I2C相关
文章目录
- Linux I2C 驱动框架分析
- 1、总体框架
- 2、软件层的主要数据结构
-
- 2.1 i2c_adapter
- 2.2 i2c_algorithm
- 2.3 i2c_bus_type
- 2.4 i2c_client 和 i2c_driver
- 2.5 i2c_msg
- 2.6 i2c_dev
- 2.7 i2c_dev_init
- 2.8 i2c_new_device
- 2.9 of_i2c_register_devices
- 2.10 i2c_register_adapter
- 2.11 i2c_register_driver
- 2.12 i2c_transfer
- 2.13 i2c_scan_static_board_info
- 3 小结
介绍i2c总线相关知识
Linux I2C 驱动框架分析
电气特性
https://www.ti.com.cn/cn/lit/an/slva704/slva704.pdf
1、总体框架
+-----------+
|Application| user space
+-----+-----+
,-------------------------------+-----------------------------------.
| | kernel space |
| | |
| +----------+ +------'---+ +-------+ |
| |i2c_driver|..........|i2c_client|............i2c_dev| |
| +----+-----+ +-----+----+ +---+---+ |
| | | | |
|+------'----------------------+--------------------+-------------+ |
|| O--------+ | |
|| |i2c_core| | |
|| +--------+ | |
|+-------+------------------------------------------+-------------+ |
| | | |
| O--+--------+ O------+------+ |
| |i2c_adapter| |i2c_algorithm| |
| +-----+-----+ +------+------+ |
| | | |
| | O------------+ | |
| |............|SoC Specific|.............. |
| +------+-----+ |
'`''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''|'''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
|
O-----------'-----------+
|Hardware/IIC Controller|
+-----------------------+
如图,大概分为8个模块
1、应用层通过标准的 open 函数操控 IIC 设备
2、每一个 i2c_client 对应一个实际硬件上的 IIC device(比如 EEPROM,LED)
3、每一个 i2c_driver 描述一种 IIC 设备的驱动(操控 EEPROM,LED)
4、i2c_dev 用于注册字符类型的设备
5、i2c_core 是 IIC 核心层,提供了总线、驱动、通信方式等的注册和钩子函数的设置
6、i2c_adapter 用于描述 SoC 的一个 IIC 控制器
7、i2c_algorithm 用于底层对接实际的控制器,产生 IIC 硬件波形的函数
8、最底层对接实际的 SoC 的 IIC 控制器(寄存器)和硬件
O----------+ O----------+
|Device 0.0| |Device 0.1|
+----------+ .----------+
,''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''| | | | |
| O----------------+---+----+----------'------+----------'--
| SoC |IIC Controller 0| | | |
| /+----------------+---+----+-----------------+-------------
| / |
| / O----------------+---+----+-----------------+--------------
| / |IIC Controller 1| | | |
| / +----------------+---+----+----------+------+----------+----
| / | | | | | | |
`'/''''''|''''''''''''''''|''' | | | |
/ | | | | | |
O--------'--+ | '----------' O----------'
|i2c_adapter| | |Device 1.0| |Device 1.1|
+-----------+ | +----------. +----------+
| | |
O-------+-----+ | |
|i2c_algorithm| | |
+-------------+ | |
O-'------'-+
|i2c_client|
+----------+
SoC 上挂了 N 个 IIC 的控制器,每个控制器上,挂载若干个设备
1、i2c_adatper:描述一个实际的 IIC 物理硬件
2、i2c_algorithm:函数指针集,钩子函数,用于描述特定 SoC 硬件的 IIC 模块产生通信波形的方法
3、i2c_client:描述一个挂接到 IIC 总线上的具体物理设备
4、i2c_driver:用于描述一个 IIC 设备的驱动
初始化流程
i2c_init()
i2c_bus_type注册
i2c_adapter_compact_class
注册dummy_driver
i2c_register_adapter()
i2c_adapter平台驱动的注册
i2c_adapter设备注册
i2c_board_info注册
i2c_register_driver()
2、软件层的主要数据结构
2.1 i2c_adapter
struct i2c_adapter {
struct module *owner; // 所属模块
unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; // 总线通信方法结构体指针
void *algo_data; // algorithm数据
/* data fields that are valid for all devices */
struct rt_mutex bus_lock; //控制并发访问的自旋锁
int timeout; /* in jiffies */
int retries; // 重试次数
struct device dev; // 适配器设备
int nr;
char name[48]; // 适配器名称
struct completion dev_released;
struct mutex userspace_clients_lock;
struct list_head userspace_clients; // client 链表头
