图解线性表顺序存储结构(附完整代码)
目录
一、前言
二、常用接口的实现
三、完整代码
一、前言
顺序表是线性表采用顺序存储结构在计算机内存中的存储方式,它由多个连续的存储单元构成,每个存储单元存放线性表的一个元素,逻辑上相邻的数据元素在内存中也是相邻的,不需要额外的内存空间来存放元素之间的逻辑关系。顺序表称为线性表的直接映射。
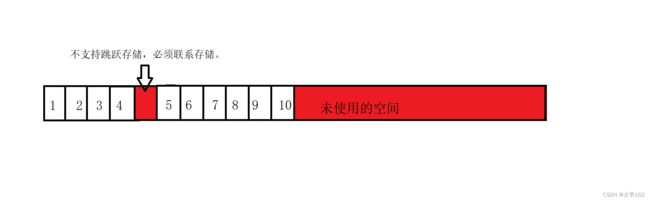
顺序存储定义:线性表的顺序存储结构,指的是用一段地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素
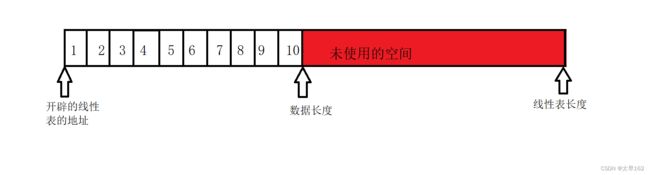
线性表的顺序存储示意图如下:
代码定义:
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a; 指向动态开辟的数组
int capacity; // 线性表长度
int size; // 数据长度
}SL;
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}顺序存储方式:就是在内存中申请一块连续的内存空间,准确的说是在堆区申请一块连续的内存空间,然后把相同数据类型依次存放在这一块内存中,所以可以用c语言(其他语言也相同)的一维数组实现顺序存储结构。
接口的实现
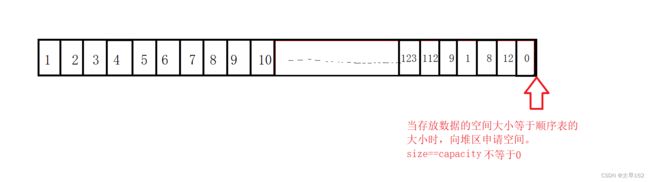
静态顺序表只适用于确定需要存多少数据的场景。静态顺序表的定长数组N定大了,导致空间浪费,开少了空间不够用。所以基本都使用动态顺序表,根据需要动态地分配空间的大小。
动态顺序表的主要操作有:头插数据,头删数据,尾插数据,尾删数据和在顺序表中任意位置删除数据(任意有效位置)和在实现这些接口时判断顺序表所申请的空间是否已完全使用及申请内存空间。如何在堆区中申请空间的相关知识在之前的博客中有讲解。在对顺序表进行数据的插入和删除前我们要先对顺序表的内存空间进行判断,如果之前申请的空间未使用完则可以进行数据的插小否则需要对顺序卷的大小进行扩容再进行数据的插入。按照以上需求我们以封装一个函数用于申请顺序表的空间。
代码如下:
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
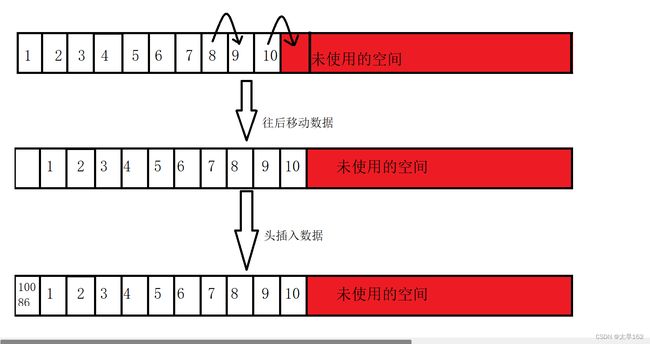
}头插数据:将新元素x插入到顺序表sl中逻辑序号为0的位置(如果插入成功,元素x成为线性表的第1个元素)。
代码如下:
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
// 挪动数据
int end = ps->size ;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end ] = ps->a[end-1];
--end;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
//SLInsert(ps, 0, x);
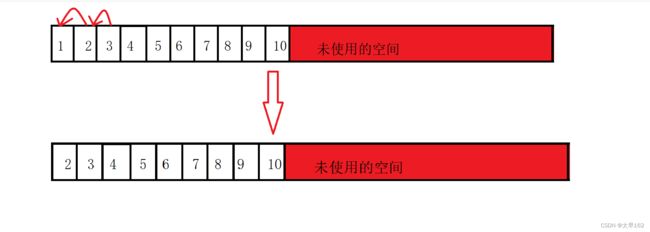
}头删数据:从前往后依次向前移动数据,使用数据覆盖实现删除。
功能如图:
代码如下:
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
/*int begin = 0;
while (begin < ps->size-1)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin+1];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;*/
int begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size )
{
ps->a[begin-1] = ps->a[begin ];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
//SLErase(ps, 0);
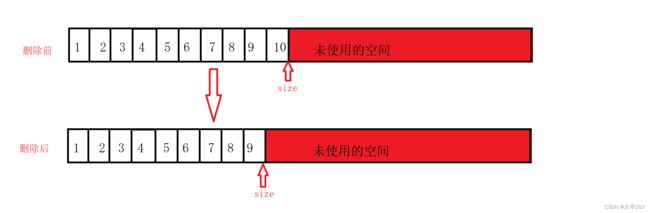
}尾部删除数据:
//尾删数据
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
ps->size=ps->size--;
}尾插数据:
//尾插数据
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
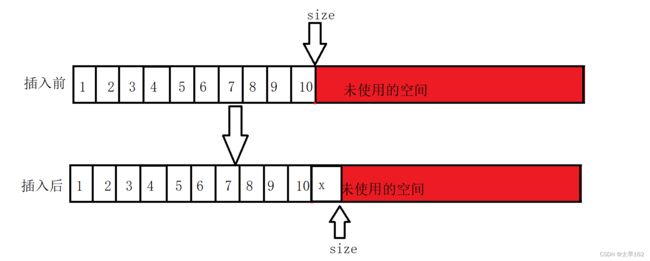
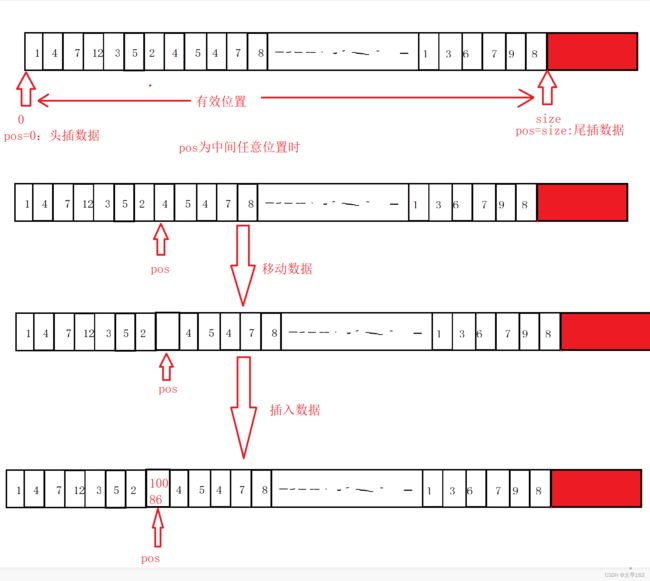
}任意位置插入数据:
