Spring Boot启动源码分析
一,前言
版本:spring-boot-starter-parent版本为2.3.0
二,源码分析
- 跟踪run方法
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* @param primarySource 启动类的class
* @param args 启动参数
* @return 可配置的应用程序上下文
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run( Class<?> primarySource, String... args ){
//调用另一个重载方法
return run( new Class<?>[]{ primarySource }, args );
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run( Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args ){
//构造一个SpringApplication实例,然后执行run方法
return new SpringApplication( primarySources ).run( args );
}
这里分两步debug:
- new SpringApplication( primarySources )
- 执行run()方法
三、new SpringApplication构建Sring应用实例
/**
* 创建一个新的SpringApplication实例,并从指定的来源加载bean的信息
*
* @param primarySources 主要bean来源
*/
public SpringApplication( Class<?>... primarySources ){
//空的资源加载器
this( null, primarySources );
}
/**
* 主要bean来源集合
*/
private Set<Class<?>> primarySources;
/**
* 应用程序初始化器集合
*/
private List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers;
/**
* 应用程序监听器集合
*/
private List<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
/**
* 主应用程序类
*/
private Class<?> mainApplicationClass;
/**
* 应用程序类型
*/
private WebApplicationType webApplicationType;
/**
* 创建一个新的SpringApplication实例,并从指定的来源加载bean的信息
*
* @param resourceLoader 要使用的资源加载器
* @param primarySources 主要bean来源
*/
@SuppressWarnings( { "unchecked", "rawtypes" } )
public SpringApplication( ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources ){
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
//必须指定主源
Assert.notNull( primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null" );
//将主要来源设置到一个集合里面,默认来源就只有一个启动类的class
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>( Arrays.asList( primarySources ) );
//设置Web应用程序类型,可能是SERVLET程序,也可能是REACTIVE响应式程序,还有可能是NONE,即非web应用程序
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//设置ApplicationContextInitializer,应用程序初始化器。通过SpringFactoriesLoader从META-INF/spring.factories文件中获取ApplicationContextInitializer 的所有实现类,ApplicationContextInitializer 是在spring容器刷新之前执行的一个回调函数。它的作用是向springboot容器中注册属性,比如注册一些属性资源和激活文件配置到Environment的环境变量中去
setInitializers( ( Collection )getSpringFactoriesInstances( ApplicationContextInitializer.class ) );
//设置ApplicationListener,应用程序监听器。从META-INF/spring.factories文件中获取,用于监听和响应应用程序中发生的事件。当特定类型的事件发生时,实现了 ApplicationListener 接口的类可以被通知,并执行相应的逻辑操作
setListeners( ( Collection )getSpringFactoriesInstances( ApplicationListener.class ) );
//设置主应用程序类,一般就是Spring boot项目的启动类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
- deduceFromClasspath推断应用程序类型
该方法根据是否存在指定路径的类来推断应用程序类型。有NONE、REACTIVE、SERVLET三种,一般都是SERVLET类型
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS =
"org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
//如果存在org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler类型,并且不存在org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet类型
//并且不存在org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer类型
//那么设置为REACTIVE,即响应式web应用程序
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
//如果不存在javax.servlet.Servlet类型,或者不存在org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext类型
//那么设置为NONE,即非web应用程序
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
//否则设置为SERVLET,即给予servlet的web应用程序,一般都是SERVLET
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
- setInitializers设置初始化器
设置ApplicationContextInitializer初始化器,后面初始化的时候会使用到,在Spring上下文被刷新之前进行初始化的操作,例如注入Property Sources属性源或者是激活Profiles环境。
这里会借助SpringFactoriesLoader工具类获取所有引入的jar包中和当前类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories文件中指定类型的实例,也就是ApplicationContextInitializer类型的实例。
spring.factories 是Spirng boot提供的一种扩展机制,实际上spring.factories就是仿照Java中的SPI扩展机制来实现的Spring Boot自己的SPI机制,它是实现Spribf Boot的自动配置的基础。
spring.factories该文件必须是 Properties 格式,其中 key 是接口或抽象类的完全限定名称,value 是逗号分隔的实现类名称列表。
public void setInitializers( Collection<? extends
ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers ){
this.initializers = new ArrayList<>( initializers );
}
/**
* 借助SpringFactoriesLoader获取所有引入的jar包中和当前类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories文件中指定类型的实例
* spring.factories 文件必须是 Properties 格式,其中 key 是接口或抽象类的完全限定名称,value 是逗号分隔的实现类名称列表。
*
* @param type 指定类型
*/
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances( Class<T> type ){
return getSpringFactoriesInstances( type, new Class<?>[]{} );
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances( Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args ){
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
//借助SpringFactoriesLoader获取所有引入的jar包中和当前类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories文件中指定类型的实例名称
//spring.factories 文件必须是 Properties 格式,其中 key 是接口或抽象类的完全限定名称,value 是逗号分隔的实现类名称列表。
//使用名称Set集合保存数据,确保唯一以防止重复
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>( SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames( type, classLoader ) );
//根据获取的类型全路径名反射创建实例
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances( type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names );