};
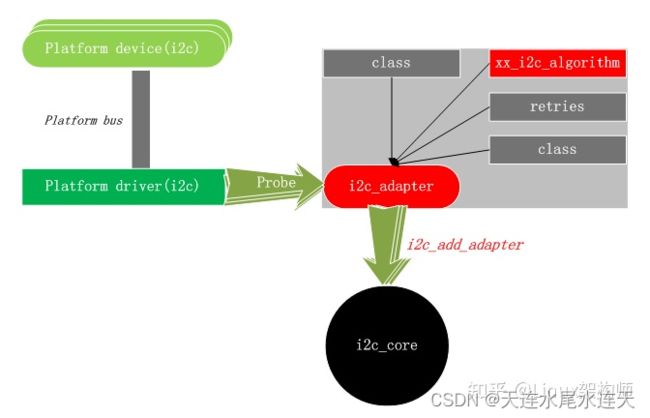
对于 Soc 来说,有多个 IIC 控制器,所以 i2c_adapter 也不止一个,他们都需要在系统上电时,进行初始化,所以通过 platform 总线连接这些 i2c_adapter 结构,并在上电时定义多个 platform device 设备和 platform_driver,通过 platform_bus 连接起来,进行多次 probe 调用,进行初始化。
比如:
static struct platform_device_id s3c24xx_driver_ids[] = {
{
.name = "s3c2410-i2c",
.driver_data = TYPE_S3C2410,
}, {
.name = "s3c2440-i2c",
.driver_data = TYPE_S3C2440,
}, {
.name = "s3c2440-hdmiphy-i2c",
.driver_data = TYPE_S3C2440_HDMIPHY,
}, { },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(platform, s3c24xx_driver_ids);
static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_i2c_driver = {
.probe = s3c24xx_i2c_probe,
.remove = s3c24xx_i2c_remove,
.id_table = s3c24xx_driver_ids,
.driver = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "s3c-i2c",
.pm = S3C24XX_DEV_PM_OPS,
},
};
static int __init i2c_adap_s3c_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&s3c24xx_i2c_driver);
}
subsys_initcall(i2c_adap_s3c_init);
这款 Soc 有 3 个 IIC 硬件控制器,所以 s3c24xx_i2c_probe 会被匹配 3 次,也就是调用 3 次。
void __init exynos4_map_io(void)
{
....
/* The I2C bus controllers are directly compatible with s3c2440 */
s3c_i2c0_setname("s3c2440-i2c");
s3c_i2c1_setname("s3c2440-i2c");
s3c_i2c2_setname("s3c2440-i2c");
....
}
由于 i2c_adapter 结构和具体的硬件相关,所以在 xxx_i2c_probe 函数中对 i2c_adapter 实例化
static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3c24xx_i2c *i2c;
struct s3c2410_platform_i2c *pdata;
struct resource *res;
int ret;
....
i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE;
i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm;
i2c->adap.retries = 2;
i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON | I2C_CLASS_SPD;
i2c->tx_setup = 50;
spin_lock_init(&i2c->lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&i2c->wait);
....
ret = request_irq(i2c->irq, s3c24xx_i2c_irq, IRQF_DISABLED,
dev_name(&pdev->dev), i2c);
....
i2c->adap.nr = pdata->bus_num;
ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(&i2c->adap);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to add bus to i2c core\n");
goto err_cpufreq;
}
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, i2c);
....
return ret;
}
通常在 probe 中申请 IRQ 资源,获取寄存器资源,初始化一个 i2c_adapter 结构,并将它注册到 i2c_core
2.2 i2c_algorithm
i2c_algorithm 表示和硬件对接的一组 IIC 控制器的操作集合
struct i2c_algorithm {
/* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer
to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set
smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated
using common I2C messages */
/* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully
processed, or a negative value on error */
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,
int num);
int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
/* To determine what the adapter supports */
u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *);
};
master_xfer 函数用于数据传送和读取,functionality 用来获取 IIC 控制器支持情况,根据 xxx_i2c_probe 分析可知,在调用 xxx_i2c_probe 时,已将其操作集 i2c_algorithm 挂接至 i2c_adapter 结构,一并注册到 i2c_core。
/* i2c bus registration info */
static const struct i2c_algorithm s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm = {
.master_xfer = s3c24xx_i2c_xfer,
.functionality = s3c24xx_i2c_func,
};
static int s3c24xx_i2c_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
...
