目标检测学习笔记
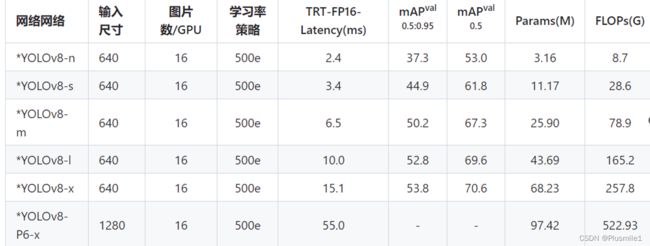
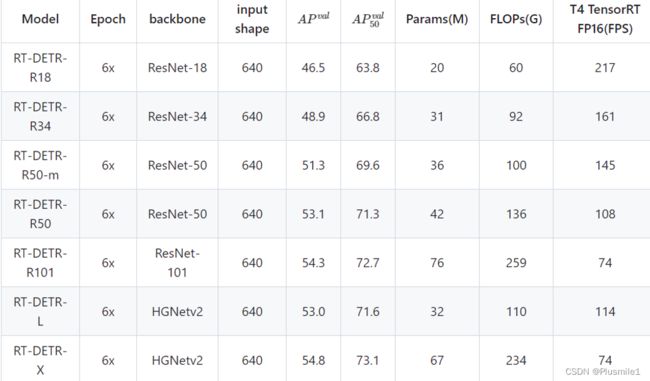
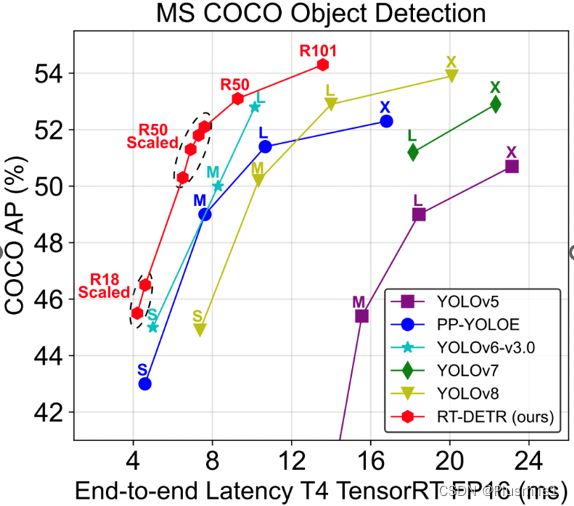
1.rt-detr与YOLOv8的比较
- 数据来源:rtdetr、yolov8
2.COCO数据集格式与转换
- COCO数据集标注详解
- Object Instance这种格式的文件从头至尾按照顺序分为以下段落:
# 整体
{
"images": [image],
"annotations": [annotation],
"categories": [category]
}
# 标注 annotation
{
"id": int,
"image_id": int, #图片id
"category_id": int, # 类别id,对应COCO 81个类中的一个
"segmentation": RLE or [polygon], # 目标的分割区域
"area": float, # 标注区域面积
"bbox": [x,y,width,height], #图片中目标的边框 ;注意这里给的是左上角坐标及宽度、高度,有时需要转化为左上角、右下角坐标
"iscrowd": 0 or 1, # 一个目标(0)还是多个目标(1)
}
# 类别 categories
{
"id": int,
"name": str, # 类别名(子类名)
"supercategory": str, # 父类名
}
# 图像 images
{
"file_name": "000000397133.jpg",
"height": 427,
"width": 640,
"id": 397133
}
TXT转COCO
- 参考https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/341801502
- 需要注意的是, yolo的数据格式为 (x_center, y_center, w, h); 而coco里面的bbox格式为(x_left, y_top, w, h) 。这是不一样的!
