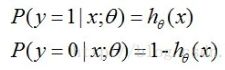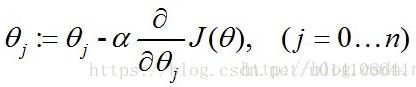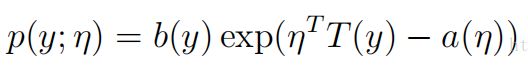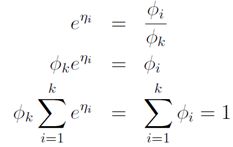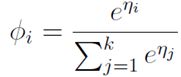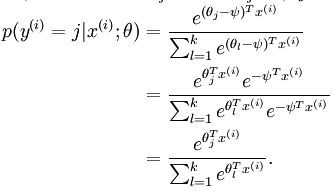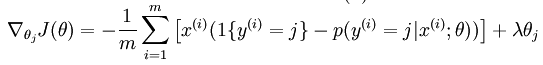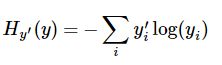深度学习2--tensorflow--Softmax回归实现手写数字识别
使用Softmax回归来实现手写数字识别,即给定一张手写数字,判断属于0--9中哪一个数字。
1.LR逻辑回归
先准备一下LR逻辑回归:
广义线性模型:实现x到y的非线性映射:
在LR逻辑回归中取g函数:实现0--1映射 输出值为 预测结果为1的概率
线性模型wx+b:
令h(x)表示结果为1的概率:
极大对数似然:
损失函数:
随机梯度下降:
2.Softmax回归
softmax属于多分类问题,多分类问题符合多项分布。可用于解决多分类问题,像决策树、朴素贝叶斯等。
首先证明多项分布属于指数分布族,这样就可以使用广义线性模型来拟合这个多项分布,由广义线性模型推导出的目标函数![]() 即为Softmax回归的分类模型。
即为Softmax回归的分类模型。
2.1指数分布族:
η被称为分布的自然参数(也称为规范参数);T(y)是充分统计量(对于我们所考虑的分布,通常情况下有T(y)=y);a(η)被称为对数划分函数。这一项![]() 本质上是起到了正则化常数的作用,确保了分布p(y;η)的总和或是积分在y到1上。
本质上是起到了正则化常数的作用,确保了分布p(y;η)的总和或是积分在y到1上。
2.2证明多项分布属于指数分布族
多分类模型的输出结果为该样本属于k个类别的概率,从这k个概率中我们选择最优的概率对应的类别(通常选概率最大的类别),作为该样本的预测类别。这k个概率用k个变量![]() ,
,![]() …,
…,![]() 表示。这个k变量和为1,即满足:
表示。这个k变量和为1,即满足:
![]() 可以用前k-1个变量来表示,即:
可以用前k-1个变量来表示,即:
使用广义线性模型拟合这个多分类问题,首先要验证这个多项分布是否符合一个指数分布族。定义T(y)为:
在这里,统计分量T(y)并没有像之前那样定义为T(y)=y,因为T(y)不是一个数值,而是一个k-1维的向量。使用符号![]() 表示向量T(y)的第i个元素。在这里引入一个新符号:
表示向量T(y)的第i个元素。在这里引入一个新符号:![]() ,如果括号内为true则这个符号取1,反之取0,即
,如果括号内为true则这个符号取1,反之取0,即![]() ,
,![]() 。所以,T(y)与y的关系就可以表示为
。所以,T(y)与y的关系就可以表示为![]()
![]() 与
与![]() 关系为:
关系为:
即:
![]()
多项分布表达式转化为指数分布族表达式过程如下:
其中:
变换过程:
第一步:![]() 取值为
取值为![]() ,
,![]() …,
…,![]() 中的一个,取决于y的取值。当y=i时,这一步可以理解为
中的一个,取决于y的取值。当y=i时,这一步可以理解为![]()
第二步:消去![]()
第三步:根据![]()
第四、五步:转换为广义线性模型的表达格式。
2.3softmax函数表达式推导
多项分布表达式可以表示为指数分布族表达式的格式,所以它属于指数分布族,那么就可以用广义线性模型来拟合这个多项式分布模型。
由η表达式可得:
这是![]() 关于
关于![]() 的表达式,把它转化为
的表达式,把它转化为![]() 关于
关于![]() 的表达式过程为:
的表达式过程为:
为了方便,令![]() ,那么
,那么
因为:
所以:
这个![]() 关于
关于![]() 的的函数称为Softmax函数(Softmax Function)
的的函数称为Softmax函数(Softmax Function)
2.4Softmax回归以及求解:
将x分类为j的概率为:
令h(x):
代价函数:
梯度下降求解:
![]()
Softmax 回归有一个特点:它有一个“冗余”的参数集。如果参数 是代价函数 的极小值点,那么 同样也是它的极小值点,其中 可以为任意向量。因此使 最小化的解不是唯一的。
证明如下:
权重衰减:
权重衰减项以后 (),代价函数就变成了严格的凸函数,这样就可以保证得到唯一的解。 此时的 Hessian矩阵变为可逆矩阵,并且因为是凸函数,梯度下降法和 L-BFGS 等算法可以保证收敛到全局最优解。
梯度下降公式:
3.tensorflow实现softmax回归
手写字体数据集的加载:
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
从MNIST_data目录下加载训练集,如果不存在则下载训练集。
读取数据集代码如下:
最终返回数据集格式:
data_sets.train |
55000 组 图片和标签, 用于训练 |
data_sets.validation |
5000 组 图片和标签, 用于迭代验证训练的准确性 |
data_sets.test |
10000 组 图片和标签, 用于最终测试训练的准确性 |
def read_data_sets(train_dir, fake_data=False, one_hot=False):
class DataSets(object):
#python里pass用来占位
pass
data_sets = DataSets()
if fake_data:
data_sets.train = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
data_sets.validation = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
data_sets.test = DataSet([], [], fake_data=True)
return data_sets
TRAIN_IMAGES = 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TRAIN_LABELS = 'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
TEST_IMAGES = 't10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
TEST_LABELS = 't10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
VALIDATION_SIZE = 5000
local_file = maybe_download(TRAIN_IMAGES, train_dir)
train_images = extract_images(local_file)
local_file = maybe_download(TRAIN_LABELS, train_dir)
train_labels = extract_labels(local_file, one_hot=one_hot)
local_file = maybe_download(TEST_IMAGES, train_dir)
test_images = extract_images(local_file)
local_file = maybe_download(TEST_LABELS, train_dir)
test_labels = extract_labels(local_file, one_hot=one_hot)
validation_images = train_images[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
validation_labels = train_labels[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
train_images = train_images[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
train_labels = train_labels[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
data_sets.train = DataSet(train_images, train_labels)
data_sets.validation = DataSet(validation_images, validation_labels)
