高级DBA教你Mysql中IF的使用并与子查询联合运用实战并附加实用小窍门
高级DBA教你Mysql中IF的使用并与子查询联合运用实战
一、IF表达式的基础用法
IF #表达式
IF(expr1 , expr2 , expr3)
expr1的值为TRUE,则返回值为expr2
expr1的值为FALSE,则返回值为expr3
SELECT IF("判断条件", 条件成立, 条件不成立);
举例:
SELECT IF(FALSE, 3, 4);
二、IF表达式联合子查询用法
SELECT COLUMN_NAME from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='表名' and TABLE_SCHEMA='数据库名称' #查询某表的所有列名称
(1)判断数据库中某个表是否存在
select DATABASE();#获取当前链接的数据库名称
select if((SELECT COUNT(*) from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='表名称' and TABLE_SCHEMA=DATABASE() )>0,1,0) #存在返回1,不存在返回0
(2)判断数据库中某个表某个字段是否存在
select if((SELECT COUNT(*) from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='表名称' and TABLE_SCHEMA=DATABASE() and COLUMN_NAME='字段名称')>0,1,0)#存在返回1,不存在返回0
(3)延申避免重复插入的方法
insert into 表1 (字段1, 字段2, 字段3, 字段4, 字段5, 字段6)
select '字段1值', 字段2值, '字段3值', '字段4值', 字段5值, 字段6值
from dual
where not exists (select 1 from 表1 t2 where t2.字段1 = '字段1值' ); #如果存在则不执行插入 字段1的值如果在现在表里存在,则该语句失效
(4)获取某表所有字段按逗号拼接
select group_concat(COLUMN_NAME separator ',') from information_schema.COLUMNS where table_schema=DATABASE() and table_name = '表名';
(5)获取某表的建立索引的语句集合
SELECT CONCAT('ALTER TABLE `',TABLE_NAME,'` ', 'ADD ', IF(NON_UNIQUE = 1, CASE UPPER(INDEX_TYPE) WHEN 'FULLTEXT' THEN 'FULLTEXT INDEX' WHEN 'SPATIAL' THEN 'SPATIAL INDEX' ELSE CONCAT('INDEX `', INDEX_NAME, '` USING ', INDEX_TYPE ) END, IF(UPPER(INDEX_NAME) = 'PRIMARY', CONCAT('PRIMARY KEY USING ', INDEX_TYPE ), CONCAT('UNIQUE INDEX `', INDEX_NAME, '` USING ', INDEX_TYPE ) ) ),'(', GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT CONCAT('`', COLUMN_NAME, '`') ORDER BY SEQ_IN_INDEX ASC SEPARATOR ', '), ');') AS 'Show_Add_Indexes' FROM information_schema.STATISTICS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA =DATABASE() AND TABLE_NAME='表名称' GROUP BY TABLE_NAME, INDEX_NAME ORDER BY TABLE_NAME ASC, INDEX_NAME ASC;
输出结果为该表下的索引索引的建造语句:
ALTER TABLE 表 ADD PRIMARY KEY USING BTREE(字段1, 字段2, 字段3);
(6)触发器例子
DROP trigger IF EXISTS `nasentest`;
CREATE DEFINER=`用户名`@`%` nasentest
before insert on 表1 for each row
begin
if new.sj=NULL then
set new.sj = now();
else
set new.sj = now();
end if;
end; #nasentest表入库的时候,看看SJ这个字段有没有赋值,入库的时候重新赋值SJ这个字段。赋值当前时间!