//对实例进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort( instances );
return instances;
- loadFactoryNames加载给定类型的全路径名
通过SpringFactoriesLoader从全部“META-INF/spring.factories”文件中根据给定的type类型获取所有对应的是实现类的全路径类名集合。这里的type就是ApplicationContextInitializer
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType,
@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
//获取工厂类型名,这里就是org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
//根据上面的名字作为key从/META-INF/spring.factories文件中获取指定的value并转换为集合
//value就是实现类的全路径名,并通过','拆分多个实现类
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
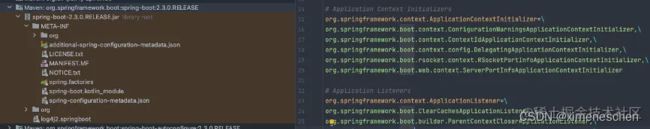
例如,与常见的自动配置类相关的是位于spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar下的/META-INF/spring.factories文件。其文件中,名为org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的key对应的value为包括三个初始化器:
在另一个spring-boot.jar包中同样有该初始化器的配置信息,同样会被加载:
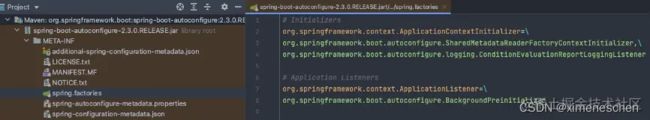
- setListeners设置监听器
设置ApplicationListener监听器。该方法和上面的setInitializers方法的逻辑是一样的。
这里是从META-INF/spring.factories文件中获取配置的ApplicationListener类型的实例。
spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar下的/META-INF/spring.factories文件中,名为org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener的key对应的value为包括一个监听器

在另一个spring-boot.jar包中同样有该初始化器的配置信息,同样会被加载:

- deduceMainApplicationClass推断应用程序主类
该方法推断应用程序主类,一般就是Spring boot项目的启动类,也就是调用main方法的类。
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 推断应用程序主类,一般就是Spring boot项目的启动类
*
* @return 主类class
*/
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass(){
try{
//获取堆栈跟踪记录
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for( StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace ){
//找到调用main方法的类,返回该类的class
if( "main".equals( stackTraceElement.getMethodName() ) ){
return Class.forName( stackTraceElement.getClassName() );
}
}
}
catch( ClassNotFoundException ex ){
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
四、run运行spring应用实例
run()方法将会运行SpringApplication实例,并且创建并刷新一个新的ApplicationContext。该方法就是Spring boot项目启动的关键方法,最终返回一个ConfigurableApplicationContext,代表着spring容器
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 运行容器
*
* @param args 启动参数,也就是main方法的参数
* @return 一个上下文环境对象,代表着spring容器
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run( String... args ){
//创建并启动一个计时器,用于统计run方法执行时常,即应用启动时常
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
//spring的应用程序上下文,代表着spring容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//SpringBootExceptionReporter异常报告者集合,用于记录项目启动过程中的异常信息
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//配置headless系统属性,Headless模式是系统的一种配置模式。在该模式下,系统缺少了显示设备、键盘或鼠标。
configureHeadlessProperty();
/*
* 1、获取全部SpringApplicationRunListener运行监听器并封装到SpringApplicationRunListeners中
* SpringApplicationRunListener的实现也是从spring.factories文件中加载的,其中一个实现就是EventPublishingRunListener
*/
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners( args );
/*
* 2、执行所有SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的starting的方法,可以用于非常早期的初始化操作
*/
//EventPublishingRunListener的starting方法会向之前初始化的所有ApplicationListener发送一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件
//ApplicationStartingEvent事件标志着SpringApplication的启动,并且此时ApplicationContext还没有初始化,这是一个早期事件
listeners.starting();
try{
//参数对象,封装了传递进来的启动参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments( args );
/*
* 3、根据SpringApplicationRunListeners和启动参数准备环境
*/
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment( listeners, applicationArguments );
/*
* 配置spring.beaninfo.ignore属性
* 这个配置用来忽略所有自定义的BeanInfo类的搜索,优化启动速度
*/
configureIgnoreBeanInfo( environment );
/*
* 4、打印启动banner图
*/
Banner printedBanner = printBanner( environment );
/*
* 5、创建spring上下文容器实例,核心方法
*/
context = createApplicationContext();
/*
* 获取SpringBootExceptionReporter异常报告者集合,用于记录项目启动过程中的异常信息
* SpringBootExceptionReporter的实现也是从spring.factories文件中加载的
*/
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances( SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ ConfigurableApplicationContext.class },
context );
/*
* 6、准备上下文容器,核心方法
* 该方法会将我们的启动类注入到容器中,后续通过该类启动自动配置
*/
prepareContext( context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner );
/*
* 7、刷新上下文容器,核心方法
* 该方法就是spring容器的启动方法,将会加载bean以及各种配置
* 这个方法的源码非常多,追踪下去就是spring启动源码里面AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
*/
refreshContext( context );
/*
* 8、刷新后处理
* 该方法是一个扩展方法,没有提供任何默认的实现,我们自定义的子类可以进行扩展。
*/
afterRefresh( context, applicationArguments );
/*
* springboot项目启动完毕,停止stopWatch计时
*/
stopWatch.stop();
/*
* 打印容器启动耗时日志
* 例如:Started SpringBootLearnApplication in 13.611 seconds (JVM running for 20.626)
*/
if( this.logStartupInfo ){
new StartupInfoLogger( this.mainApplicationClass ).logStarted( getApplicationLog(), stopWatch );
}
/*
* 9、应用SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的started方法
* EventPublishingRunListener将会发出ApplicationStartedEvent事件,表明容器已启动
*/
listeners.started( context );
/*
* 10、执行容器中的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner类型的bean的run方法
* 这也是一个扩展点,用于实现spring容器启动后需要做的事
*/
callRunners( context, applicationArguments );