data_sets.test = DataSet(test_images, test_labels)
return data_sets从指定目录下寻找数据集,如果不存在则下载:
def maybe_download(filename, work_directory):
"""Download the data from Yann's website, unless it's already here."""
if not os.path.exists(work_directory):
os.mkdir(work_directory)
filepath = os.path.join(work_directory, filename)
if not os.path.exists(filepath):
filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(SOURCE_URL + filename, filepath)
statinfo = os.stat(filepath)
print('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.')
return filepath如果是图片,则处理图片数据
#提取图片到四维uint8数组
def extract_images(filename):
"""Extract the images into a 4D uint8 numpy array [index, y, x, depth]."""
print('Extracting', filename)
with gzip.open(filename) as bytestream:
magic = _read32(bytestream)
if magic != 2051:
raise ValueError(
'Invalid magic number %d in MNIST image file: %s' %
(magic, filename))
num_images = _read32(bytestream)
rows = _read32(bytestream)
cols = _read32(bytestream)
buf = bytestream.read(rows * cols * num_images)
data = numpy.frombuffer(buf, dtype=numpy.uint8)
data = data.reshape(num_images, rows, cols, 1)
return data如果是标签,则处理标签:数字标签数据被解压称1维的tensor: [image index],它定义了每个样本数值的类别分类
def extract_labels(filename, one_hot=False):
"""Extract the labels into a 1D uint8 numpy array [index]."""
print('Extracting', filename)
with gzip.open(filename) as bytestream:
magic = _read32(bytestream)
if magic != 2049:
raise ValueError(
'Invalid magic number %d in MNIST label file: %s' %
(magic, filename))
num_items = _read32(bytestream)
buf = bytestream.read(num_items)
labels = numpy.frombuffer(buf, dtype=numpy.uint8)
if one_hot:
return dense_to_one_hot(labels)
return labels函数——read32需要修改如下;numpy.frombuffer返回为一个数组,这里只需要返回数组值即可。
def _read32(bytestream):
#采用大尾端存储
dt = numpy.dtype(numpy.uint32).newbyteorder('>')
#此处需要修改只返回[0]位置结果 numpy.frombuffer函数返回时一个数组
return numpy.frombuffer(bytestream.read(4), dtype=dt)[0]使用tensorflow代码如下:
加载数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
构造线性模型 z=wx+b ,预测输出为y=softmax(z)=softmax(wx+b)
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 784])
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W)+b)
代价函数使用交叉熵
yi 为预测的分布 yi`为真实分布
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W)+b)
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10])
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y))
梯度下降算法来求解最优值
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cross_entropy)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Nov 18 19:46:33 2018
@author: chen
"""
import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True)
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 784])
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W)+b)
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10])
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01).minimize(cross_entropy)
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
correct_prediction =tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
print (sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images, y_:mnist.test.labels}))随机梯度下降训练:每次选取100样本执行随机梯度下降,迭代1000次
for i in range(1000):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
计算准确率:
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
argmax函数作用:
Returns the index with the largest value across axes of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
结果correct_prediction为1*10维bool向量,将其转化为为float求其平均值
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
y为n*10维矩阵,第i行存储着模型对于第i张图片的各种类别预测值
y_存储着第i张图片的类别真实值
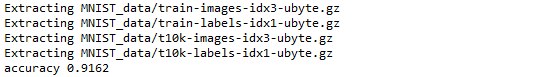
最终结果:准确率约为91%
tensorflow的使用规则得学习一下,直接只需定义变量以及代价函数,可用自带算法来执行优化求解真的是牛,以后有机会把算法求解过程源码看一下。
参考地址:
https://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/p/4905420.html
https://yq.aliyun.com/ziliao/571823
http://www.tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/tutorials/mnist_beginners.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31589695/article/details/79936938