深度学习实战(2)用Pytorch搭建双向LSTM
用Pytorch搭建双向LSTM
应最近的课程实验要求,要做LSTM和GRU的实验效果对比。LSTM的使用和GRU十分相似,欢迎参考我的另外一篇介绍搭建双向GRU的Blog:https://blog.csdn.net/icestorm_rain/article/details/108395515
参考Pytorch介绍LSTM的官方文档:
其中其定义层时的参数声明方法与GRU完全一致:

所以,我定义LSTM使用以下代码:
torch.nn.LSTM(out_channels, hidden_size, n_layers, batch_first=True,bidirectional=self.bidirectional)
最关键的地方来了,那就是LSTM在做forward计算时要求输入的参数列表和GRU是不一样的!
在官方文档中GRU的输入格式如下:
它只需要 Input以及所有GRU单元的初始隐藏层状态
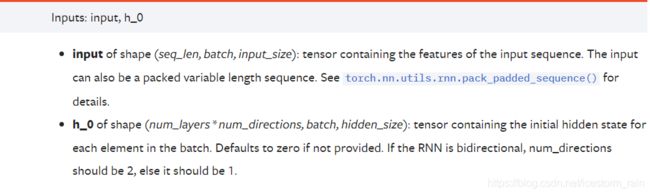
但是对于LSTM来说,还需要所有cell的初始状态,与初始隐藏层状态构成一个二元组进行输入,这是因为LSTM这个神经网络结构的参数是比GRU要多的,具体的可以去学习下两者架构的区别,在此就不做具体介绍了。LSTM的输入格式如下:

所以,我们来看看GRU与LSTM做forward时的代码区别:
# LSTM
output, (hidden, cell_state) = self.lstm(pooled,(hidden,hidden))
# GRU
output, hidden = self.gru(word_inputs, hidden)
其实区别就是在输入输出LSTM比GRU多了一个cell state。
总结到此结束,给个完整的神经网络代码供大家参考,这是一个CNN与LSTM结合的神经网络。
class HomorNetv3(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim,hidden_size, out_size, n_layers=1, batch_size=1,window_size=3,out_channels=200,bidirectional=True):
super(HomorNetv3, self).__init__()
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.n_layers = n_layers
self.out_size = out_size
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.bidirectional = bidirectional
# convolute the word_vectors first
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=out_channels,kernel_size=(window_size, input_dim))
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=out_channels,kernel_size=(20, input_dim))
# 这里指定了 BATCH FIRST
# then put it into GRU layers
self.lstm = torch.nn.LSTM(out_channels, hidden_size, n_layers, batch_first=True,bidirectional=self.bidirectional)
# 加了一个线性层,全连接
if self.bidirectional:
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size*2, 200)
else:
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, 200)
# output_layer
self.fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(200, out_size)
def forward(self, word_inputs, hidden):
# hidden 就是上下文输出,output 就是 RNN 输出
#print("word_inputs",word_inputs.shape)
embedded = word_inputs.unsqueeze(1)
feature_maps1 = self.conv(embedded)
feature_maps2 = self.conv2(embedded)
feature_maps = torch.cat((feature_maps1,feature_maps2),2)
pooled = self.pool_normalize_function(feature_maps)
#print("pooled",pooled)
output, (hidden, cell_state) = self.lstm(pooled,(hidden,hidden))
#print("gruoutput",output.shape)
output = self.fc1(output)
output = self.fc2(output)
# 仅仅获取 time seq 维度中的最后一个向量
# the last of time_seq
output = output[:,-1,:]
#print("beforesoftmax",output.shape)
output = F.softmax(output,dim=1)
print("output",output)
return output, hidden
def init_hidden(self):
# 这个函数写在这里,有一定迷惑性,这个不是模型的一部分,是每次第一个向量没有上下文,在这里捞一个上下文,仅此而已。
if self.bidirectional:
hidden = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(2*self.n_layers, self.batch_size, self.hidden_size, device='cuda'))
else:
hidden = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(self.n_layers, self.batch_size, self.hidden_size, device='cuda'))
return hidden
def pool_normalize_function(self,feature_maps):
''' pool the vector '''
feature_maps = feature_maps.squeeze(3)
# Apply ReLU
feature_maps = F.relu(feature_maps)
# Apply the max pooling layer
pooled = F.max_pool1d(feature_maps, 2)
pooled = pooled.permute(0,2,1) # 转置矩阵
normalized = F.normalize(pooled,p=2,dim=2)
#normalized = normalized.unsqueeze(2)
return normalized