i2c->adap.owner = THIS_MODULE;
i2c->adap.algo = &s3c24xx_i2c_algorithm;
i2c->adap.retries = 2;
i2c->adap.class = I2C_CLASS_HWMON | I2C_CLASS_SPD;
i2c->tx_setup = 50;
...
return ret;
}
2.3 i2c_bus_type
现在 i2c_adapter 已经注册到 i2c_core,接下来重点分析 i2c_core,根据 Linux 的设备、驱动、总线的思想,i2c 设备应该通过 Linux 的 i2c 总线(bus)挂接上去,并和其固定的 driver 进行匹配,所以在 i2c_core 初始化的时候,必须先注册 i2c bus,在 i2c-core.c 中:
static int __init i2c_init(void)
{
int retval;
retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type);
if (retval)
return retval;
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
i2c_adapter_compat_class = class_compat_register("i2c-adapter");
if (!i2c_adapter_compat_class) {
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto bus_err;
}
#endif
retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver);
if (retval)
goto class_err;
return 0;
class_err:
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class);
bus_err:
#endif
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
return retval;
}
static void __exit i2c_exit(void)
{
i2c_del_driver(&dummy_driver);
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
class_compat_unregister(i2c_adapter_compat_class);
#endif
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
}
/* We must initialize early, because some subsystems register i2c drivers
* in subsys_initcall() code, but are linked (and initialized) before i2c.
*/
postcore_initcall(i2c_init);
module_exit(i2c_exit);
这里建立起了 i2c bus:
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.match = i2c_device_match,
.probe = i2c_device_probe,
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
.pm = &i2c_device_pm_ops,
};
i2c bus 定义 match 的规则:
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
if (!client)
return 0;
/* Attempt an OF style match */
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);
/* match on an id table if there is one */
if (driver->id_table)
return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;
return 0;
}
通过 match 它的 id_table 进行匹配,至此,i2c_core 建立起 i2c bus,接下来挂接 device 和 driver
2.4 i2c_client 和 i2c_driver
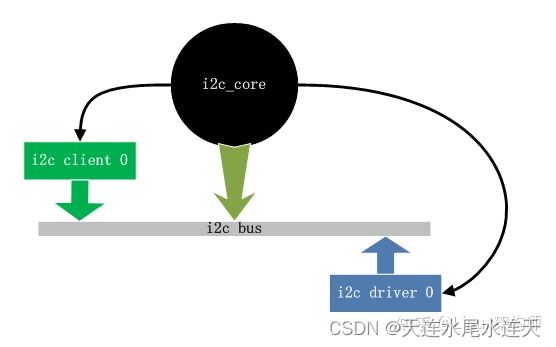
目前, i2c_adapter ,i2c_algorithm (操作硬件函数),i2c bus(软件抽象的)已准备完毕,接下来添加 i2c 设备进总线,i2c 设备使用 i2c_client 结构来描述。
struct i2c_client {
unsigned int flags; /* 标志 */
unsigned short addr; /* 低 7 位为芯片地址 */
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; /* 设备名称 */
struct i2c_adapter *adapter; /*依附的 i2c_adapter*/
struct i2c_driver *driver; /*依附的 i2c_driver */
int irq;
struct device dev; /* 设备结构体 */
struct list_head detected; /* 链表头 */
};
四种方式
1、i2c_new_device
2、i2c_register_board_info
3、i2c_scan_static_board_info
4、i2c_detect_address
struct i2c_board_info {
char type[I2C_NAME_SIZE];
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short addr;
void *platform_data;
struct dev_archdata *archdata;
struct device_node *of_node;
int irq;
}
一个 IIC 外设的驱动用一个 i2c_driver 结构描述
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;
/* Notifies the driver that a new bus has appeared or is about to be
* removed. You should avoid using this, it will be removed in a
* near future.