}
catch( Throwable ex ){
/*
* 如果启动过程中出现了异常,那么会将异常信息加入到exceptionReporters中并抛出IllegalStateException
*/
handleRunFailure( context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners );
throw new IllegalStateException( ex );
}
try{
/*
* 11、应用SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的running方法
* EventPublishingRunListener将会发出ApplicationReadyEvent事件,表明容器已就绪,可以被使用了
*/
listeners.running( context );
}
catch( Throwable ex ){
/*
* 如果发布事件的过程中出现了异常,那么会将异常信息加入到exceptionReporters中并抛出IllegalStateException
*/
handleRunFailure( context, ex, exceptionReporters, null );
throw new IllegalStateException( ex );
}
//返回容器
return context;
}
- 该方法主要步骤总结:
- 获取全部SpringApplicationRunListener运行监听器并封装到SpringApplicationRunListeners中。SpringApplicationRunListener的实现也是从spring.factories文件中加载的,其中一个实现就是EventPublishingRunListener。
执行所有SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的starting的方法,可以用于非常早期的初始化操作。EventPublishingRunListener的starting方法会向之前初始化的所有ApplicationListener发送一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件,标志着SpringApplication的启动。- 根据SpringApplicationRunListeners和启动参数准备环境。这一步会查找项目的配置文件以及激活的profile等信息。
- 打印启动banner图。
- 创建spring上下文容器实例,核心方法。基于servlet的web项目容器是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类型。
- 准备上下文容器,核心方法。该方法会将我们的启动类注入到springboot的容器上下文内部的beanfactory中,有了这一步,后面就可以解析启动类的注解和各种配置,进而执行springboot的自动配置(启动类上有@SpringBootApplication注解,还有其他各种注解)。
- 刷新上下文容器,核心方法。该方法就是spring容器的启动方法,将会加载和解析容器中的bean以及各种配置。这个方法的源码非常多,我们在之前的spring启动源码部分花了大量时间已经讲过了,在此不再赘述。之前的文章链接Spring IoC容器初始化源码。
- 刷新后处理。该方法是一个扩展方法,没有提供任何默认的实现,我们自定义的子类可以进行扩展。
- 应用SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的started方法。EventPublishingRunListener将会发出ApplicationStartedEvent事件,表明容器已启动
- 调用runner,即执行容器中的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner类型bean的run方法。这也是一个扩展点,用于执行spring容器完全启动后需要做的逻辑。
- 应用SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的running方法。EventPublishingRunListener将会发出ApplicationReadyEvent事件,表明容器已就绪,可以被使用了。
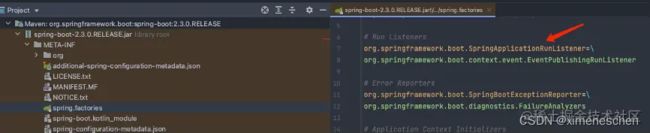
1. getRunListeners获取运行监听器
该方法用于获取运行监听器SpringApplicationRunListener,其也是从spring.factories文件中加载的,key为org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener。
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
*
* 获取运行监听器SpringApplicationRunListener并封装到SpringApplicationRunListeners中
*/
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners( String[] args ){
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[]{ SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
//借助SpringFactoriesLoader获取所有引入的jar包中和当前类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories文件中指定类型的实例
//这里指定类型为SpringApplicationRunListener,默认情况下spring.factories文件中有一个实现,即EventPublishingRunListener
//最终所有的SpringApplicationRunListener集合会被封装到一个SpringApplicationRunListeners对象中。
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners( logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances( SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args ) );
}
//SpringApplicationRunListeners的属性
private final Log log;
private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners;
/**
* SpringApplicationRunListeners的构造器
*/
SpringApplicationRunListeners(Log log, Collection<? extends SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners) {
this.log = log;
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
}
这个key对应的属性仅在spring-boot.jar的spring.factories文件中被设置,且只有一个实现类EventPublishingRunListener。
1.1. EventPublishingRunListener事件发布运行监听器
EventPublishingRunListener是一个很有趣的监听器,在上一步被找到之后会对监听器进行实例化,他的构造器如下
//EventPublishingRunListener的属性
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
/**
* 事件广播器,用于广播事件
*/
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
public EventPublishingRunListener( SpringApplication application, String[] args ){
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
/*
* 创建一个 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象
* 事件广播器,用于向多个监听器广播事件
*/
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
//将此前获取的ApplicationListener全部加入到事件广播器中
for( ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners() ){
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener( listener );
}
}
EventPublishingRunListener的starting方法会向之前初始化的所有ApplicationListener发送一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件。ApplicationStartingEvent事件标志着SpringApplication的启动,并且此时ApplicationContext还没有初始化,这是一个早期事件
/**
* EventPublishingRunListener的方法
*/
@Override
public void starting(){
//通过内部的广播器向所有的ApplicationListener发送一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent( new ApplicationStartingEvent( this.application, this.args ) );
}
/**
* EventPublishingRunListener广播器的方法
*
* @param event 发布的事件
*/
@Override
public void multicastEvent( ApplicationEvent event ){
multicastEvent( event, resolveDefaultEventType( event ) );
}
/**
* EventPublishingRunListener广播器的方法
*
* @param event 发布的事件
* @param eventType 事件的ResolvableType
*/
@Override
public void multicastEvent( final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType ){
