽高比,将图片高度填充容器)等。
-
alignment:指定图片在容器中的对齐方式,可以是Alignment.center(居中对齐)、Alignment.topLeft(左上对齐)、Alignment.bottomRight(右下对齐)等。
-
repeat:指定图片的重复方式,可以是ImageRepeat.noRepeat(不重复)、ImageRepeat.repeat(水平和垂直方向都重复)、ImageRepeat.repeatX(水平方向重复)、ImageRepeat.repeatY(垂直方向重复)等。
下面是一个使用注释说明的例子:
Image(
image: AssetImage('assets/images/flutter_logo.png'), // 指定要显示的本地图片
width: 200, // 指定图片的宽度
height: 200, // 指定图片的高度
fit: BoxFit.cover, // 图片适应方式为完整地显示在容器内并裁剪超出部分
alignment: Alignment.center, // 图片居中对齐
repeat: ImageRepeat.noRepeat, // 图片不重复
)Row(水平布局)和Column(垂直布局)
用于将子组件按水平或垂直方向排列。
-
mainAxisAlignment(主轴对齐方式):用于控制子组件在主轴上的对齐方式。
- MainAxisAlignment.start:子组件在主轴上靠近起始位置。
- MainAxisAlignment.end:子组件在主轴上靠近结束位置。
- MainAxisAlignment.center:子组件在主轴上居中对齐。
- MainAxisAlignment.spaceBetween:子组件在主轴上均匀分布,首尾不留空隙。
- MainAxisAlignment.spaceAround:子组件在主轴上均匀分布,首尾留有空隙。
- MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly:子组件在主轴上均匀分布,包括首尾。
-
crossAxisAlignment(交叉轴对齐方式):用于控制子组件在交叉轴上的对齐方式。
- CrossAxisAlignment.start:子组件在交叉轴上靠近起始位置。
- CrossAxisAlignment.end:子组件在交叉轴上靠近结束位置。
- CrossAxisAlignment.center:子组件在交叉轴上居中对齐。
- CrossAxisAlignment.stretch:子组件在交叉轴上拉伸填充父容器。
- CrossAxisAlignment.baseline:子组件在交叉轴上以基线对齐。
-
mainAxisSize(主轴尺寸):用于控制主轴的尺寸。
- MainAxisSize.max:主轴尽可能地占用父容器的空间。
- MainAxisSize.min:主轴尽可能地缩小到子组件所需的最小空间。
-
verticalDirection(垂直方向):用于控制子组件的布局方向。
- VerticalDirection.down:子组件从上到下排列。
- VerticalDirection.up:子组件从下到上排列。
以下是一个使用注释说明的示例:
Row(
// 主轴对齐方式:居中对齐
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
// 交叉轴对齐方式:居中对齐
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
// 主轴尺寸:尽可能地占用父容器的空间
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
// 垂直方向:从上到下排列
verticalDirection: VerticalDirection.down,
children: [
// 子组件
Text('Child 1'),
Text('Child 2'),
Text('Child 3'),
],
);ListView(列表视图)
用于显示一个可滚动的列表,可以是垂直或水平方向。
-
scrollDirection(滚动方向):指定列表的滚动方向,可以是垂直方向(默认值)或水平方向。
- 值:Axis.vertical(垂直方向,默认值)、Axis.horizontal(水平方向)
-
reverse(反向滚动):指定列表是否反向滚动。
- 值:true、false(默认值)
-
controller(滚动控制器):指定列表的滚动控制器,可以用于控制滚动位置或监听滚动事件。
- 值:ScrollController对象
-
primary(主轴方向上是否填充):指定列表的主轴方向上是否填充。
- 值:true、false(默认值)
-
physics(滚动物理效果):指定列表的滚动物理效果。
- 值:ScrollPhysics对象
-
shrinkWrap(是否根据子组件尺寸调整大小):指定列表是否根据子组件尺寸调整大小。
- 值:true、false(默认值)
-
padding(内边距):指定列表的内边距。
- 值:EdgeInsets对象
-
itemExtent(子组件固定尺寸):指定子组件的固定尺寸,用于优化性能。
- 值:double类型
-
children(子组件列表):指定列表的子组件列表。
- 值:List
对象
- 值:List
使用注释说明如下:
ListView(
// 滚动方向为垂直方向
scrollDirection: Axis.vertical,
// 不反向滚动
reverse: false,
// 使用自定义的滚动控制器
controller: ScrollController(),
// 主轴方向上不填充
primary: false,
// 使用默认的滚动物理效果
physics: null,
// 根据子组件尺寸调整大小
shrinkWrap: true,
// 内边距为10.0
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10.0),
// 子组件固定尺寸为50.0
itemExtent: 50.0,
// 子组件列表
children: [
// 子组件1
Container(),
// 子组件2
Container(),
// ...
