2D&3D融合
概述
截止目前为止,我们学习了机器人学,学习了2D和3D视觉算法。我们也学习了2D相机(图像数据的来源)和3D相机(点云数据的来源)工作原理。
实际上,我们最终要做的,是一个手眼机器人系统。在这个系统里,相机与机器人构成了两个非常关键的部分,它们之间需要密切配合,因此,它们之间的关系,也就非常重要。确定相机与机器人之间的关系,这是手眼标定要解决的问题。
另一方面,在很多场合,为了增强算法的鲁棒性,我们通常同时使用图像数据与点云数据,这又涉及到2D与3D配准的问题。
相机配准

通过双重循环遍历
/**
* 将彩色图和深度图合并成点云
* @param matrix 相机内参矩阵3x3
* @param rgb 彩色图
* @param depth 深度图
* @param cloud 输出点云
*/
static void convert(Mat &matrix, Mat &rgb, Mat &depth, PointCloud::Ptr &cloud) {
double camera_fx = matrix.at(0, 0);
double camera_fy = matrix.at(1, 1);
double camera_cx = matrix.at(0, 2);
double camera_cy = matrix.at(1, 2);
cout << "fx: " << camera_fx << endl;
cout << "fy: " << camera_fy << endl;
cout << "cx: " << camera_cx << endl;
cout << "cy: " << camera_cy << endl;
// 遍历深度图
for (int v = 0; v < depth.rows; v++)
for (int u = 0; u < depth.cols; u++) {
// 获取深度图中(m,n)处的值
ushort d = depth.ptr(v)[u];
// d 可能没有值,若如此,跳过此点
if (isnan(d) && abs(d) < 0.0001)
continue;
// d 存在值,则向点云增加一个点
PointT p;
// 计算这个点的空间坐标
p.z = double(d) / 1000; //单位是米
p.x = (u - camera_cx) * p.z / camera_fx;
p.y = (v - camera_cy) * p.z / camera_fy;
// 从rgb图像中获取它的颜色
// rgb是三通道的BGR格式图,所以按下面的顺序获取颜色
Vec3b bgr = rgb.at(v, u);
p.b = bgr[0];
p.g = bgr[1];
p.r = bgr[2];
// 把p加入到点云中
cloud->points.push_back(p);
//cout << cloud->points.size() << endl;
}
// 设置并保存点云
cloud->height = 1;
cloud->width = cloud->points.size();
cout << "point cloud size = " << cloud->points.size() << endl;
cloud->is_dense = false;
}
int main(){
cv::Mat cameraMatrix; // 从文件加载相机内参
cv::Mat rgb; // 从相机得到RGB彩色图
cv::Mat depth; // 从相机得到depth深度图
PointCloud::Ptr pCloud = PointCloud::Ptr(new PointCloud);
convert(cameraMatrix, rgb, depth, pCloud);
}
通过指针遍历,并提前准备好计算矩阵
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
float qnan_ = std::numeric_limits::quiet_NaN();
const char *cameraInCailFile = "./assets/3DCameraInCailResult.xml";
Eigen::Matrix colmap;
Eigen::Matrix rowmap;
//const short w = 512, h = 424;
const short w = 1920, h = 1080;
void prepareMake3D(const double cx, const double cy,
const double fx, const double fy) {
float *pm1 = colmap.data();
float *pm2 = rowmap.data();
