大并发下请求合并(并发处理技巧)
大并发下请求合并
- 一次请求消耗的资源
- 旧的方式
- 改造后
-
-
- 批量请求处理器
- 批量请求包装类
- 使用
-
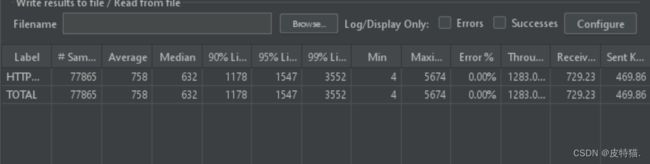
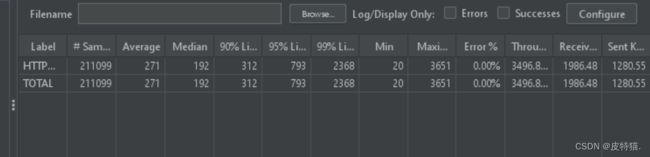
- 性能测试
-
-
-
- 旧的
- 改造后的
-
-
一次请求消耗的资源
我们经常碰到查询请求的操作,例如根据用户id查询该用户的信息,接口仓储层查询用户正常的做法是通过id去数据库查询该用户id,例如:
where id =xxx
这样的一次请求可能会涉及tomcat、数据库连接池的链接获取,以及可能存在的链接创建和销毁
链接资源是宝贵的,并发比较高的情况1000个请求进来,每一个请求都会去尝试获取数据库链接,打开并执行查询然后关闭。这会导致链接资源挤兑,同时也提高了数据库压力,因此解决以上问题,可以通过批处理请求合并的方式
旧的方式
@GetMapping("/test/user")
public ResponseResult<IamUserContext> user(@RequestParam String loginId) {
return ResponseResult.success(iamUserMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(Long.parseLong(uid)););
}
改造后
批量请求处理器
/**
* 解决大并发下,各类连接池链接快速消耗及创建销毁带来的性能损耗
* 将单个请求合并为多个请求,批量请求仓储层,增加并发性能
* @classDesc: 批量请求合并处理器
* @author: cyjer
* @date: 2023/7/25 13:28
*/
@Slf4j
public abstract class BatchCollapseProcessor<T, R> implements InitializingBean {
private static final ScheduledExecutorService SCHEDULE_EXECUTOR = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
private final LinkedBlockingDeque<BatchCollapseRequest<T, R>> batchContainer = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(defaultCountThreshold() * 5);
/**
* 默认数量阈值
*
* @return
*/
int defaultCountThreshold() {
int maxCountThreshold = 1000;
if (countThreshold() == null) {
return 500;
}
return Math.min(countThreshold(), maxCountThreshold);
}
/**
* 默认时间阈值
*
* @return
*/
int defaultTimeThresholdMilliSeconds() {
return timeThresholdMilliSeconds() == null ? 50 : timeThresholdMilliSeconds();
}
/**
* 使用者自定义数量阈值
*
* @return
*/
public abstract Integer countThreshold();
/**
* 时间阈值(秒)
*
* @return
*/
public abstract Integer timeThresholdMilliSeconds();
/**
* 处理用户请求
*
* @param requests
* @return
*/
Map<String, R> fetchResult(List<BatchCollapseRequest<T, R>> requests) {
List<T> reqParam = requests.stream()
.map(BatchCollapseRequest::getReqParam)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<R> data = fetchData(reqParam);
return transferResult(requests, data);
}
/**
* 用户自行实现具体请求方法
*
* @param requests
* @return
*/
public abstract List<R> fetchData(List<T> requests);
/**
* 用户自行实现
*
* @param requests
* @return
*/
public abstract Map<String, R> transferResult(List<BatchCollapseRequest<T, R>> requests, List<R> res);
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
SCHEDULE_EXECUTOR.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
List<BatchCollapseRequest<T, R>> requests = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>(defaultCountThreshold()));
batchContainer.drainTo(requests, defaultCountThreshold());
if (requests.size() < 1) {
return;
}
log.info("合并处理[{}]个请求", requests.size());
Map<String, R> response = fetchResult(requests);
for (BatchCollapseRequest<T, R> request : requests) {
request.getCompletableFuture().complete(response.get(request.getReqId()));
}
}, defaultTimeThresholdMilliSeconds(), defaultTimeThresholdMilliSeconds(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public R doRequest(T input) {
BatchCollapseRequest<T, R> request = new BatchCollapseRequest<>();
request.setReqId(IdGenerator.ins().generator().toString());
CompletableFuture<R> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
request.setCompletableFuture(future);
request.setReqParam(input);
batchContainer.offer(request);
try {
return future.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("合并获取结果异常 error:", e);
throw BusinessException.build(AdviceErrorCode.OTHER_EX, "系统有点拥堵,请稍后重试~");
}
}
}
批量请求包装类
/**
* @classDesc: 批量请求
* @author: cyjer
* @date: 2023/9/20 10:34
*/
@Data
public class BatchCollapseRequest<T, R> {
/**
* 请求id 唯一
*/
private String reqId;
/**
* 请求体
*/
private T reqParam;
/**
* 异步处理
*/
private CompletableFuture<R> completableFuture;
}
使用
@Component
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class TestService extends BatchCollapseProcessor<String, IamUserContext> {
private final IamUserMapper iamUserMapper;
private final BizConvert bizConvert;
@Override
public Integer countThreshold() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Integer timeThresholdMilliSeconds() {
return null;
}
@Override
public List<IamUserContext> fetchData(List<String> requests) {
List<Long> collect = requests.stream().map(Long::parseLong).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<IamUser> iamUsers = iamUserMapper.selectBatchByPrimaryKey(collect);
return bizConvert.iamUserPOS2VOS(iamUsers);
}
@Override
public Map<String, IamUserContext> transferResult(List<BatchCollapseRequest<String, IamUserContext>> batchCollapseRequests, List<IamUserContext> res) {
Map<String, IamUserContext> collect = res.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(IamUserContext::getUid, Function.identity()));
Map<String, IamUserContext> result = new HashMap<>();
batchCollapseRequests.forEach(val -> {
IamUserContext userContext = collect.getOrDefault(val.getReqParam(), null);
result.put(val.getReqId(), userContext);
});
return result;
}
}
private final TestService testService;
@GetMapping("/test/user/batch")
public ResponseResult<IamUserContext> batch(@RequestParam String loginId) {
IamUserContext iamUserContext = testService.doRequest(loginId);
return ResponseResult.success(iamUserContext);
}