代码说明:
将yolo格式数据集修改成coco格式。$ROOT_PATH是根目录,需要按下面的形式组织数据:
└── $ROOT_PATH
├── classes.txt
├── images
└──labels
classes.txt 是类的声明,一行一类。
images 目录包含所有图片 (目前支持png和jpg格式数据)
labels 目录包含所有标签(与图片同名的txt格式数据)
配置好文件夹后,执行:python yolo2coco.py --root_dir $ROOT_PATH ,然后就能看见生成的 annotations 文件夹。
参数说明
--root_path 输入根目录 R O O T P A T H 的位置。 ‘ − − s a v e p a t h ‘ 如果不进行数据集划分,可利用此参数指定输出文件的名字,默认保存为 t r a i n . j s o n ‘ − − r a n d o m s p l i t ‘ 随机划分参数,若指定 ‘ − − r a n d o m s p l i t ‘ 参数,则输出在 a n n o t a t i o n s 文件夹下包含 t r a i n . j s o n v a l . j s o n t e s t . j s o n (默认随机划分成 8 : 1 : 1 ) ‘ − − s p l i t b y f i l e ‘ 自定义数据集划分,若指定 ‘ − − s p l i t b y f i l e ‘ 参数,则输出在 a n n o t a t i o n s 文件夹 t r a i n . j s o n v a l . j s o n t e s t . j s o n 。需要在 ROOT_PATH的位置。 `--save_path` 如果不进行数据集划分,可利用此参数指定输出文件的名字,默认保存为train.json `--random_split` 随机划分参数,若指定`--random_split`参数,则输出在annotations文件夹下包含 train.jsonval.jsontest.json (默认随机划分成8:1:1) `--split_by_file` 自定义数据集划分,若指定`--split_by_file`参数,则输出在annotations文件夹 train.jsonval.jsontest.json。需要在 ROOTPATH的位置。‘−−savepath‘如果不进行数据集划分,可利用此参数指定输出文件的名字,默认保存为train.json‘−−randomsplit‘随机划分参数,若指定‘−−randomsplit‘参数,则输出在annotations文件夹下包含train.jsonval.jsontest.json(默认随机划分成8:1:1)‘−−splitbyfile‘自定义数据集划分,若指定‘−−splitbyfile‘参数,则输出在annotations文件夹train.jsonval.jsontest.json。需要在ROOT_PATH文件下有 ./train.txt ./val.txt ./test.txt ,可以这3个文件来定义训练集、验证集、测试集。注意, 这里里面填写的应是图片文件名字,而不是图片的绝对地址。(在line 43也自行可以修改一下读取方式,为了方便起见,不推荐把图片放在不同位置)
VOC转COCO
- VOC数据集所必须的文件内容如下所示,数据集根目录需有VOCdevkit/VOC2007或VOCdevkit/VOC2012文件夹,该文件夹中需有Annotations,JPEGImages和ImageSets/Main三个子目录,Annotations存放图片标注的xml文件,JPEGImages存放数据集图片,ImageSets/Main存放训练trainval.txt和测试test.txt列表。
VOCdevkit
├──VOC2007(或VOC2012)
│ ├── Annotations
│ ├── xxx.xml
│ ├── JPEGImages
│ ├── xxx.jpg
│ ├── ImageSets
│ ├── Main
│ ├── trainval.txt
│ ├── test.txt
3.paddle 训练、可视化等命令
学习率调整规则
- PP-YOLOE模型训练过程中使用8 GPUs进行混合精度训练,如果GPU卡数或者batch size发生了改变,你需要按照公式 lrnew = lrdefault * (batch_sizenew * GPU_numbernew) / (batch_sizedefault * GPU_numberdefault) 调整学习率
对于cuda719错误/gather.cu.h:68错误
- 下面的连接完美解决了这个问题,注意到该freeze_norm选项仅针对 ResNet50 打开(对于 ResNet34 和 ResNet18 已关闭),认为这可能有助于防止值变得非常大,因此我尝试通过在
configs/rtdetr/_base_/rtdetr_r50vd.yaml添加freeze_norm: false来关闭它。还通过将行freeze_at: 0修改为freeze_at: -1来关闭参数冻结选项. - https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleDetection/issues/8402