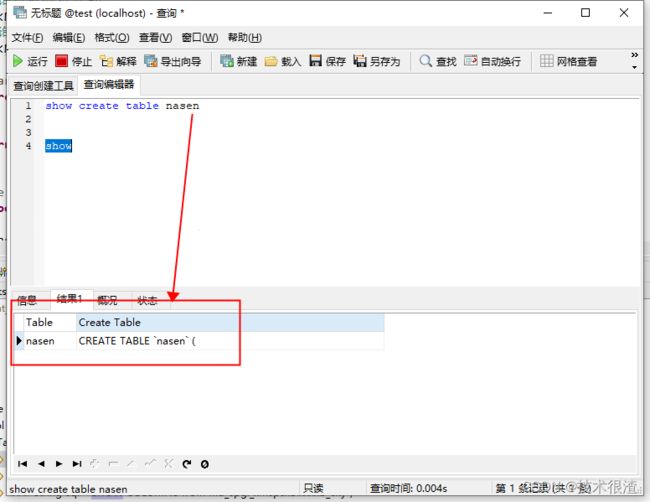
(7)查询某表的建表DLL语句
show create table 表名称
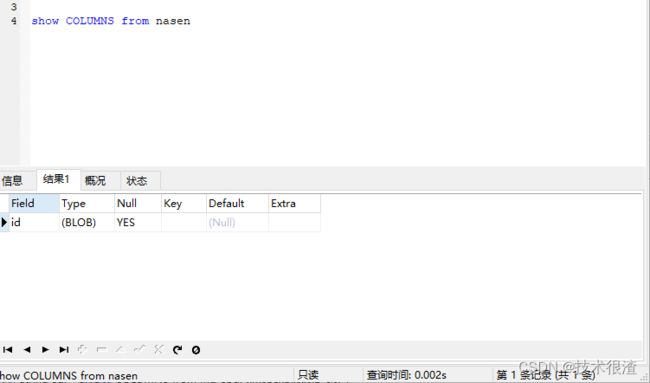
(8)查询某表的所有字段
SHOW COLUMNS FROM 表名称
三、IF表达式,嵌套多层IF表达式方法
2层判断举例:
if(表1存在){
if(表2存在){
表1表2都存在
}else{
表1存在表2不存在
}
}else{
输出表1不存在
}
mysql如下:
select if((SELECT COUNT(*) from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='表名1' and TABLE_SCHEMA=DATABASE() )>0,
if((SELECT COUNT(*) from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where TABLE_NAME='表名2' and TABLE_SCHEMA=DATABASE() )>0,
'表1表2都在','表1存在,表2不存在'),
'表1不存在')
四、查询MYSQL数据库表占用硬盘情况排列语句
SELECT--
TABLE_NAME,
DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH,
TABLE_ROWS,
concat(round((DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH) / 1024 / 1024,2),'MB') AS DATA
FROM
information_schema. TABLES
WHERE
TABLE_SCHEMA = DATABASE() -- 数据库名
ORDER BY
DATA + 0 DESC;
五、查看my.cnf的配置文件位置
Linux如下:
which mysql
mysql --help | grep 'Default options' -A 1
show variables like 'log_%';
show global variables like '%datadir%';
show global variables like '%datadir%';
whereis mysql
六、命令笔记
mysqldump -h 10.1.12.198 -P 3306 -uroot -p密码 --default-character-set=utf8 数据库名称> /home/文件名.sql
SET GLOBAL tmp_table_size=2147483648;#临时表 内存表 阈值配置
SET GLOBAL max_heap_table_size=2147483648;#临时表 内存表 阈值配置
MySQL8配置文件demo
# Other default tuning values
# MySQL Server Instance Configuration File
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
# Generated by the MySQL Server Instance Configuration Wizard
#
#
# Installation Instructions
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# On Linux you can copy this file to /etc/my.cnf to set global options,
# mysql-data-dir/my.cnf to set server-specific options
# (@localstatedir@ for this installation) or to
# ~/.my.cnf to set user-specific options.
#
# On Windows you should keep this file in the installation directory
# of your server (e.g. C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y). To
# make sure the server reads the config file use the startup option
# "--defaults-file".
#
# To run the server from the command line, execute this in a
# command line shell, e.g.
# mysqld --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini"
#
# To install the server as a Windows service manually, execute this in a
# command line shell, e.g.
# mysqld --install MySQLXY --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini"
#
# And then execute this in a command line shell to start the server, e.g.
# net start MySQLXY
#
#
# Guidelines for editing this file
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# In this file, you can use all long options that the program supports.
# If you want to know the options a program supports, start the program
# with the "--help" option.
#
# More detailed information about the individual options can also be
# found in the manual.
#
# For advice on how to change settings please see
# https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/server-configuration-defaults.html
#
#
# CLIENT SECTION
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# The following options will be read by MySQL client applications.
# Note that only client applications shipped by MySQL are guaranteed
# to read this section. If you want your own MySQL client program to
# honor these values, you need to specify it as an option during the
# MySQL client library initialization.
#
[client]
# pipe=
# socket=MYSQL
port=3306
[mysql]
no-beep
# default-character-set=
# SERVER SECTION
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------
#
# The following options will be read by the MySQL Server. Make sure that
# you have installed the server correctly (see above) so it reads this
# file.
#
# server_type=3
[mysqld]
secure_file_priv=''