*/
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated; /*依附 i2c_adapter 函数指针 */
int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *) __deprecated;
/* Standard driver model interfaces */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
/* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);
int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);
/* Alert callback, for example for the SMBus alert protocol.
* The format and meaning of the data value depends on the protocol.
* For the SMBus alert protocol, there is a single bit of data passed
* as the alert response's low bit ("event flag").
*/
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);
/* a ioctl like command that can be used to perform specific functions
* with the device.
*/
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;
/* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);
const unsigned short *address_list;
struct list_head clients;
};
具体的设备需要实现对应的 i2c_driver,并注册到 i2c_core,比如 EEPROM 设备,在 drivers/misc/eeprom.c中
static const struct i2c_device_id eeprom_id[] = {
{ "eeprom", 0 },
{ }
};
static struct i2c_driver eeprom_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "eeprom",
},
.probe = eeprom_probe,
.remove = eeprom_remove,
.id_table = eeprom_id,
.class = I2C_CLASS_DDC | I2C_CLASS_SPD,
.detect = eeprom_detect,
.address_list = normal_i2c,
};
static int __init eeprom_init(void)
{
return i2c_add_driver(&eeprom_driver);
}
通过 i2c_add_driver 函数注册到 i2c_core
+--------+
...............|i2c_core|..............
| +---+----+ |
| | |
| | |
| | |
+------'-----+ | +----'-------+
|i2c_client_0| | |i2c_driver_0|
+-------.----+ | +---+--------+
| | |
.....|.................:.................:............
| +-------+ |
| |i2c_bus| |
| +-------+ |
'`''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''''
2.5 i2c_msg
现在开始传输数据,内核使用 i2c_msg 来描述一个 i2c 数据的构成
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* slave address */
__u16 flags;
#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */
#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */
__u16 len; /* msg length */
__u8 *buf; /* pointer to msg data */
};
数据传输,主要是指定设备地址,数据长度,以及数据 buffer,flags 标记了传输的一些属性。
当数据准备OK,即填充好 i2c_msg 后,可以调用 i2c 核心层提供的函数进行数据的收发。
1、i2c_transfer:调用 adap->algo->master_xfer 进行数据收发
2、i2c_master_send:包装了 i2c_transfer 调用,填充 i2c_msg 进行数据发送一次
3、i2c_master_recv:包装了 i2c_transfer 调用,填充 i2c_msg 进行数据接收一次
2.6 i2c_dev
需要给驱动层留一个访问 i2c 的通道,所以有了 i2c_dev,i2c_core 只是做了一些管理和提供接口的工作,具体的支撑用户层的访问由 i2c_dev 负责,在 i2c_dev.c 中,首先进行 i2c-dev 的分配和注册
static int __init i2c_dev_init(void)
{
int res;
printk(KERN_INFO "i2c /dev entries driver\n");
res = register_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c", &i2cdev_fops);
if (res)
goto out;
i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev");
if (IS_ERR(i2c_dev_class)) {
res = PTR_ERR(i2c_dev_class);
goto out_unreg_chrdev;
}
/* Keep track of adapters which will be added or removed later */
res = bus_register_notifier(&i2c_bus_type, &i2cdev_notifier);
if (res)
goto out_unreg_class;
/* Bind to already existing adapters right away */
i2c_for_each_dev(NULL, i2cdev_attach_adapter);
return 0;
out_unreg_class:
class_destroy(i2c_dev_class);
out_unreg_chrdev:
unregister_chrdev(I2C_MAJOR, "i2c");
out:
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: Driver Initialisation failed\n", __FILE__);
return res;
}
同时提供了用户层的操作集合 i2cdev_fops
static const struct file_operations i2cdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = i2cdev_read,
.write = i2cdev_write,
.unlocked_ioctl = i2cdev_ioctl,
.open = i2cdev_open,
.release = i2cdev_release,
};
用户层调用的 open、read、write、ioclt,都会先走到这里,看一个 i2cdev_read
static ssize_t i2cdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *offset)
{
char *tmp;
int ret;
struct i2c_client *client = file->private_data;
if (count > 8192)
count = 8192;
tmp = kmalloc(count, GFP_KERNEL);
if (tmp == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
pr_debug("i2c-dev: i2c-%d reading %zu bytes.\n",
iminor(file->f_path.dentry->d_inode), count);
ret = i2c_master_recv(client, tmp, count);
if (ret >= 0)
ret = copy_to_user(buf, tmp, count) ? -EFAULT : ret;
kfree(tmp);
return ret;
}
调用到 i2c 核心层的i2c_master_recv函数后,将结果通过 copy_to_user 返回给用户层
2.7 i2c_dev_init
static int __init i2c_dev_init(void)
{
int res;
printk(KERN_INFO "i2c /dev entries driver\n");
res = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, 0), I2C_MINORS, "i2c");
if (res)
goto out;
i2c_dev_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "i2c-dev");
if (IS_ERR(i2c_dev_class)) {
res = PTR_ERR(i2c_dev_class);
goto out_unreg_chrdev;
}
i2c_dev_class->dev_groups = i2c_groups;
/* Keep track of adapters which will be added or removed later */
res = bus_register_notifier(&i2c_bus_type, &i2cdev_notifier);
if (res)
goto out_unreg_class;
/* Bind to already existing adapters right away */
i2c_for_each_dev(NULL, i2cdev_attach_adapter);
return 0;
out_unreg_class:
class_destroy(i2c_dev_class);
out_unreg_chrdev:
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(I2C_MAJOR, 0), I2C_MINORS);
out:
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: Driver Initialisation failed\n", __FILE__);
return res;
}
2.8 i2c_new_device
struct i2c_client *
i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)
{
struct i2c_client *client;
int status;
client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client)
return NULL;
client->adapter = adap;
client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;
client->flags = info->flags;
client->addr = info->addr;
client->init_irq = info->irq;
if (!client->init_irq)
client->init_irq = i2c_dev_irq_from_resources(info->resources,
info->num_resources);
client->irq = client->init_irq;
strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));
status = i2c_check_addr_validity(client->addr, client->flags);
if (status) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "Invalid %d-bit I2C address 0x%02hx\n",
client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN ? 10 : 7, client->addr);
goto out_err_silent;
}
/* Check for address business */
status = i2c_check_addr_busy(adap, i2c_encode_flags_to_addr(client));
if (status)
goto out_err;
client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;
client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type;