ResolvableType type = ( eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType( event ) );
//获取事件发布执行器,如果设置了多线程的执行器,那么就可以异步的发布事件
//EventPublishingRunListener的执行器是null,即同步发布
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
//执行所有ApplicationListener的onApplicationEvent方法,触发对事件的处理
for( ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners( event, type ) ){
if( executor != null ){
executor.execute( () -> invokeListener( listener, event ) );
}
else{
invokeListener( listener, event );
}
}
}
2. starting启动监听器
在run()方法开始执行时,该方法就立即被调用,启动所有运行监听器,可用于在初始化最早期时做一些工作。
/**
* SpringApplicationRunListeners的方法
* 启动所有运行监听器
*/
void starting(){
for( SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners ){
//调用所有运行监听器的starting方法
listener.starting();
}
}
- EventPublishingRunListener的starting方法会向之前初始化的所有ApplicationListener发送一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件。
- ApplicationStartingEvent事件标志着SpringApplication的启动,并且此时ApplicationContext还没有初始化,这是一个早期事件。
/**
* EventPublishingRunListener的方法
*/
@Override
public void starting(){
//通过内部的广播器向所有的ApplicationListener发送一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent( new ApplicationStartingEvent( this.application, this.args ) );
}
/**
* EventPublishingRunListener广播器的方法
*
* @param event 发布的事件
*/
@Override
public void multicastEvent( ApplicationEvent event ){
multicastEvent( event, resolveDefaultEventType( event ) );
}
/**
* EventPublishingRunListener广播器的方法
*
* @param event 发布的事件
* @param eventType 事件的ResolvableType
*/
@Override
public void multicastEvent( final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType ){
ResolvableType type = ( eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType( event ) );
//获取事件发布执行器,如果设置了多线程的执行器,那么就可以异步的发布事件
//EventPublishingRunListener的执行器是null,即同步发布
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
//执行所有ApplicationListener的onApplicationEvent方法,触发对事件的处理
for( ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners( event, type ) ){
if( executor != null ){
executor.execute( () -> invokeListener( listener, event ) );
}
else{
invokeListener( listener, event );
}
}
}
3. prepareEnvironment准备环境
启动监听器之后,首先需要准备容器环境,根据SpringApplicationRunListeners和启动参数准备环境。这里会对外部配置的参数进行设置,比如端口号之类的
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 准备环境
*
* @param listeners 运行监听器
* @param applicationArguments 配置参数
* @return 环境
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment( SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments ){
/*
* 获取或者创建环境对象,一般都是StandardServletEnvironment类型
*/
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
/*
* 配置环境
* 主要配置属性源和激活的环境,将来自外部的配置源放在属性源集合的头部
*/
configureEnvironment( environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs() );
//继续封装属性源
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach( environment );
/*
* 环境准备完毕之后,向所有的ApplicationListener发出ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
*/
listeners.environmentPrepared( environment );
/*
* 将环境对象绑定到SpringApplication
* */
bindToSpringApplication( environment );
/*
* 如果不是自定义的环境变量,若有必要则进行转换,一般都需要转换
*/
if( !this.isCustomEnvironment ){
environment = new EnvironmentConverter( getClassLoader() ).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary( environment, deduceEnvironmentClass() );
}
//继续封装属性源
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach( environment );
return environment;
}
/**
* SpringApplication的属性
* 环境对象
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 创建和配置环境
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment(){
//如果已存在就直接返回
if( this.environment != null ){
return this.environment;
}
//根据应用程序类型创建不同的环境对象
switch( this.webApplicationType ){
//一般都是SERVLET项目,因此一般都是StandardServletEnvironment
case SERVLET:
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
}
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 配置环境
*/
protected void configureEnvironment( ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args ){
//是否需要添加转换服务,默认需要
if( this.addConversionService ){
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService( ( ConfigurableConversionService )conversionService );
}
//配置属性源,所谓属性源实际上可以看做是多个配置集的集合,来自外部的配置集将会被放在配置集合的首位
configurePropertySources( environment, args );
//配置激活的环境
configureProfiles( environment, args );
}
3.1 environmentPrepared发布事件
在环境准备好之后,会向所有的SpringApplicationRunListener发布事件。而EventPublishingRunListener又会通过内部的广播器向所有的 ApplicationListener发出ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,即会发布环境已准备事件
/**
* SpringApplicationRunListeners的方法
*
* 发布环境已准备事件
*
* @param environment 已准备好的环境对象
*/
void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared方法
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}
}
/**
* EventPublishingRunListener的方法
*
* @param environment 已准备好的环境对象
*/
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//向所有ApplicationListener发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
}
3.1.1 ConfigFileApplicationListener配置文件监听器
不同的监听器在接收到不同的事件之后,会进行不同的处理。这里就有一个非常关键的监听器ConfigFileApplicationListener,它会监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,并在监听到该事件的发布之后,去加载项目中的 properties 和yml配置文件并添加到Environment的PropertySources列表里,所以他是一个很关键的监听器。