// 在pos位置插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//移动数据,实现留有空间
/*int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}*/
int end = ps->size ;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end ] = ps->a[end-1];
end--;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
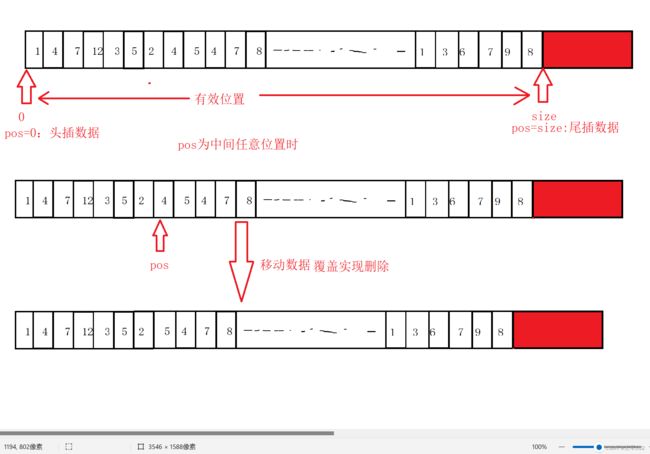
}任意位置删除数据:
代码如下:
// 删除pos位置数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos < ps->size);
//assert(ps->size > 0);
// 数据覆盖,实现删除
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
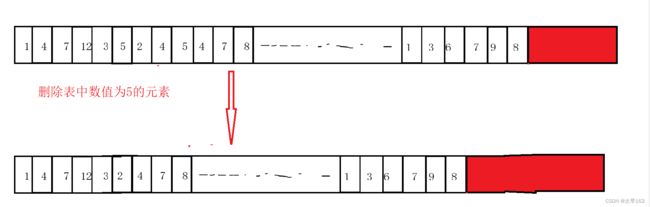
}按值查找删除数据:
查找接口:
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x,int begin)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; ++i)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
printf("没有了\n");
return -1;
}
删除接口:
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos < ps->size);
//assert(ps->size > 0);
// 数据覆盖,实现删除
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}三、完整代码
Test.c文件
#include"SeqList.h"
void menu()
{
printf("1、尾插数据 2、尾删数据\n");
printf("3、头插数据 4、头删数据\n");
printf("5、打印数据 -1、退出\n");
printf("6、任意位置删除 7、任意位置插入\n");
printf("8、按值删除\n");
}
int main()
{
SL s;
SLDataType x;
SLInit(&s);
int option = 0;
int val = 0;
do
{
menu();
printf("请输入你的操作:>");
scanf_s("%d", &option);
switch (option)
{
case 1:
printf("请依次输入你要尾插的数据,以-1结束\n");
scanf_s("%d", &val);
while (val != -1)
{
SLPushBack(&s, val);
scanf_s("%d", &val);
}
system("cls");
break;
case 2:
system("cls");
SLPopBack(&s);
break;
case 3:
printf("请依次输入你要头插的数据,以-1结束\n");
scanf_s("%d", &x);
while (x != -1)
{
SLPushFront(&s, x);
scanf_s("%d", &x);
}
system("cls");
break;
case 4:
SLPopFront(&s);
system("cls");
break;
case 5:
system("cls");
SLPrint(&s);
break;
default:
break;
case 6:
printf("请依次输入你要删除的位置\n");
scanf_s("%d", &x);
SLErase(&s, x);
system("cls");
break;
case 7:
printf("请依次输入你要插入的位置pos\n");
int pos;
scanf_s("%d", &pos);
printf("请依次输入你要插入的值\n");
scanf_s("%d", &x);
SLInsert(&s, pos, x);
system("cls");
break;
case 8:
{
int data = 0;
printf("请依次输入你要删除的值\n");
scanf_s("%d", &data);
int pos=SLFind(&s, data,0);
while(pos != -1)
{
SLErase(&s, pos);
printf("删除成功\n");