client->dev.of_node = of_node_get(info->of_node);
client->dev.fwnode = info->fwnode;
i2c_dev_set_name(adap, client, info);
if (info->properties) {
status = device_add_properties(&client->dev, info->properties);
if (status) {
dev_err(&adap->dev,
"Failed to add properties to client %s: %d\n",
client->name, status);
goto out_err_put_of_node;
}
}
status = device_register(&client->dev);
if (status)
goto out_free_props;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "client [%s] registered with bus id %s\n",
client->name, dev_name(&client->dev));
return client;
out_free_props:
if (info->properties)
device_remove_properties(&client->dev);
out_err_put_of_node:
of_node_put(info->of_node);
out_err:
dev_err(&adap->dev,
"Failed to register i2c client %s at 0x%02x (%d)\n",
client->name, client->addr, status);
out_err_silent:
kfree(client);
return NULL;
}
2.9 of_i2c_register_devices
void of_i2c_register_devices(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
struct device_node *bus, *node;
struct i2c_client *client;
/* Only register child devices if the adapter has a node pointer set */
if (!adap->dev.of_node)
return;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "of_i2c: walking child nodes\n");
bus = of_get_child_by_name(adap->dev.of_node, "i2c-bus");
if (!bus)
bus = of_node_get(adap->dev.of_node);
for_each_available_child_of_node(bus, node) {
if (of_node_test_and_set_flag(node, OF_POPULATED))
continue;
client = of_i2c_register_device(adap, node);
if (IS_ERR(client)) {
dev_err(&adap->dev,
"Failed to create I2C device for %pOF\n",
node);
of_node_clear_flag(node, OF_POPULATED);
}
}
of_node_put(bus);
}
2.10 i2c_register_adapter
static int i2c_register_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
int res = -EINVAL;
/* Can't register until after driver model init */
if (WARN_ON(!is_registered)) {
res = -EAGAIN;
goto out_list;
}
/* Sanity checks */
if (WARN(!adap->name[0], "i2c adapter has no name"))
goto out_list;
if (!adap->algo) {
pr_err("adapter '%s': no algo supplied!\n", adap->name);
goto out_list;
}
if (!adap->lock_ops)
adap->lock_ops = &i2c_adapter_lock_ops;
rt_mutex_init(&adap->bus_lock);
rt_mutex_init(&adap->mux_lock);
mutex_init(&adap->userspace_clients_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&adap->userspace_clients);
/* Set default timeout to 1 second if not already set */
if (adap->timeout == 0)
adap->timeout = HZ;
/* register soft irqs for Host Notify */
res = i2c_setup_host_notify_irq_domain(adap);
if (res) {
pr_err("adapter '%s': can't create Host Notify IRQs (%d)\n",
adap->name, res);
goto out_list;
}
dev_set_name(&adap->dev, "i2c-%d", adap->nr);
adap->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
adap->dev.type = &i2c_adapter_type;
res = device_register(&adap->dev);
if (res) {
pr_err("adapter '%s': can't register device (%d)\n", adap->name, res);
goto out_list;
}
res = of_i2c_setup_smbus_alert(adap);
if (res)
goto out_reg;
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "adapter [%s] registered\n", adap->name);
pm_runtime_no_callbacks(&adap->dev);
pm_suspend_ignore_children(&adap->dev, true);
pm_runtime_enable(&adap->dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_I2C_COMPAT