server-id=162
default_authentication_plugin=mysql_native_password
#gtid-mode=on
#enforce-gtid-consistency=1 # 设置为主从强一致性
#log-slave-updates=1 # 记录日志
federated
wait_timeout=1440000
interactive_timeout = 1440000
skip-log-bin
slave-skip-errors=1049,1032,1062
replicate_do_db =
replicate-ignore-db=mysql,performance_schema,information_schema
# 服务端使用的字符集默认为8比特编码的latin1字符集
character-set-server=utf8
# 创建新表时将使用的默认存储引擎
default-storage-engine=INNODB
sql_mode=STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
# The next three options are mutually exclusive to SERVER_PORT below.
# skip-networking
# enable-named-pipe
# shared-memory
# shared-memory-base-name=MYSQL
# The Pipe the MySQL Server will use
# socket=MYSQL
# The TCP/IP Port the MySQL Server will listen on
port=3306
# Path to installation directory. All paths are usually resolved relative to this.
# basedir="C:/Program Files/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/"
# Path to the database root
datadir=C:\MYSQL_DATA\Data
# The default character set that will be used when a new schema or table is
# created and no character set is defined
# character-set-server=
# The default authentication plugin to be used when connecting to the server
# default_authentication_plugin=caching_sha2_password
# The default storage engine that will be used when create new tables when
default-storage-engine=INNODB
# Set the SQL mode to strict
sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION"
# General and Slow logging.
log-output=FILE
general-log=0
general_log_file="DESKTOP-Q6SJEH9.log"
slow-query-log=1
slow_query_log_file="DESKTOP-Q6SJEH9-slow_nasen.log"
long_query_time=4
# Error Logging.
log-error="DESKTOP-Q6SJEH9.err"
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Specifies the base name to use for binary log files. With binary logging
# enabled, the server logs all statements that change data to the binary
# log, which is used for backup and replication.
# log-bin="DESKTOP-Q6SJEH9-bin"
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Sets the binary logging format, and can be any one of STATEMENT, ROW,
# or MIXED. ROW is suggested for Group Replication.
# binlog_format
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Causes the master to write a checksum for each event in the binary log.
# binlog_checksum supports the values NONE (disabled) and CRC32.
# The default is CRC32. When disabled (value NONE), the server verifies
# that it is writing only complete events to the binary log by writing
# and checking the event length (rather than a checksum) for each event.
# NONE must be used with Group Replication.
# binlog_checksum
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# The base name for the relay log. The server creates relay log files in
# sequence by adding a numeric suffix to the base name. If you specify this
# option, the value specified is also used as the base name for the relay log
# index file. Relay logs increase speed by using load-balancing between disks.
# relay_log
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Specifies the server ID. For servers that are used in a replication topology,
# you must specify a unique server ID for each replication server, in the
# range from 1 to 2^32 − 1. “Unique” means that each ID must be different
# from every other ID in use by any other replication master or slave.
server-id=1
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# The host name or IP address of the slave to be reported to the master
# during slave registration. This value appears in the output of SHOW SLAVE HOSTS
# on the master server. Leave the value unset if you do not want the slave to
# register itself with the master.
# report_host=0.0
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# The TCP/IP port number for connecting to the slave, to be reported to the master during
# slave registration. Set this only if the slave is listening on a nondefault port or if
# you have a special tunnel from the master or other clients to the slave.
report_port=3306
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# This option specifies whether global transaction identifiers (GTIDs) are
# used to identify transactions. ON must be used with Group Replication.
# gtid_mode
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# When enabled, the server enforces GTID consistency by allowing execution of
# only statements that can be safely logged using a GTID. You must set this
# option to ON before enabling GTID based replication.
# enforce_gtid_consistency
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Whether updates received by a slave server from a master server should be
# logged to the slave's own binary log. Binary logging must be enabled on
# the slave for this variable to have any effect. ON must be used with
# Group Replication.
# log_slave_updates
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Determines whether the slave server logs master status and connection information
# to an InnoDB table in the mysql database, or to a file in the data directory.
# The TABLE setting is required when multiple replication channels are configured.
# master_info_repository
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Determines whether the slave server logs its position in the relay logs to an InnoDB
# table in the mysql database, or to a file in the data directory. The TABLE setting is
# required when multiple replication channels are configured.
# relay_log_info_repository
# ***** Group Replication Related *****
# Defines the algorithm used to hash the writes extracted during a transaction. If you
# are using Group Replication, this variable must be set to XXHASH64 because the process
# of extracting the writes from a transaction is required for conflict detection on all
# group members.
# transaction_write_set_extraction
# NOTE: Modify this value after Server initialization won't take effect.
lower_case_table_names=1
# Secure File Priv.
secure-file-priv="C:/ProgramData/MySQL/MySQL Server 8.0/Uploads"