下面是ConfigFileApplicationListener处理事件的方法,其内部会从spring.factories文件中加载加载环境后处理器EnvironmentPostProcessor,然后委托给EnvironmentPostProcessor来处理事件。而ConfigFileApplicationListener本身也是一个EnvironmentPostProcessor,他的postProcessEnvironment方法就会去加载配置文件
/**
* ConfigFileApplicationListener的方法
* 应用程序事件处理的方法
*
* @param event
*/
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent( ApplicationEvent event ){
if( event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent ){
//如果是坏境准备完毕事件,那么调用该方法处理
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent( ( ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent )event );
}
if( event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent ){
onApplicationPreparedEvent( event );
}
}
/**
* ConfigFileApplicationListener的方法
* 处理环境准备就绪事件的方法
*
* @param event
*/
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent( ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event ){
//加载环境后处理器EnvironmentPostProcessor,很明显其也是从spring.factories文件中加载的
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
//将自己页加入其中,因为ConfigFileApplicationListener本身也是一个EnvironmentPostProcessor
postProcessors.add( this );
//排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort( postProcessors );
//循环调用EnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment方法执行环境处理
for( EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors ){
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment( event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication() );
}
}
ConfigFileApplicationListener的是通过一个内部类的实例Loader对象来加载配置文件的,Loader用于加载候选属性源并配置活动配置文件
/**
* ConfigFileApplicationListener的方法
*/
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment( ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application ){
addPropertySources( environment, application.getResourceLoader() );
}
/**
* ConfigFileApplicationListener的方法
*/
protected void addPropertySources( ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader ){
//随机数属性源加入到环境对象中
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment( environment );
/*
* 关键代码
* 通过ConfigFileApplicationListener的内部类Loader来加载配置文件
*/
new Loader( environment, resourceLoader ).load();
}
Loader的load方法就是加载配置的关键方法。实际上,从ConfigFileApplicationListener这个类中,就可以得知配置文件的加载位置,以及加载顺序:

需要注意的是,这里的加载优先级和这里的顺序是相反的,因此,加载顺序为:
- 项目根目录下的/config目录下的配置文件。
- 项目根目录下的配置文件。
- 项目类路径(resources)下的/config目录下的配置文件。
- 项目类路径(resources)下的配置文件。
同时,符合给定环境profile的配置文件优先于默认的配置文件。
4. printBanner打印启动banner图
这个方法用于打印banner图,首先会查找自定义的banner资源,banner可以是图片或者txt文本格式,默认自定义资源是txt格式,名字是banner.txt,位于resources目录下。
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
*
* @param environment
* @return
*/
private Banner printBanner( ConfigurableEnvironment environment ){
//如果没有启动banner打印,则返回null
if( this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF ){
return null;
}
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = ( this.resourceLoader != null ) ? this.resourceLoader : new DefaultResourceLoader( getClassLoader() );
SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter( resourceLoader, this.banner );
//banner输出到日志文件中还是控制台,默认是CONSOLE,即控制台
if( this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.LOG ){
return bannerPrinter.print( environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger );
}
return bannerPrinter.print( environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out );
}
/**
* SpringApplicationBannerPrinter的方法
*/
Banner print( Environment environment, Class<?> sourceClass, PrintStream out ){
//从当前环境中获取banner资源
//banner可以是图片或者txt文本格式,默认自定义资源名字是banner.txt,位于resources目录下
//一般是没有自定义banner资源的,此时采用SpringBootBanner,也就是默认的banner配置
Banner banner = getBanner( environment );
//打印banner图
banner.printBanner( environment, sourceClass, out );
return new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter.PrintedBanner( banner, sourceClass );
}
一般是没有自定义banner资源的,此时采用SpringBootBanner,也就是默认的banner配置:
要想自定义banner资源很简单,根据上面的源码,最简单的是我们只需要在springboot项目的resources文件夹下面创建一个banner.txt文件,springboot启动的时候会去加载这个文件,当然图片也可以。下面是几个定制banner的网站:
- patorjk.com/software/taag
- www.network-science.de/ascii/
- www.degraeve.com/img2txt.php
5. createApplicationContext创建spring容器
在准备好环境并且加载了配置文件之后,通过createApplicationContext方法创建spring容器对象,基于servlet的web项目容器是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类型。
/**
* 自定义的容器类型
*/
private Class<? extends ConfigurableApplicationContext> applicationContextClass;
/**
* 默认情况下将用于非 Web 的应用程序上下文的类名。
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.context." + "annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext";
/**
* 默认情况下将用于 Web 的应用程序上下文的类名。
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot." + "web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext";
/**
* 默认情况下将用于反应式 Web 的应用程序上下文的类名。
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework." + "boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext";
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 用于创建 ApplicationContext 即spring容器的策略方法。