res = class_compat_create_link(i2c_adapter_compat_class, &adap->dev,
adap->dev.parent);
if (res)
dev_warn(&adap->dev,
"Failed to create compatibility class link\n");
#endif
i2c_init_recovery(adap);
/* create pre-declared device nodes */
of_i2c_register_devices(adap);
i2c_acpi_install_space_handler(adap);
i2c_acpi_register_devices(adap);
if (adap->nr < __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)
i2c_scan_static_board_info(adap);
/* Notify drivers */
mutex_lock(&core_lock);
bus_for_each_drv(&i2c_bus_type, NULL, adap, __process_new_adapter);
mutex_unlock(&core_lock);
return 0;
out_reg:
init_completion(&adap->dev_released);
device_unregister(&adap->dev);
wait_for_completion(&adap->dev_released);
out_list:
mutex_lock(&core_lock);
idr_remove(&i2c_adapter_idr, adap->nr);
mutex_unlock(&core_lock);
return res;
}
2.11 i2c_register_driver
int i2c_register_driver(struct module *owner, struct i2c_driver *driver)
{
int res;
/* Can't register until after driver model init */
if (WARN_ON(!is_registered))
return -EAGAIN;
/* add the driver to the list of i2c drivers in the driver core */
driver->driver.owner = owner;
driver->driver.bus = &i2c_bus_type;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&driver->clients);
/* When registration returns, the driver core
* will have called probe() for all matching-but-unbound devices.
*/
res = driver_register(&driver->driver);
if (res)
return res;
pr_debug("driver [%s] registered\n", driver->driver.name);
/* Walk the adapters that are already present */
i2c_for_each_dev(driver, __process_new_driver);
return 0;
}
2.12 i2c_transfer
int i2c_transfer(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
int ret;
if (adap->algo->master_xfer) {
#ifdef DEBUG
for (ret = 0; ret < num; ret++) {
dev_dbg(&adap->dev,
"master_xfer[%d] %c, addr=0x%02x, len=%d%s\n",
ret, (msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RD) ? 'R' : 'W',
msgs[ret].addr, msgs[ret].len,
(msgs[ret].flags & I2C_M_RECV_LEN) ? "+" : "");
}
#endif
if (in_atomic() || irqs_disabled()) {
ret = i2c_trylock_bus(adap, I2C_LOCK_SEGMENT);
if (!ret)
/* I2C activity is ongoing. */
return -EAGAIN;
} else {
i2c_lock_bus(adap, I2C_LOCK_SEGMENT);
}
ret = __i2c_transfer(adap, msgs, num);
i2c_unlock_bus(adap, I2C_LOCK_SEGMENT);
return ret;
} else {
dev_dbg(&adap->dev, "I2C level transfers not supported\n");
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
}
}
2.13 i2c_scan_static_board_info
static void i2c_scan_static_board_info(struct i2c_adapter *adapter)
{
struct i2c_devinfo *devinfo;
down_read(&__i2c_board_lock);
list_for_each_entry(devinfo, &__i2c_board_list, list) {
if (devinfo->busnum == adapter->nr
&& !i2c_new_device(adapter,
&devinfo->board_info))
dev_err(&adapter->dev,
"Can't create device at 0x%02x\n",
devinfo->board_info.addr);
}
up_read(&__i2c_board_lock);
}
3 小结
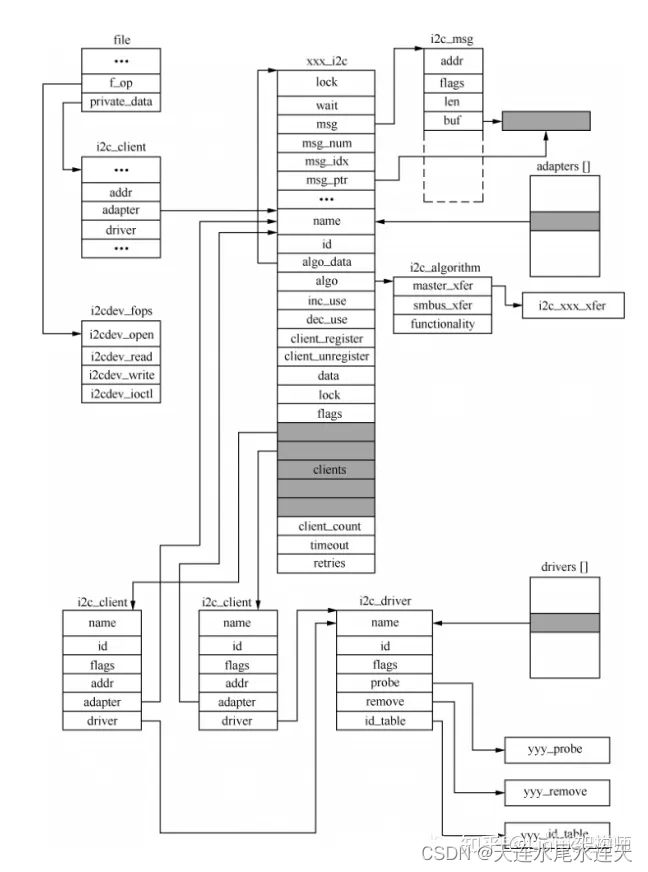
数据结构之间的关系
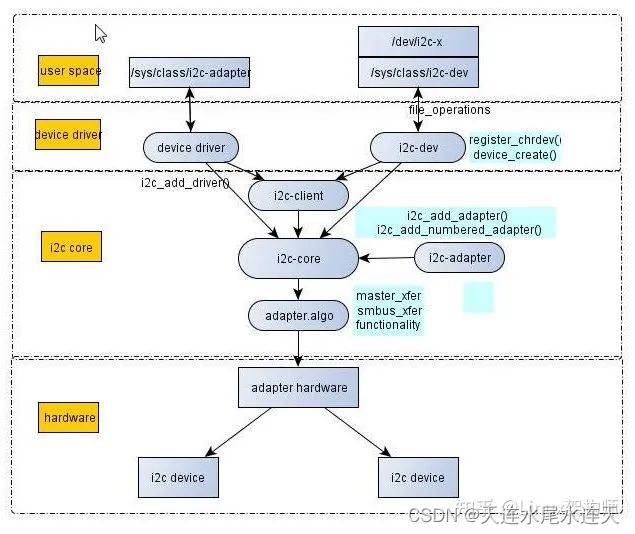
结构之间的注册和初始化
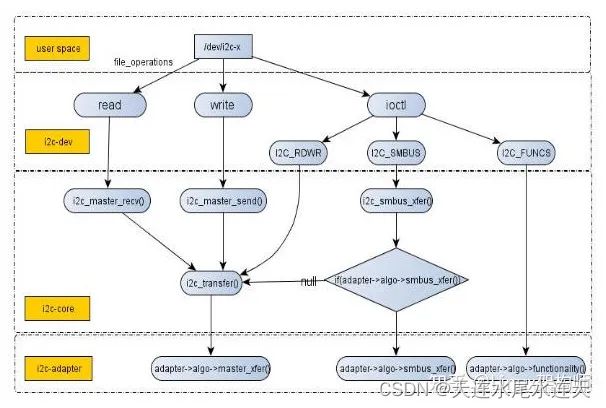
用户层调用的流程

参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/455521103
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42017846/article/details/128163421