],
)遇到多布局的时候,我们使用ListView.builder来创建一个包含10个项的ListView。在itemBuilder中,我们根据index的奇偶性来决定使用不同的布局。偶数项使用红色背景的布局,奇数项使用蓝色背景的布局。每个布局都包含一个居中的文本,显示对应的项号,运行一下代码,你将看到一个多布局的ListView,其中偶数项的背景为红色,奇数项的背景为蓝色。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class MultiLayoutListView extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return ListView.builder(
itemCount: 10,
itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
if (index % 2 == 0) {
// 偶数项使用红色背景的布局
return Container(
color: Colors.red,
height: 100,
child: Center(
child: Text(
'Item $index',
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 20,
),
),
),
);
} else {
// 奇数项使用蓝色背景的布局
return Container(
color: Colors.blue,
height: 150,
child: Center(
child: Text(
'Item $index',
style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 20,
),
),
),
);
}
},
);
}
}
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Multi Layout ListView'),
),
body: MultiLayoutListView(),
),
));
}GridView(网格视图)
用于显示一个二维网格布局的列表。
- scrollDirection:设置滚动方向,可选值为Axis.vertical(垂直方向)和Axis.horizontal(水平方向)。
- reverse:设置是否反向滚动,默认为false。
- controller:设置滚动控制器,可以用于控制滚动位置和监听滚动事件。
- primary:设置是否使用父级的PrimaryScrollController,默认为false。
- physics:设置滚动物理效果,例如BouncingScrollPhysics、ClampingScrollPhysics等。
- shrinkWrap:设置是否根据子项的总长度来确定GridView的长度,默认为false。
- padding:设置GridView的内边距。
- crossAxisSpacing:设置子项在交叉轴方向的间距。
- mainAxisSpacing:设置子项在主轴方向的间距。
- childAspectRatio:设置子项的宽高比。
- children:设置GridView的子项列表
使用注释说明的示例代码如下:
GridView(
// 设置滚动方向为垂直方向
scrollDirection: Axis.vertical,
// 设置是否反向滚动
reverse: false,
// 设置滚动控制器
controller: ScrollController(),
// 设置是否使用父级的PrimaryScrollController
primary: false,
// 设置滚动物理效果
physics: BouncingScrollPhysics(),
// 设置是否根据子项的总长度来确定GridView的长度
shrinkWrap: false,
// 设置GridView的内边距
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10),
// 设置子项在交叉轴方向的间距
crossAxisSpacing: 10,
// 设置子项在主轴方向的间距
mainAxisSpacing: 10,
// 设置子项的宽高比
childAspectRatio: 1,
// 设置GridView的子项列表
children: [
// 子项1
Container(),
// 子项2
Container(),
// 子项3
Container(),
],
)Stack(层叠布局)
用于将子组件按照层叠的方式进行布局。
-
alignment(对齐方式):指定子组件在Stack中的对齐方式。
- Alignment对象,默认值为AlignmentDirectional.topStart
-
fit(未定位子组件的处理方式):指定未定位的子组件在Stack中的处理方式。
- StackFit枚举类型,默认值为StackFit.loose
- StackFit.loose:未定位的子组件根据自身大小来确定位置
- StackFit.expand:未定位的子组件填充满Stack的大小
-
overflow(溢出处理方式):指定子组件超出Stack范围时的处理方式。
- Overflow枚举类型,默认值为Overflow.clip
- Overflow.clip:超出部分裁剪掉
- Overflow.visible:超出部分仍然可见
使用注释说明如下:
Stack(
// 对齐方式为居中对齐