coco128
- https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/ultralytics/coco128
- 只设置训练集,使其训练到过拟合,并测试推理,在这个过程中学习paddle的操作和目标检测的整体流程
- 下载coco128数据集,并从txt转为coco,class.txt设置为coco正常的80个分类,使用上面的代码时时注意对两个词的分类加下划线
[‘person’, ‘bicycle’, ‘car’, ‘motorcycle’, ‘airplane’, ‘bus’, ‘train’, ‘truck’, ‘boat’, ‘traffic light’, ‘fire hydrant’, ‘stop sign’, ‘parking meter’, ‘bench’, ‘bird’, ‘cat’, ‘dog’, ‘horse’, ‘sheep’, ‘cow’, ‘elephant’, ‘bear’, ‘zebra’, ‘giraffe’, ‘backpack’, ‘umbrella’, ‘handbag’, ‘tie’, ‘suitcase’, ‘frisbee’, ‘skis’, ‘snowboard’, ‘sports ball’, ‘kite’, ‘baseball bat’, ‘baseball glove’, ‘skateboard’, ‘surfboard’, ‘tennis racket’, ‘bottle’, ‘wine glass’, ‘cup’, ‘fork’, ‘knife’, ‘spoon’, ‘bowl’, ‘banana’, ‘apple’, ‘sandwich’, ‘orange’, ‘broccoli’, ‘carrot’, ‘hot dog’, ‘pizza’, ‘donut’, ‘cake’, ‘chair’, ‘couch’, ‘potted plant’, ‘bed’, ‘dining table’, ‘toilet’, ‘tv’, ‘laptop’, ‘mouse’, ‘remote’, ‘keyboard’, ‘cell phone’, ‘microwave’, ‘oven’, ‘toaster’, ‘sink’, ‘refrigerator’, ‘book’, ‘clock’, ‘vase’, ‘scissors’, ‘teddy bear’, ‘hair drier’, ‘toothbrush’]
- 修改rtdetr_r18vd_6x_coco.yml,修改base中的dataset为coco128的yml,optimizer_6x中epoch改为5000,学习率改为0.000025,并使用官方预训练权重
- 复制创建coco128_detection.yml,确保类别为80,修改image_dir、anno_path和dataset_dir
- 训练命令
cd Desktop/ppdet/PaddleDetection/
conda activate re-detr
# --use_vdl=true表示使用可视化
python tools/train.py -c configs/rtdetr/rtdetr_r18vd_6x_coco.yml --use_vdl=true --vdl_log_dir=vdl_dir/scalar
# 如需断训重续,使用-r
python tools/train.py -c configs/rtdetr/rtdetr_r18vd_6x_coco.yml --use_vdl=true --vdl_log_dir=vdl_dir/scalar -r output/model_final
# 折线图可视化,网页打开http://localhost:8040/即可
visualdl --logdir vdl_dir/scalar/
-
训练loss图:5000轮
-
尝试推理:
python tools/infer.py -c configs/rtdetr/rtdetr_r18vd_6x_coco.yml -o weights=output/model_final --infer_dir=dataset/coco128/train2017 -
尝试评估mAP等参数
python tools/eval.py -c configs/rtdetr/rtdetr_r18vd_6x_coco.yml -o weights=output/model_final -
5000轮训练后
制作自己的数据集
-
拍摄RGB图和深度图 https://github.com/Incalos/Image-Capture-With-RealSense
-
拍摄方案:8:1:1,四种不同尺寸,两大两小,大的每种三个,小的每种五个,单,两,三,四组合一下共575张
-
形状相同,尺寸不同的两个物体怎么分类:好像没啥好办法,尺度不变,算面积;深度相机获取点云,说到底要有长宽的信息;先仿个标志物或者增强中不使用缩放试试,又看了眼好像不用,肉眼可分辨
-
先标注然后再进行增强,增强好像可以直接用paddel的
-
先进行检测的标注,之后再进行抓取标注
-
在