*
* @return 可配置的spring容器
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext(){
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
//如果没有设置容器类型
if( contextClass == null ){
try{
//根据web应用程序类型选择spring容器的类型
switch( this.webApplicationType ){
//一般都是servlet应用,因此spring容器就是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类型
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName( DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS );
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName( DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS );
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName( DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS );
}
}
catch( ClassNotFoundException ex ){
throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex );
}
}
//调用无参构造器反射创建实例
return ( ConfigurableApplicationContext )BeanUtils.instantiateClass( contextClass );
}
6. prepareContext准备上下文
- 该方法用于准备容器上下文,
主要是进行ApplicationContextInitializer扩展点的应用,以及打印启动日志,比如激活的profiles图,设置是否允许同名bean覆盖(默认不允许),是否懒加载(默认不允许)等操作。- 最重要的是该方法会
将我们的启动类注入到springboot的容器上下文内部的beanfactory中,有了这一步,后面就可以解析启动类的注解和各种配置,进而执行springboot的自动配置(启动类上有@SpringBootApplication注解,还有其他各种注解(@Configuration、@Import),进而递归解析beanDefinition)。
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 准备容器上下文
*
* @param context spring容器
* @param environment 环境对象
* @param listeners 监听器
* @param applicationArguments 配置参数
* @param printedBanner banner
*/
private void prepareContext( ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner ){
//设置环境变量
context.setEnvironment( environment );
/*
* 对于容器的后处理,会尝试注入BeanNameGenerator,设置resourceLoader,设置ConversionService等操作
* 子类可以根据需要应用额外的处理。
*/
postProcessApplicationContext( context );
/*
* 应用ApplicationContextInitializer扩展点的initialize方法
* 从而实现自定义容器的逻辑,这是一个扩展点
*/
applyInitializers( context );
/*
* 应用SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的contextPrepared方法
* EventPublishingRunListener将会发出ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件
*/
listeners.contextPrepared( context );
//是否打印启动相关日志,默认true
if( this.logStartupInfo ){
//记录启动日志信息,即banner图日志下面的第一行日志信息
logStartupInfo( context.getParent() == null );
//记录激活的配置环境profiles日志信息
//即The following profiles are active: dev,或者No active profile set, falling back to default profiles:
logStartupProfileInfo( context );
}
// 获取此上下文内部的beanFactory,即bean工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//将applicationArguments作为一个单例对象注册到bean工厂中
beanFactory.registerSingleton( "springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments );
if( printedBanner != null ){
//将banner作为一个单例对象注册到bean工厂中
beanFactory.registerSingleton( "springBootBanner", printedBanner );
}
//如果是该类型,servlet项目默认就是该类型
if( beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory ){
//设置是否允许同名bean的覆盖,这里默认false,如果有同名bean就会抛出异常
( ( DefaultListableBeanFactory )beanFactory ).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding( this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding );
}
//设置是否允许懒加载,即延迟初始化bean,即仅在需要bean时才创建该bean,并注入其依赖项。
//默认false,即所有定义的bean及其依赖项都是在创建应用程序上下文时创建的。
if( this.lazyInitialization ){
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor( new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor() );
}
// 加载启动源,默认就是我们的启动类
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty( sources, "Sources must not be empty" );
/*
* 加载启动类,并将启动类注入到容器,关键方法
* 有了这一步,后面就可以解析启动了伤的竹节和各种配置,进行执行springboot的自动配置
*/
load( context, sources.toArray( new Object[ 0 ] ) );
/*
* 应用SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的contextLoaded方法
* EventPublishingRunListener将会发出ApplicationPreparedEvent事件
*/
listeners.contextLoaded( context );
}
7. refreshContext刷新上下文
该方法就是spring容器的启动方法,将会加载bean以及各种配置。该方法是spring项目的核心方法,该方法还会向当前的JVM运行时环境注册一个钩子函数,该函数会在JVM关闭之前进行执行,并且会执行当前spring上下文容器的doClose方法,即关闭容器。
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
*
* @param context
*/
private void refreshContext( ConfigurableApplicationContext context ){
/*
* 刷新容器
*/
refresh( ( ApplicationContext )context );
//判断是否注册销毁容器的钩子方法,默认true
if( this.registerShutdownHook ){
try{
//注册销毁容器时的钩子
//该方法向 JVM 运行时环境注册一个关闭钩子函数,在 JVM 关闭时会先关闭此上下文,即执行此上线文的close方法
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch( AccessControlException ex ){
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
/**
* AbstractApplicationContext的方法
* 向JVM注册钩子函数,该函数将会在JVM关闭时被执行,进行spring上下文的关闭操作
*/
public void registerShutdownHook(){
if( this.shutdownHook == null ){
// 钩子函数
this.shutdownHook = new Thread( SHUTDOWN_HOOK_THREAD_NAME ){
@Override
public void run(){
synchronized( startupShutdownMonitor ){
//执行当前上下文环境的close方法
doClose();
}
}
};
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook( this.shutdownHook );
}
}
8. afterRefresh刷新后处理
该方法是一个扩展方法,没有提供任何默认的实现,我们自定义的子类可以进行扩展。
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}
9. callRunners调用runner
runner是一类特殊的bean,如果该bean属于ApplicationRunner或者CommandLineRunner类型,那么该bean就被称为runner,那么在springboot启动之后会自动调用该bean的run方法,这里就是调用的源码!