alignment: Alignment.center,
// 未定位的子组件根据自身大小来确定位置
fit: StackFit.loose,
// 超出部分裁剪掉
overflow: Overflow.clip,
children: [
// 子组件1
Positioned(
// 子组件1的左上角对齐Stack的左上角
top: 0,
left: 0,
child: Container(),
),
// 子组件2
Positioned(
// 子组件2的右下角对齐Stack的右下角
bottom: 0,
right: 0,
child: Container(),
),
// 子组件3
Container(),
],
)Card(卡片)
用于创建一个带有圆角和阴影效果的卡片。
-
color:卡片的背景颜色,可以是一个Color对象。 示例:color: Colors.blue
-
elevation:卡片的高度,用于创建阴影效果,可以是一个double值。 示例:elevation: 4.0
-
shape:卡片的形状,可以是一个ShapeBorder对象。 示例:shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0))
-
margin:卡片的外边距,可以是一个EdgeInsets对象。 示例:margin: EdgeInsets.all(10.0)
-
child:卡片的内容部件,可以是任何Widget。 示例:child: Text('Hello World')
使用注释说明可以通过在属性前添加注释来提供更多信息,例如:
Card(
// 设置卡片的背景颜色为红色
color: Colors.red,
// 设置卡片的高度为8.0
elevation: 8.0,
// 设置卡片的形状为圆角矩形
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0)),
// 设置卡片的外边距为10.0
margin: EdgeInsets.all(10.0),
// 设置卡片的内容为一个文本部件
child: Text('Hello World'),
)AppBar(应用栏)
用于创建一个顶部导航栏,通常包含标题、图标和操作按钮。
- leading:Widget类型,设置在AppBar左侧的控件,通常是一个图标按钮或者返回按钮。
- title:Widget类型,设置AppBar中间的标题控件。
- actions:List
类型,设置在AppBar右侧的控件列表。 - backgroundColor:Color类型,设置AppBar的背景颜色。
- elevation:double类型,设置AppBar的阴影高度。
- brightness:Brightness类型,设置AppBar的亮度模式,可以是Brightness.light(浅色模式)或Brightness.dark(深色模式)。
- centerTitle:bool类型,设置标题是否居中显示。
- automaticallyImplyLeading:bool类型,设置是否自动显示leading控件,默认为true。
- flexibleSpace:Widget类型,设置AppBar的可伸缩空间,通常用于实现一些特殊的效果,比如渐变背景。
- bottom:PreferredSizeWidget类型,设置AppBar底部的控件,通常是一个TabBar或者PreferredSize组件。
- shape:ShapeBorder类型,设置AppBar的形状,比如RoundedRectangleBorder。
- toolbarHeight:double类型,设置AppBar的高度。
- toolbarOpacity:double类型,设置AppBar的透明度。
以下是一个使用注释说明的例子:
AppBar(
// 设置AppBar左侧的返回按钮
leading: IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.arrow_back),
onPressed: () {
// 返回上一页的操作
},
),
// 设置AppBar中间的标题
title: Text('App Bar'),
// 设置AppBar右侧的控件列表
actions: [
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.search),
onPressed: () {
// 执行搜索操作
},
),
IconButton(
icon: Icon(Icons.more_vert),
onPressed: () {
// 执行更多操作
},
),
],
// 设置AppBar的背景颜色
backgroundColor: Colors.blue,
// 设置AppBar的阴影高度
elevation: 4.0,
// 设置AppBar的亮度模式为浅色模式
brightness: Brightness.light,
// 设置标题居中显示
centerTitle: true,
// 设置AppBar的高度
toolbarHeight: 56.0,
)FloatingActionButton(浮动操作按钮)
用于创建一个悬浮在界面上的圆形按钮,通常用于执行主要操作。
- onPressed:点击按钮时触发的回调函数。
- tooltip:当用户长按按钮时显示的文本提示。
- child:按钮的子组件,通常是一个图标。
- backgroundColor:按钮的背景颜色。
- foregroundColor:按钮的前景颜色,用于图标和文本。