pos = SLFind(&s, data, pos);
}
}
break;
}
} while (option != -1);
SLDestroy(&s);
return 0;
}SeqLIst.h
#include
#include
#include
#pragma once
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a; 指向动态开辟的数组
int capacity; // 线性表长度
int size; // 数据长度
}SL;
// begin查找x的起始位置
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x,int begin);
void SLInit(SL* ps);
void SLPushBack(SL* ps,SLDataType x);
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
SeqList.c:
#include"SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
//打印顺序表
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)//销毁线性表
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->a)
{
free(ps->a);//释放
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
}
//尾插数据
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//尾删数据
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
ps->size=ps->size--;
}
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
// 挪动数据
int end = ps->size ;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end ] = ps->a[end-1];
--end;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
//SLInsert(ps, 0, x);
}
// 在pos位置插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
//移动数据,实现留有空间
/*int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
end--;
}*/
int end = ps->size ;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end ] = ps->a[end-1];
end--;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
// 删除pos位置数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0);
assert(pos < ps->size);
//assert(ps->size > 0);
// 数据覆盖,实现删除
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
/*int begin = 0;
while (begin < ps->size-1)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin+1];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;*/
int begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size )
{
ps->a[begin-1] = ps->a[begin ];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
//SLErase(ps, 0);
}
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x,int begin)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; ++i)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
printf("没有了\n");
return -1;
}