/**
* SpringApplication的方法
* 调用runner
*/
private void callRunners( ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args ){
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
//从容器中查找全部ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner类型的bean实例,并且加入到集合中
runners.addAll( context.getBeansOfType( ApplicationRunner.class ).values() );
runners.addAll( context.getBeansOfType( CommandLineRunner.class ).values() );
//排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort( runners );
//依次运行这些runner
for( Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>( runners ) ){
if( runner instanceof ApplicationRunner ){
callRunner( ( ApplicationRunner )runner, args );
}
if( runner instanceof CommandLineRunner ){
callRunner( ( CommandLineRunner )runner, args );
}
}
}
private void callRunner( ApplicationRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args ){
try{
//运行ApplicationRunner,参数就是当前的配置参数
( runner ).run( args );
}
catch( Exception ex ){
throw new IllegalStateException( "Failed to execute ApplicationRunner", ex );
}
}
private void callRunner( CommandLineRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args ){
try{
//运行CommandLineRunner,参数就是当前返回传递给应用程序的原始未处理参数
( runner ).run( args.getSourceArgs() );
}
catch( Exception ex ){
throw new IllegalStateException( "Failed to execute CommandLineRunner", ex );
}
}
五、关于内置的tomcat服务器的疑问
常常听别人说Spring Boot内嵌了Tomcat服务器,但是本次源码分析却没有Tomcat服务器的影子,那么Tomcat是在哪里地方,是在什么时候启动的呢?实际上Tomcat服务器也是在Spring Boot自动装配的环节进行配置的,那么Spring Boot自动装配的原理是什么呢?这个我们之前也有了分析:Spring Boot自动配置的原理简介以及@Conditional条件注解。实际上这一切都是在refreshContext方法中去完成的。那么与Tomcat服务器相关的自动配置类是哪一个呢?
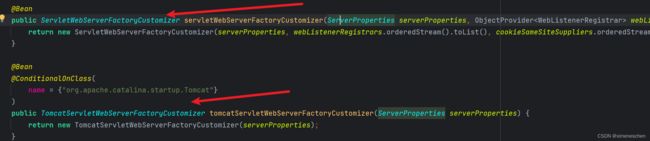
1. ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
实际上它是位于spring-boot-autoconfigure.jar下的/META-INF/spring.factories文件中的一个名为ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration的自动配置类。
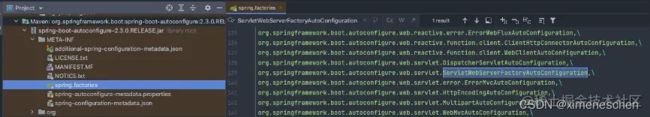
在该自动配置类中,会通过@Import想容器中注入四个配置类,我们可以看到,各种容器的web服务配置,Tomcat、Jetty、Undertow,其中Tomcat对应EmbeddedTomcat。
![]()
这个EmbeddedTomcat配置类又会向Spring容器注入TomcatServletWebServerFactory,这个类就是Tomcat启动的关键类,用于创建TomcatWebServer

另外,ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration中还会注入一系列的Customizer,用于修改内嵌Tomcat的参数和配置
2. onRefresh启动web服务
那么,这个TomcatServletWebServerFactory是怎么在什么时候被加载到容器中并使用的呢?Tomcat又是什么时候被启动的呢?在spring boot容器启动过程中,在创建容器之后,会执行刷新容器的操作,也就是refresh()操作,这个操作实际上就是spring容器的启动方法,将会加载bean以及各种配置。该方法是spring项目的核心方法,源码非常多,在refresh()方法中,有一个onRefresh()方法。在单纯的spring源代码中,这个onRefresh方法默认是一个空的实现,这是留给子类容器实现的扩展方法。而在springboot源码中,这个方法并非空实现,该方法在所有的bean定义被注入到容器中之后调用的,而在onRefresh方法之后,则会对所有的普通单例bean进行实例化和初始化。springboot默认的web服务容器是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext,它又继承了ServletWebServerApplicationContext,该类就对onRefresh方法进行了实现,并且Spring boot的web服务器就是在此启动的!