- elevation:按钮的阴影高度。
- highlightElevation:按钮在被按下时的阴影高度。
- disabledElevation:按钮被禁用时的阴影高度。
- shape:按钮的形状,可以是圆形、矩形等。
- heroTag:用于在页面切换时指定按钮的唯一标识符。
- mini:是否将按钮设置为小尺寸。
- isExtended:是否将按钮设置为扩展尺寸。
- clipBehavior:按钮的裁剪行为,用于处理子组件超出按钮范围的情况。
这些属性可以根据需要进行组合使用,例如:
FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
// 点击按钮时触发的回调函数
},
tooltip: 'Add',
child: Icon(Icons.add),
backgroundColor: Colors.blue,
foregroundColor: Colors.white,
elevation: 4.0,
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(20.0),
),
)在上面的例子中,当用户点击按钮时,会触发一个回调函数。按钮上显示一个加号图标,背景颜色为蓝色,前景颜色为白色,阴影高度为4.0,形状为圆角矩形。
TextField(文本输入框)
用于接收用户的文本输入。
- controller:TextEditingController类型,用于控制文本输入框的内容。
- focusNode:FocusNode类型,用于控制文本输入框的焦点。
- decoration:InputDecoration类型,用于设置文本输入框的装饰样式,比如边框、提示文本等。
- keyboardType:TextInputType类型,用于设置键盘类型,比如数字键盘、邮箱键盘等。
- textInputAction:TextInputAction类型,用于设置键盘动作按钮的类型,比如完成、下一步等。
- style:TextStyle类型,用于设置文本输入框中文本的样式,比如字体、颜色等。
- onChanged:ValueChanged
类型,当文本输入框的内容发生变化时触发的回调函数。 - onSubmitted:ValueChanged
类型,当用户提交文本输入时触发的回调函数。 - maxLength:int类型,限制文本输入框的最大字符数。
- obscureText:bool类型,是否将输入内容隐藏为密码形式。
- autocorrect:bool类型,是否自动纠正用户输入的文本。
- autofocus:bool类型,是否自动获取焦点。
- enabled:bool类型,是否启用文本输入框。
- textAlign:TextAlign类型,设置文本在文本输入框中的对齐方式。
- cursorColor:Color类型,设置光标的颜色。
以下是一个使用注释说明的例子:
TextField(
// 用于控制文本输入框的内容
controller: _textEditingController,
// 用于控制文本输入框的焦点
focusNode: _focusNode,
// 用于设置文本输入框的装饰样式
decoration: InputDecoration(
labelText: 'Username',
hintText: 'Enter your username',
border: OutlineInputBorder(),
),
// 用于设置键盘类型
keyboardType: TextInputType.text,
// 用于设置键盘动作按钮的类型
textInputAction: TextInputAction.done,
// 用于设置文本输入框中文本的样式
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16.0,
color: Colors.black,
),
// 当文本输入框的内容发生变化时触发的回调函数
onChanged: (value) {
// 处理文本变化的逻辑
},
// 当用户提交文本输入时触发的回调函数
onSubmitted: (value) {
// 处理文本提交的逻辑
},
// 限制文本输入框的最大字符数
maxLength: 20,
// 是否将输入内容隐藏为密码形式
obscureText: false,
// 是否自动纠正用户输入的文本
autocorrect: true,
// 是否自动获取焦点
autofocus: false,
// 是否启用文本输入框
enabled: true,
// 设置文本在文本输入框中的对齐方式
textAlign: TextAlign.start,
// 设置光标的颜色
cursorColor: Colors.blue,
)Button(按钮)
用于创建一个可点击的按钮,可以设置样式和点击事件。
-
onPressed:指定按钮被点击时的回调函数。通常使用匿名函数或方法引用来定义回调函数。例如:onPressed: () { /* 点击按钮后执行的代码 */ }
-
child:指定按钮上显示的子部件。可以是Text、Icon等。例如:child: Text('按钮文本')
-
color:指定按钮的背景颜色。可以使用Color对象或者Color值。例如:color: Colors.blue
-
textColor:指定按钮文本的颜色。可以使用Color对象或者Color值。例如:textColor: Colors.white
-
disabledColor:指定按钮在禁用状态下的背景颜色。例如:disabledColor: Colors.grey
