驱动开发,IO模型,信号驱动IO实现过程
1.信号驱动IO框架图
 分析:
分析:
信号驱动IO是一种异步IO方式。linux预留了一个信号SIGIO用于进行信号驱动IO。进程主程序注册一个SIGIO信号的信号处理函数,当硬件数据准备就绪后会发起一个硬件中断,在中断的处理函数中向当前进程发送一个SIGIO信号。进程收到SIGIO信号后执行信号处理函数,在信号处理函数中将数据读走即可。
应用层:1.打开设备文件,2注册SIGIO信号处理函数,3回调驱动中的fasync方法,4设置fd对应的驱动程序发送SIGIO信号只发送给当前进程
驱动层:完成异步对象的空间分配和初始化
硬件层:中断处理函数:发送SIGIO信号(用到异步对象的二级指针)
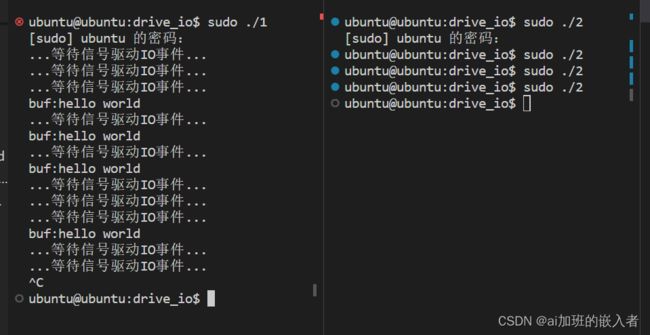
2.实现代码
---pro1.c---应用程序(信号驱动IO)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
char buf[128] = {0};
int fd;
void sigio_handler(int sig)
{
read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("buf:%s\n", buf);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
// 1打开设备文件
fd = open("/dev/mmyled0", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("自定义事件文件失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
// 2注册SIGIO信号的处理函数
signal(SIGIO, sigio_handler);
// 3回调驱动中的fasync方法,完成发送信号之前的准备工作
int flags = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL); //获取文件描述符属性
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,flags|FASYNC); //添加FASYNC属性就可以回调fasync操作方法
// 4驱动发送信号只发送给当前进程
fcntl(fd,F_SETOWN,getpid());
while(1)
{
printf("...等待信号驱动IO事件...\n");
sleep(1);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
---pro2.c---应用程序(模拟模拟硬件数据到达)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
char buf[128] = "hello world";
int fd = open("/dev/mmyled0", O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("打开设备文件失败\n");
exit(-1);
}
write(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
close(fd);
return 0;
} ---driceio.c---驱动程序
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
char kbuf[128] = {0};
unsigned int major;
struct class *cls;
struct device *dev;
struct fasync_struct *fp; //定义一个异步对象指针
// 封装操作方法
int mycdev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n", __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
ssize_t mycdev_read(struct file *file, char *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *lof)
{
int ret;
ret = copy_to_user(ubuf, kbuf, size);
if (ret)
{
printk("copy_to_ user err\n");
return -EIO;
}
return 0;
}
ssize_t mycdev_write(struct file *file, const char *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *lof)
{
int ret;
// 从用户拷贝数据,模拟硬件数据
ret = copy_from_user(kbuf, ubuf, size);
if (ret)
{
printk("copy_from_user err\n");
return -EIO;
}
//内核模块发送信号
kill_fasync(&fp,SIGIO,POLL_IN);
return 0;
}
int mycdev_fasync(int fd,struct file *file,int on) //异步操作方法
{
//完成发送信号之前的准备工作
//异步对象空间的分配语言初始化
fasync_helper(fd,file,on,&fp);
return 0;
}
int mycdev_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s:%s:%d\n", __FILE__, __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
struct file_operations fops = {
.open = mycdev_open,
.read = mycdev_read,
.fasync = mycdev_fasync,
.write = mycdev_write,
.release = mycdev_close,
};
// 入口函数
static int __init mycdev_init(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, "myled", &fops);
if (major < 0)
{
printk("字符设备驱动注册失败\n");
return major;
}
printk("字符设备驱动注册成功:major=%d\n", major);
// 向上提交目录
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "MYLED");
if (IS_ERR(cls))
{
printk("向上提交目录失败\n");
return -PTR_ERR(cls);
}
printk("向上提交目录成功\n");
// 向上提交设备节点信息
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
dev = device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, i), NULL, "mmyled%d", i);
if (IS_ERR(dev))
{
printk("向上提交设备节点信息失败\n");
return -PTR_ERR(dev);
}
}
printk("向上提交设备节点信息成功\n");
return 0;
}
// 出口函数
static void __exit mycdev_exit(void)
{
// 销毁设备节点信息
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, i));
}
// 销毁目录信息
class_destroy(cls);
// 字符设备驱动注销
unregister_chrdev(major, "myled");
}
// 声明
// 入口函数地址
module_init(mycdev_init);
// 出口函数地址
module_exit(mycdev_exit);
// 遵循的GPL协议
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");