# The maximum amount of concurrent sessions the MySQL server will
# allow. One of these connections will be reserved for a user with
# SUPER privileges to allow the administrator to login even if the
# connection limit has been reached.
max_connections=1000
# The number of open tables for all threads. Increasing this value
# increases the number of file descriptors that mysqld requires.
# Therefore you have to make sure to set the amount of open files
# allowed to at least 4096 in the variable "open-files-limit" in
# section [mysqld_safe]
table_open_cache=2000
# Maximum size for internal (in-memory) temporary tables. If a table
# grows larger than this value, it is automatically converted to disk
# based table This limitation is for a single table. There can be many
# of them.
tmp_table_size=2000M
max_heap_table_size=2000M
# How many threads we should keep in a cache for reuse. When a client
# disconnects, the client's threads are put in the cache if there aren't
# more than thread_cache_size threads from before. This greatly reduces
# the amount of thread creations needed if you have a lot of new
# connections. (Normally this doesn't give a notable performance
# improvement if you have a good thread implementation.)
thread_cache_size=10
#*** MyISAM Specific options
# The maximum size of the temporary file MySQL is allowed to use while
# recreating the index (during REPAIR, ALTER TABLE or LOAD DATA INFILE.
# If the file-size would be bigger than this, the index will be created
# through the key cache (which is slower).
myisam_max_sort_file_size=100G
# The size of the buffer that is allocated when sorting MyISAM indexes
# during a REPAIR TABLE or when creating indexes with CREATE INDEX
# or ALTER TABLE.
myisam_sort_buffer_size=987M
# Size of the Key Buffer, used to cache index blocks for MyISAM tables.
# Do not set it larger than 30% of your available memory, as some memory
# is also required by the OS to cache rows. Even if you're not using
# MyISAM tables, you should still set it to 8-64M as it will also be
# used for internal temporary disk tables.
key_buffer_size=8M
# Size of the buffer used for doing full table scans of MyISAM tables.
# Allocated per thread, if a full scan is needed.
read_buffer_size=64K
read_rnd_buffer_size=256K
#*** INNODB Specific options ***
# innodb_data_home_dir=
# Use this option if you have a MySQL server with InnoDB support enabled
# but you do not plan to use it. This will save memory and disk space
# and speed up some things.
# skip-innodb
# If set to 1, InnoDB will flush (fsync) the transaction logs to the
# disk at each commit, which offers full ACID behavior. If you are
# willing to compromise this safety, and you are running small
# transactions, you may set this to 0 or 2 to reduce disk I/O to the
# logs. Value 0 means that the log is only written to the log file and
# the log file flushed to disk approximately once per second. Value 2
# means the log is written to the log file at each commit, but the log
# file is only flushed to disk approximately once per second.
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1
# The size of the buffer InnoDB uses for buffering log data. As soon as
# it is full, InnoDB will have to flush it to disk. As it is flushed
# once per second anyway, it does not make sense to have it very large
# (even with long transactions).
innodb_log_buffer_size=1M
# InnoDB, unlike MyISAM, uses a buffer pool to cache both indexes and
# row data. The bigger you set this the less disk I/O is needed to
# access data in tables. On a dedicated database server you may set this
# parameter up to 80% of the machine physical memory size. Do not set it
# too large, though, because competition of the physical memory may
# cause paging in the operating system. Note that on 32bit systems you
# might be limited to 2-3.5G of user level memory per process, so do not
# set it too high.
innodb_buffer_pool_size=8000M
# Size of each log file in a log group. You should set the combined size
# of log files to about 25%-100% of your buffer pool size to avoid
# unneeded buffer pool flush activity on log file overwrite. However,
# note that a larger logfile size will increase the time needed for the
# recovery process.
innodb_log_file_size=48M
# Number of threads allowed inside the InnoDB kernel. The optimal value
# depends highly on the application, hardware as well as the OS
# scheduler properties. A too high value may lead to thread thrashing.
innodb_thread_concurrency=49
# The increment size (in MB) for extending the size of an auto-extend InnoDB system tablespace file when it becomes full.
innodb_autoextend_increment=64
# The number of regions that the InnoDB buffer pool is divided into.
# For systems with buffer pools in the multi-gigabyte range, dividing the buffer pool into separate instances can improve concurrency,
# by reducing contention as different threads read and write to cached pages.
innodb_buffer_pool_instances=8
# Determines the number of threads that can enter InnoDB concurrently.
innodb_concurrency_tickets=5000
# Specifies how long in milliseconds (ms) a block inserted into the old sublist must stay there after its first access before
# it can be moved to the new sublist.
innodb_old_blocks_time=1000
# It specifies the maximum number of .ibd files that MySQL can keep open at one time. The minimum value is 10.
innodb_open_files=300
# When this variable is enabled, InnoDB updates statistics during metadata statements.
innodb_stats_on_metadata=0
# When innodb_file_per_table is enabled (the default in 5.6.6 and higher), InnoDB stores the data and indexes for each newly created table
# in a separate .ibd file, rather than in the system tablespace.
innodb_file_per_table=1
# Use the following list of values: 0 for crc32, 1 for strict_crc32, 2 for innodb, 3 for strict_innodb, 4 for none, 5 for strict_none.