-
disabledTextColor:指定按钮在禁用状态下的文本颜色。例如:disabledTextColor: Colors.white
-
padding:指定按钮的内边距。可以使用EdgeInsets对象来定义上、下、左、右的边距值。例如:padding: EdgeInsets.all(10.0)
-
shape:指定按钮的形状。可以使用RoundedRectangleBorder、CircleBorder等形状。例如:shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0))
-
splashColor:指定按钮被按下时的水波纹颜色。例如:splashColor: Colors.red
-
elevation:指定按钮的阴影高度。例如:elevation: 5.0
使用注释说明可以在代码中添加注释来解释每个属性的作用,例如:
FlatButton(
onPressed: () {
// 点击按钮后执行的代码
},
child: Text('按钮文本'),
color: Colors.blue, // 按钮背景颜色
textColor: Colors.white, // 按钮文本颜色
disabledColor: Colors.grey, // 禁用状态下的背景颜色
disabledTextColor: Colors.white, // 禁用状态下的文本颜色
padding: EdgeInsets.all(10.0), // 按钮内边距
shape: RoundedRectangleBorder(borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(10.0)), // 按钮形状
splashColor: Colors.red, // 按钮按下时的水波纹颜色
elevation: 5.0, // 按钮阴影高度
)Checkbox(复选框)
用于表示一个可选中或取消选中的选项。
- value:bool类型,表示复选框的选中状态。如果为true,则复选框被选中;如果为false,则复选框未被选中。
- onChanged:ValueChanged
类型,表示当复选框的选中状态发生改变时的回调函数。可以在回调函数中更新复选框的选中状态。 - activeColor:Color类型,表示复选框选中时的颜色。默认为主题颜色。
- checkColor:Color类型,表示复选框内部勾选标记的颜色。默认为白色。
- tristate:bool类型,表示复选框是否支持三态(选中、未选中、不确定)。默认为false,即不支持三态。
- materialTapTargetSize:MaterialTapTargetSize类型,表示复选框的点击目标大小。默认为MaterialTapTargetSize.padded。
- visualDensity:VisualDensity类型,表示复选框的视觉密度。默认为VisualDensity.comfortable。
使用注释说明可以在代码中添加注释来解释每个属性的作用,例如:
Checkbox(
value: _isChecked, // 当前复选框的选中状态
onChanged: (bool newValue) {
setState(() {
_isChecked = newValue; // 更新复选框的选中状态
});
},
activeColor: Colors.blue, // 复选框选中时的颜色
checkColor: Colors.white, // 复选框内部勾选标记的颜色
tristate: false, // 不支持三态
materialTapTargetSize: MaterialTapTargetSize.padded, // 复选框的点击目标大小
visualDensity: VisualDensity.comfortable, // 复选框的视觉密度
)Radio(单选框)
用于表示一组选项中的单个选项。
- value:T类型,表示单选框的值。当单选框被选中时,它的值将被传递给groupValue。
- groupValue:T类型,表示单选框组的值。当单选框的值与groupValue相等时,该单选框将被选中。
- onChanged:ValueChanged
类型,表示当单选框的选中状态发生改变时的回调函数。可以在回调函数中更新groupValue的值。 - activeColor:Color类型,表示单选框选中时的颜色。默认为主题颜色。
- materialTapTargetSize:MaterialTapTargetSize类型,表示单选框的点击目标大小。默认为MaterialTapTargetSize.padded。
- visualDensity:VisualDensity类型,表示单选框的视觉密度。默认为VisualDensity.comfortable。
使用注释说明可以在代码中添加注释来解释每个属性的作用,例如:
Radio(
value: _selectedValue, // 当前单选框的值
groupValue: _groupValue, // 单选框组的值
onChanged: (T newValue) {
setState(() {
_groupValue = newValue; // 更新单选框组的值
});
},
activeColor: Colors.blue, // 单选框选中时的颜色
materialTapTargetSize: MaterialTapTargetSize.padded, // 单选框的点击目标大小