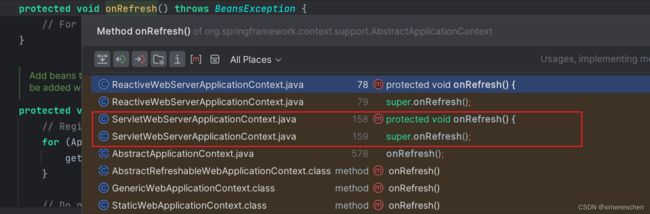
/**
* ServletWebServerApplicationContext实现的方法
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(){
//调用父类的逻辑
super.onRefresh();
try{
/*
* 关键方法,创建webserver
*/
createWebServer();
}
catch( Throwable ex ){
throw new ApplicationContextException( "Unable to start web server", ex );
}
}
可以看到,内部调用了createWebServer方法创建web服务器。
3. createWebServer创建web服务
- createWebServer方法的代码如下,它会通过之前配置的ServletWebServerFactory,获取webServer,即创建web服务器。
- 一般我们使用的ServletWebServerFactory就是TomcatServletWebServerFactory,使用的webserver就是TomcatWebServer。
- 在创建了webserver之后,会想容器注入两个SmartLifecycle类型的bean实例,这实际上是一个扩展点的实例,用于实现容器回调。
- 其中,注册的WebServerStartStopLifecycle实例,在ServletWebServerApplicationContext类型的容器启动完毕后会调用该实例的start方法启动webServer并发送事件,在ServletWebServerApplicationContext类型的容器销毁时将会调用该实例的stop方法销毁webServer。
private volatile WebServer webServer;
/**
* ServletWebServerApplicationContext的方法
*
* 创建web服务
*/
private void createWebServer(){
//获取WebServer,这里默认是空的
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
//获取ServletContext,即servlet上下文,这里默认是空的
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
/*
* 获取webServer,初始化web服务
*/
if( webServer == null && servletContext == null ){
//获取web服务工厂,默认就是TomcatServletWebServerFactory
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
/*
* 通过web服务工厂获取web服务,核心代码
* 创建内嵌的Tomcat并启动
*/
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer( getSelfInitializer() );
/*
* 注册WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle的实例到容器中
* ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext容器启动完毕后会调用该实例的start方法
* ReactiveWebServerApplicationContext容器销毁时将会调用该实例的stop方法
*/
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton( "webServerGracefulShutdown", new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle( this.webServer ) );
/*
* 注册WebServerStartStopLifecycle的实例到容器中
* ServletWebServerApplicationContext容器启动完毕后会调用该实例的start方法尝试启动webServer并发送事件
* ServletWebServerApplicationContext容器销毁时将会调用该实例的stop方法销毁webServer
*/
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton( "webServerStartStop", new WebServerStartStopLifecycle( this, this.webServer ) );
}
else if( servletContext != null ){
try{
getSelfInitializer().onStartup( servletContext );
}
catch( ServletException ex ){
throw new ApplicationContextException( "Cannot initialize servlet context", ex );
}
}
//初始化ConfigurableWebEnvironment类型的配属数据源
initPropertySources();
}
3.1 getWebServerFactory获取web服务工厂
该方法获取web服务工厂,工厂用于创建web服务。
/**
* ServletWebServerApplicationContext的方法
*
* 获取ServletWebServerFactory,用于初始化webServer
* 默认返回TomcatServletWebServerFactory
*/
protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory(){
//从容器中搜索ServletWebServerFactory类型的beanName数组
//之前的ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration配置类就会像容器中
//注入ServletWebServerFactory的bean,默认就是TomcatServletWebServerFactory
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType( ServletWebServerFactory.class );
//没有web服务工厂
if( beanNames.length == 0 ){
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing " + "ServletWebServerFactory bean." );
}
//有多个web服务工厂
if( beanNames.length > 1 ){
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple " + "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(
beanNames ) );
}
//从容器中获取web服务工厂的实例
return getBeanFactory().getBean( beanNames[ 0 ], ServletWebServerFactory.class );
}
3.2 getWebServer获取web服务
- ServletWebServerFactory的方法,用于获取web服务。
其中TomcatServletWebServerFactory的方法用于创建Tomcat实例并返回TomcatServer。- 该方法中的一些名词比如baseDir、connector、Service、Host、AutoDeploy、Engine等等都是Tomcat中的概念。
- 在最后的getTomcatWebServer方法中会对Tomcat服务器进行启动。控制台会输出日志:Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)。
/**
* TomcatServletWebServerFactory的方法
* 创建内嵌的Tomcat
*
* @param initializers 初始化器
* @return Tomcat的web服务
*/
@Override
public WebServer getWebServer( ServletContextInitializer... initializers ){
if( this.disableMBeanRegistry ){
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
//创建Tomcat实例
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
//设置Tomcat的基本目录
File baseDir = ( this.baseDirectory != null ) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir( "tomcat" );
tomcat.setBaseDir( baseDir.getAbsolutePath() );
//设置Connector,用于接受请求发挥响应
Connector connector = new Connector( this.protocol );
connector.setThrowOnFailure( true );
tomcat.getService().addConnector( connector );
//自定义连接器
customizeConnector( connector );
tomcat.setConnector( connector );
//是否自动部署
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy( false );
//设置Engine
configureEngine( tomcat.getEngine() );
//自己扩展的连接器
for( Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors ){
tomcat.getService().addConnector( additionalConnector );
}
//准备上下文
prepareContext( tomcat.getHost(), initializers );
//创建TomcatWebServer,启动Tomcat,返回TomcatWebServer
return getTomcatWebServer( tomcat );
}
Tomcat启动后的继续执行Spring的逻辑,初始化bean实例等等,Spring容器初始化完毕之后,调用WebServerStartStopLifecycle的start方法,对TomcatWebServer进行启动,此时控制台会输出日志:Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ‘’。
参考文章