innodb_checksum_algorithm=0
# The number of outstanding connection requests MySQL can have.
# This option is useful when the main MySQL thread gets many connection requests in a very short time.
# It then takes some time (although very little) for the main thread to check the connection and start a new thread.
# The back_log value indicates how many requests can be stacked during this short time before MySQL momentarily
# stops answering new requests.
# You need to increase this only if you expect a large number of connections in a short period of time.
back_log=80
# If this is set to a nonzero value, all tables are closed every flush_time seconds to free up resources and
# synchronize unflushed data to disk.
# This option is best used only on systems with minimal resources.
flush_time=0
# The minimum size of the buffer that is used for plain index scans, range index scans, and joins that do not use
# indexes and thus perform full table scans.
join_buffer_size=16M
# The maximum size of one packet or any generated or intermediate string, or any parameter sent by the
# mysql_stmt_send_long_data() C API function.
max_allowed_packet=1000M
# If more than this many successive connection requests from a host are interrupted without a successful connection,
# the server blocks that host from performing further connections.
max_connect_errors=100
# Changes the number of file descriptors available to mysqld.
# You should try increasing the value of this option if mysqld gives you the error "Too many open files".
open_files_limit=4161
# If you see many sort_merge_passes per second in SHOW GLOBAL STATUS output, you can consider increasing the
# sort_buffer_size value to speed up ORDER BY or GROUP BY operations that cannot be improved with query optimization
# or improved indexing.
sort_buffer_size=256K
# The number of table definitions (from .frm files) that can be stored in the definition cache.
# If you use a large number of tables, you can create a large table definition cache to speed up opening of tables.
# The table definition cache takes less space and does not use file descriptors, unlike the normal table cache.
# The minimum and default values are both 400.
table_definition_cache=1400
# Specify the maximum size of a row-based binary log event, in bytes.
# Rows are grouped into events smaller than this size if possible. The value should be a multiple of 256.
binlog_row_event_max_size=8K
# If the value of this variable is greater than 0, a replication slave synchronizes its master.info file to disk.
# (using fdatasync()) after every sync_master_info events.
sync_master_info=10000
# If the value of this variable is greater than 0, the MySQL server synchronizes its relay log to disk.
# (using fdatasync()) after every sync_relay_log writes to the relay log.
sync_relay_log=10000
# If the value of this variable is greater than 0, a replication slave synchronizes its relay-log.info file to disk.
# (using fdatasync()) after every sync_relay_log_info transactions.
sync_relay_log_info=10000
# Load mysql plugins at start."plugin_x ; plugin_y".
# plugin_load
# The TCP/IP Port the MySQL Server X Protocol will listen on.
# loose_mysqlx_port=33060
select version() #获取当前MYSQL的版本
处理锁表的相关命令
-- 查询是否锁表
show OPEN TABLES ;
-- 查询进程
show processlist ;
-- 查询到相对应的进程,然后杀死进程
kill id; -- 一般到这一步就解锁了
-- 查看正在锁的事务
SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_LOCKS;
-- 查看等待锁的事务
SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.INNODB_LOCK_WAITS;
-- 解锁表
UNLOCK TABLES;
#关闭log_bin
show variables like 'log_bin';#查询当前状态
skip-log-bin #配置文件里面加
mysql 8重置密码
my.cnf 加 skip-grant-tables
use mysql
update user set authentication_string = '' where user = 'root';
重启服务
七、导入导出命令专栏
(1)导出某个数据库
mysqldump -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 -u用户名密码 -p密码 --default-character-set=utf8 数据库名称> /home/备份.sql
(2)导出某个数据库的某些表
方法1
mysqldump -uroot -p1234 --host=localhost --databases test1 --tables hd_acl_entry > /root/db_back/all.sql
mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 --host=IP地址端口 --databases 数据库名称 --tables 表名名称1,表名称2,表名称3 > /root/db_back/all.sql
mysqldump database -u username -ppassword --tables table_name1 table_name2 table_name3 >D:\db_script.sql
方法2
mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 --default-character-set=utf8 数据库名称 表名1 表名2 表名3> d://备份.sql #导出数据库的表名1、2、3注意用空格隔开,按顺序
(3)只导出表结构建表语句不带数据
导出整个数据库的建表语句
mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 数据库名称 --no-data > d://备份.sql #导出某个数据库的所有建表语句,不包含表数据
导出某个表以及多个表的建表语句
mysqldump -u用户名 -p密码 数据库名称 表名1 表名2 --no-data > d://备份.sql #单独导出某些表的表结构
mysqldump -uroot -p123456 test nasen1 nasen2 --no-data > d://bak.sql #test是数据库名称,nasen1,nasen2是表名称空格隔开
(4)只导出表的数据,不带建表语句
-t #代表只导出数据
mysqldump -t database -u username -ppassword --tables table_name1 table_name2 table_name3 >D:\db_script.sql #-t代表只导出数据,不包含建表DLL
(5)导出过程中排除忽略一些表
--ignore-table=database_name.table_name3 #多个表配置需要写几轮
mysqldump -h IP -u username -ppassword --default-character-set=utf8 --database database_name --ignore-table=database_name.table_name1
--ignore-table=database_name.table_name2 --ignore-table=database_name.table_name3 >D:\db_script.sql
(6)MYSQL导出命令的集合文本
# 1.--all-databases , -A 导出全部数据库。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases
# 2.--all-tablespaces , -Y 导出全部表空间。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --all-tablespaces
# 3.--no-tablespaces , -y 不导出任何表空间信息。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --no-tablespaces
# 4.--add-drop-database 每个数据库创建之前添加drop数据库语句。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --add-drop-database
# 5.--add-drop-table 每个数据表创建之前添加drop数据表语句。(默认为打开状态,使用--skip-add-drop-table取消选项)
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases (默认添加drop语句)
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases –skip-add-drop-table (取消drop语句)
# 6.--add-locks 在每个表导出之前增加LOCK TABLES并且之后UNLOCK TABLE。(默认为打开状态,使用--skip-add-locks取消选项)
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases (默认添加LOCK语句)
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases –skip-add-locks (取消LOCK语句)
# 7.--allow-keywords 许创建是关键词的列名字。这由表名前缀于每个列名做到。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --allow-keywords
# 8.--apply-slave-statements 'CHANGE MASTER'前添加'STOP SLAVE',并且在导出的最后添加'START SLAVE'。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --apply-slave-statements
# 9.--character-sets-dir 符集文件的目录
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --character-sets-dir=/usr/local/mysql/share/mysql/charsets
# 10.--comments 附加注释信息。默认为打开,可以用--skip-comments取消
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases (默认记录注释)
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --skip-comments (取消注释)
# 11.--compatible导出的数据将和其它数据库或旧版本的MySQL 相兼容。值可以为ansi、mysql323、mysql40、postgresql、oracle、mssql、db2、maxdb、no_key_options、 no_tables_options、no_field_options等,要使用几个值,用逗号将它们隔开。它并不保证能完全兼容,而是尽量兼容。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --compatible=ansi
# 12.--compact导出更少的输出信息(用于调试)。去掉注释和头尾等结构。
可以使用选项:--skip-add-drop-table --skip-add-locks --skip-comments --skip-disable-keys
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --compact
# 13.--complete-insert, -c 用完整的insert语句(包含列名称)。这么做能提高插入效率,但是可能会受到max_allowed_packet参数的影响而导致插入失败。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --complete-insert
# 14.--compress, -C 客户端和服务器之间启用压缩传递所有信息
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --compress
# 15.--create-options, -a CREATE TABLE语句中包括所有MySQL特性选项。(默认为打开状态)
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases
# 16.--databases, -B 出几个数据库。参数后面所有名字参量都被看作数据库名。
mysqldump -uroot -p --databases test mysql
# 17.--debug输出debug信息,用于调试。默认值为:d:t:o,/tmp/mysqldump.trace
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --debug
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --debug=” d:t:o,/tmp/debug.trace”
# 18.--debug-check 查内存和打开文件使用说明并退出。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --debug-check
# 19.--debug-info 出调试信息并退出
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --debug-info
# 20.--default-character-set 设置默认字符集,默认值为utf8
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --default-character-set=latin1
# 21.--delayed-insert 用延时插入方式(INSERT DELAYED)导出数据
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --delayed-insert
# 22.--delete-master-logs master备份后删除日志. 这个参数将自动激活--master-data。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --delete-master-logs
# 23.--dump-slave 该选项将导致主的binlog位置和文件名追加到导出数据的文件中。设置为1时,将会以CHANGE MASTER命令输出到数据文件;设置为2时,在命令前增加说明信息。该选 项将会打开--lock-all-tables,除非--single-transaction被指定。该选项会自动关闭--lock-tables选项。默认值为0。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --dump-slave=1
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --dump-slave=2