visualDensity: VisualDensity.comfortable, // 单选框的视觉密度
)Switch(开关)
用于表示一个开关状态的组件。
-
value:bool类型,表示开关的当前状态,true表示开启,false表示关闭。
-
onChanged:Function类型,当开关状态发生改变时触发的回调函数。
-
activeColor:Color类型,表示开启状态下的颜色。
-
activeTrackColor:Color类型,表示开启状态下的轨道颜色。
-
inactiveThumbColor:Color类型,表示关闭状态下的滑块颜色。
-
inactiveTrackColor:Color类型,表示关闭状态下的轨道颜色。
-
activeThumbImage:ImageProvider类型,表示开启状态下的滑块图片。
-
inactiveThumbImage:ImageProvider类型,表示关闭状态下的滑块图片。
-
dragStartBehavior:DragStartBehavior类型,表示滑动开始的行为。
下面是一个例子,演示了如何使用Switch组件及其属性:
bool switchValue = false; // 开关的初始状态为关闭
Switch(
value: switchValue, // 开关的当前状态
onChanged: (bool newValue) {
setState(() {
switchValue = newValue; // 开关状态改变时更新状态值
});
},
activeColor: Colors.blue, // 开启状态下的颜色为蓝色
activeTrackColor: Colors.blue[200], // 开启状态下的轨道颜色为浅蓝色
inactiveThumbColor: Colors.grey, // 关闭状态下的滑块颜色为灰色
inactiveTrackColor: Colors.grey[300], // 关闭状态下的轨道颜色为浅灰色
activeThumbImage: AssetImage('assets/images/switch_on.png'), // 开启状态下的滑块图片为switch_on.png
inactiveThumbImage: AssetImage('assets/images/switch_off.png'), // 关闭状态下的滑块图片为switch_off.png
dragStartBehavior: DragStartBehavior.start, // 滑动开始的行为为从滑块开始
)在上述例子中,当开关的状态发生改变时,会调用onChanged回调函数来更新开关的状态值。开启状态下的颜色为蓝色,轨道颜色为浅蓝色,滑块颜色为灰色,轨道颜色为浅灰色。同时,开启状态下的滑块图片为switch_on.png,关闭状态下的滑块图片为switch_off.png。滑动开始的行为为从滑块开始。
Slider(滑块)
用于表示一个可拖动的滑块,可以选择一个范围内的值。
-
value:double类型,表示滑块的当前值。
-
onChanged:Function类型,当滑块的值发生改变时触发的回调函数。
-
onChangeStart:Function类型,当滑块开始滑动时触发的回调函数。
-
onChangeEnd:Function类型,当滑块停止滑动时触发的回调函数。
-
min:double类型,表示滑块的最小值。
-
max:double类型,表示滑块的最大值。
-
divisions:int类型,表示滑块的离散间隔数量。
-
label:String类型,表示滑块当前值的标签。
-
activeColor:Color类型,表示滑块的激活颜色。
-
inactiveColor:Color类型,表示滑块的非激活颜色。
下面是一个例子,演示了如何使用Slider组件及其属性:
double sliderValue = 0.0; // 滑块的初始值为0
Slider(
value: sliderValue, // 滑块的当前值
onChanged: (double newValue) {
setState(() {
sliderValue = newValue; // 滑块值改变时更新状态值
});
},
onChangeStart: (double startValue) {
print('滑块开始滑动,当前值为:$startValue'); // 滑块开始滑动时的回调函数
},
onChangeEnd: (double endValue) {
print('滑块停止滑动,当前值为:$endValue'); // 滑块停止滑动时的回调函数
},
min: 0.0, // 滑块的最小值为0
max: 100.0, // 滑块的最大值为100
divisions: 5, // 滑块的离散间隔数量为5
label: sliderValue.toString(), // 滑块当前值的标签
activeColor: Colors.blue, // 滑块的激活颜色为蓝色
inactiveColor: Colors.grey, // 滑块的非激活颜色为灰色
)在上述例子中,当滑块的值发生改变时,会调用onChanged回调函数来更新滑块的状态值。滑块的最小值为0,最大值为100,离散间隔数量为5。滑块的激活颜色为蓝色,非激活颜色为灰色。滑块当前值的标签显示在滑块上方。当滑块开始滑动时,会触发onChangeStart回调函数,并打印当前值。当滑块停止滑动时,会触发onChangeEnd回调函数,并打印当前值。
ProgressIndicator(进度指示器)