# 24.--events, -E 导出事件。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --events
# 25.--extended-insert, -e使用具有多个VALUES列的INSERT语法。这样使导出文件更小,并加速导入时的速度。默认为打开状态,使用--skip-extended-insert取消选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases--skip-extended-insert (取消选项)
# 26.--fields-terminated-by 导出文件中忽略给定字段。与--tab选项一起使用,不能用于--databases和--all-databases选项
mysqldump -uroot -p test test --tab=”/home/mysql” --fields-terminated-by=”#”
# 27.--fields-enclosed-by 输出文件中的各个字段用给定字符包裹。与--tab选项一起使用,不能用于--databases和--all-databases选项
mysqldump -uroot -p test test --tab=”/home/mysql” --fields-enclosed-by=”#”
# 28.--fields-optionally-enclosed-by 输出文件中的各个字段用给定字符选择性包裹。与--tab选项一起使用,不能用于--databases和--all-databases选项
mysqldump -uroot -p test test --tab=”/home/mysql” --fields-enclosed-by=”#” --fields-optionally-enclosed-by =”#”
# 29.--fields-escaped-by 输出文件中的各个字段忽略给定字符。与--tab选项一起使用,不能用于--databases和--all-databases选项
mysqldump -uroot -p mysql user --tab=”/home/mysql” --fields-escaped-by=”#”
# 30.--flush-logs 开始导出之前刷新日志。
请注意:假如一次导出多个数据库(使用选项--databases或者--all-databases),将会逐个数据库刷新日志。除使用--lock-all-tables或者--master-data外。在这种情况下,日志将会被刷新一次,相应的所以表同时被锁定。因此,如果打算同时导出和刷新日志应该使用--lock-all-tables 或者--master-data 和--flush-logs。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --flush-logs
# 31.--flush-privileges 在导出mysql数据库之后,发出一条FLUSH PRIVILEGES 语句。为了正确恢复,该选项应该用于导出mysql数据库和依赖mysql数据库数据的任何时候。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --flush-privileges
# 32.--force 在导出过程中忽略出现的SQL错误。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --force
# 33.--help 显示帮助信息并退出。
mysqldump --help
# 34.--hex-blob 使用十六进制格式导出二进制字符串字段。如果有二进制数据就必须使用该选项。影响到的字段类型有BINARY、VARBINARY、BLOB。
mysqldump -uroot -p --all-databases --hex-blob
# 35.--host, -h 需要导出的主机信息
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases
# 36.--ignore-table 不导出指定表。指定忽略多个表时,需要重复多次,每次一个表。每个表必须同时指定数据库和表名。例如:--ignore-table=database.table1 --ignore- table=database.table2 ……
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --ignore-table=mysql.user
# 37.--include-master-host-port 在--dump-slave产生的'CHANGE MASTER TO..`语句中增加'MASTER_HOST=,MASTER_PORT=`
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --include-master-host-port
# 38.--insert-ignore 在插入行时使用INSERT IGNORE语句.
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --insert-ignore
# 39.lines-terminated-by 输出文件的每行用给定字符串划分。与--tab选项一起使用,不能用于--databases和--all-databases选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost test test --tab=”/tmp/mysql” --lines-terminated-by=”##”
# 40.--lock-all-tables, -x 提交请求锁定所有数据库中的所有表,以保证数据的一致性。这是一个全局读锁,并且自动关闭--single-transaction 和--lock-tables 选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --lock-all-tables
# 41.--lock-tables, -l
开始导出前,锁定所有表。用READ LOCAL锁定表以允许MyISAM表并行插入。对于支持事务的表例如InnoDB和BDB,--single-transaction是一个更好的选择,因为它根本不需要锁定表。
请注意当导出多个数据库时,--lock-tables分别为每个数据库锁定表。因此,该选项不能保证导出文件中的表在数据库之间的逻辑一致性。不同数据库表的导出状态可以完全不同。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --lock-tables
# 42.--log-error 附加警告和错误信息到给定文件
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --log-error=/tmp/mysqldump_error_log.err
# 43.--master-data 该选项将binlog的位置和文件名追加到输出文件中。如果为1,将会输出CHANGE MASTER 命令;如果为2,输出的CHANGE MASTER命令前添加注释信息。该选项将 打开--lock-all-tables 选项,除非--single-transaction也被指定(在这种情况下,全局读锁在开始导出时获得很短的时间;其他内容参考下面的--single-transaction选 项)。该选项自动关闭--lock-tables选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --master-data=1;
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --master-data=2;
# 44.--max_allowed_packet 服务器发送和接受的最大包长度。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --max_allowed_packet=10240
# 45.--net_buffer_length TCP/IP和socket连接的缓存大小。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --net_buffer_length=1024
# 46.--no-autocommit 使用autocommit/commit 语句包裹表。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --no-autocommit
# 47.--no-create-db, -n 只导出数据,而不添加CREATE DATABASE 语句。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --no-create-db
# 48.--no-create-info, -t 只导出数据,而不添加CREATE TABLE 语句。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --no-create-info
# 49.--no-data, -d 不导出任何数据,只导出数据库表结构。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --no-data
# 50.--no-set-names, -N 等同于--skip-set-charset
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --no-set-names
# 51.--opt 等同于--add-drop-table, --add-locks, --create-options, --quick, --extended-insert, --lock-tables, --set-charset, --disable-keys 该选项默认开启, 可以用--skip-opt禁用.