用于显示一个进度指示器,可以是圆形、线性或自定义样式。
- value:表示当前进度的值,取值范围为0.0到1.0,默认为0.0。
- backgroundColor:指示器的背景颜色。
- valueColor:指示器的前景颜色,可以是固定颜色或动画颜色。
- strokeWidth:指示器的线条宽度。
- semanticsLabel:用于辅助功能的标签,描述进度指示器的含义。
下面是一个示例,演示了如何使用CircularProgressIndicator(圆形进度指示器)并设置其属性:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class MyProgressIndicator extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Progress Indicator Example'),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
CircularProgressIndicator( // 使用CircularProgressIndicator
value: 0.5, // 设置进度值为0.5
backgroundColor: Colors.grey, // 设置背景颜色为灰色
valueColor: AlwaysStoppedAnimation(Colors.blue), // 设置前景颜色为蓝色
strokeWidth: 5.0, // 设置线条宽度为5.0
semanticsLabel: 'Loading', // 设置辅助功能标签
),
SizedBox(height: 20.0), // 添加间距
LinearProgressIndicator( // 使用LinearProgressIndicator
value: 0.8, // 设置进度值为0.8
backgroundColor: Colors.grey, // 设置背景颜色为灰色
valueColor: AlwaysStoppedAnimation(Colors.green), // 设置前景颜色为绿色
minHeight: 10.0, // 设置最小高度为10.0
semanticsLabel: 'Loading', // 设置辅助功能标签
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(
home: MyProgressIndicator(),
));
} 在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个包含两个进度指示器的页面。第一个是CircularProgressIndicator,它的进度值为0.5,背景颜色为灰色,前景颜色为蓝色,线条宽度为5.0,辅助功能标签为"Loading"。第二个是LinearProgressIndicator,它的进度值为0.8,背景颜色为灰色,前景颜色为绿色,最小高度为10.0,辅助功能标签为"Loading"。
AlertDialog(对话框)
用于显示一个对话框,通常用于提示用户或获取用户的确认。
- title:对话框的标题,类型为Widget,默认为。
- content:对话框的内容,类型为Widget,默认为。
- actions:对话框的操作按钮,类型为List
,默认为。 - shape:对话框的形状,类型为ShapeBorder,默认为一个圆角矩形。
- backgroundColor:对话框的背景颜色,类型为Color,默认为白色。
- elevation:对话框的高度,类型为double,默认为24.0。
- semanticLabel:对话框的语义标签,类型为String,默认为。
下面是一个例子,演示了如何创建一个AlertDialog并设置其属性:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('AlertDialog Example'),
),
body: Center(
child: RaisedButton(
child: Text('Show Dialog'),
onPressed: () {
showDialog(
context: context,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
title: Text('Confirmation'),
content: Text('Are you sure you want to delete this item?'),
actions: [
FlatButton(
child: Text('Cancel'),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
),
FlatButton(
child: Text('Delete'),
onPressed: () {
// Perform delete operation
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
),
],
);
},
);
},
),
),
),
);
}
}在这个例子中,我们创建了一个AlertDialog,设置了标题为"Confirmation",内容为"Are you sure you want to delete this item?"。对话框有两个操作按钮,一个是"Cancel",点击后关闭对话框,另一个是"Delete",点击后执行删除操作并关闭对话框。