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --opt
# 52.--order-by-primary 如果存在主键,或者第一个唯一键,对每个表的记录进行排序。在导出MyISAM表到InnoDB表时有效,但会使得导出工作花费很长时间。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --order-by-primary
# 53.--password, -p 连接数据库密码
# 54.--pipe(windows系统可用) 使用命名管道连接mysql
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --pipe
# 45.--port, -P 连接数据库端口号
# 56.--protocol 使用的连接协议,包括:tcp, socket, pipe, memory.
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --protocol=tcp
# 57.--quick, -q 不缓冲查询,直接导出到标准输出。默认为打开状态,使用--skip-quick取消该选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --skip-quick
# 58.--quote-names,-Q 使用(`)引起表和列名。默认为打开状态,使用--skip-quote-names取消该选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --skip-quote-names
# 42.--replace 使用REPLACE INTO 取代INSERT INTO.
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --replace
# 43.--result-file, -r 直接输出到指定文件中。该选项应该用在使用回车换行对(\\r\\n)换行的系统上(例如:DOS,Windows)。该选项确保只有一行被使用。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --result-file=/tmp/mysqldump_result_file.txt
# 44.--routines, -R 导出存储过程以及自定义函数。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --routines
# 45.--set-charset 添加'SET NAMES default_character_set'到输出文件。默认为打开状态,使用--skip-set-charset关闭选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --skip-set-charset
# 46.--single-transaction 该选项在导出数据之前提交一个BEGIN SQL语句,BEGIN 不会阻塞任何应用程序且能保证导出时数据库的一致性状态。它只适用于多版本存储引擎,仅 InnoDB。本选项和--lock-tables 选项是互斥的,因为LOCK TABLES 会使任何挂起的事务隐含提交。要想导出大表的话,应结合使用--quick 选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --single-transaction
# 47.--dump-date 将导出时间添加到输出文件中。默认为打开状态,使用--skip-dump-date关闭选项。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --skip-dump-date
# 48.--skip-opt 禁用–opt选项.
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --skip-opt
# 49.--socket,-S 指定连接mysql的socket文件位置,默认路径/tmp/mysql.sock
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --socket=/tmp/mysqld.sock
# 50.--tab,-T 为每个表在给定路径创建tab分割的文本文件。注意:仅仅用于mysqldump和mysqld服务器运行在相同机器上。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost test test --tab="/home/mysql"
# 51.--tables 覆盖--databases (-B)参数,指定需要导出的表名。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --databases test --tables test
# 52.--triggers 导出触发器。该选项默认启用,用--skip-triggers禁用它。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --triggers
# 53.--tz-utc 在导出顶部设置时区TIME_ZONE='+00:00' ,以保证在不同时区导出的TIMESTAMP 数据或者数据被移动其他时区时的正确性。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --tz-utc
# 54.--user, -u 指定连接的用户名。
# 55.--verbose, --v 输出多种平台信息。
# 56.--version, -V 输出mysqldump版本信息并退出
# 57.--where, -w 只转储给定的WHERE条件选择的记录。请注意如果条件包含命令解释符专用空格或字符,一定要将条件引用起来。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --where=” user=’root’”
# 58.--xml, -X 导出XML格式.
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --xml
# 59.--plugin_dir 客户端插件的目录,用于兼容不同的插件版本。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --plugin_dir=”/usr/local/lib/plugin”
# 60.--default_auth 客户端插件默认使用权限。
mysqldump -uroot -p --host=localhost --all-databases --default-auth=”/usr/local/lib/plugin/<PLUGIN>