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
*pm1++ = (i - cx + 0.5) / fx;
}
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
*pm2++ = (i - cy + 0.5) / fy;
}
}
/**
* 根据内参,合并RGB彩色图和深度图到点云
* @param cloud
* @param depthMat
* @param rgbMat
*/
void getCloud(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr &cloud, Mat &depthMat, Mat &rgbMat) {
const float *itD0 = (float *) depthMat.ptr();
const char *itRGB0 = (char *) rgbMat.ptr();
if (cloud->size() != w * h)
cloud->resize(w * h);
pcl::PointXYZRGB *itP = &cloud->points[0];
bool is_dense = true;
for (size_t y = 0; y < h; ++y) {
const unsigned int offset = y * w;
const float *itD = itD0 + offset;
const char *itRGB = itRGB0 + offset * 4;
const float dy = rowmap(y);
for (size_t x = 0; x < w; ++x, ++itP, ++itD, itRGB += 4) {
const float depth_value = *itD / 1000.0f;
if (!isnan(depth_value) && abs(depth_value) >= 0.0001) {
const float rx = colmap(x) * depth_value;
const float ry = dy * depth_value;
itP->z = depth_value;
itP->x = rx;
itP->y = ry;
itP->b = itRGB[0];
itP->g = itRGB[1];
itP->r = itRGB[2];
} else {
itP->z = qnan_;
itP->x = qnan_;
itP->y = qnan_;
itP->b = qnan_;
itP->g = qnan_;
itP->r = qnan_;
is_dense = false;
}
}
}
cloud->is_dense = is_dense;
}
int main(){
Mat cameraMatrix = cv::Mat_(3, 3);
FileStorage paramFs(cameraInCailFile, FileStorage::READ);
paramFs["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix;
// 内参数据
double fx = cameraMatrix.at(0, 0);
double fy = cameraMatrix.at(1, 1);
double cx = cameraMatrix.at(0, 2);
double cy = cameraMatrix.at(1, 2);
// 提前准备计算所需参数
prepareMake3D(cx, cy, fx, fy);
cv::Mat rgbMat; // 从相机得到RGB彩色图
cv::Mat depthMat; // 从相机得到depth深度图
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud());
getCloud(cloud, depthMat, rgbMat)
}
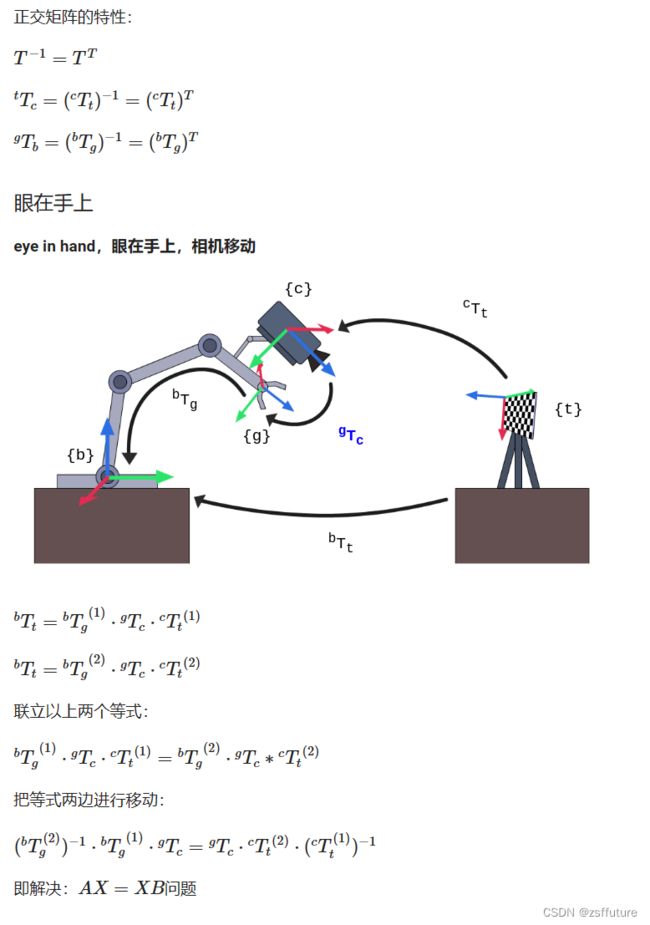
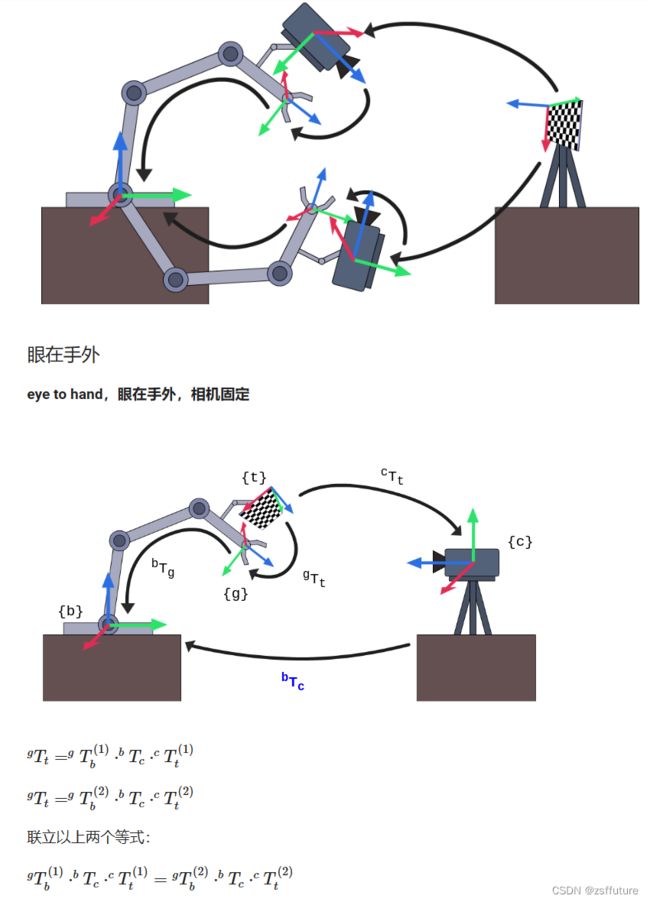
手眼标定(外参标定)
一、手眼标定的原理
图例说明:
- {b}:base基座标系
- {g}:gripper抓手坐标系
- {t}:target标定板坐标系
- {c}:camera相机坐标系

二、手眼标定的操作¶

- 将标定板固定在机械臂末端
- 开启机械臂,开启摄像头
- 在距离摄像头40、60、80cm的距离上,在摄像头可见范围内,使用各种角度各拍照15-20张照片,一共45-60张。
- 同时保存照片以及对应拍照时机械臂位姿
- 准备好之前标定的相机内参
- 执行手眼标定API,得到相机在基坐标系的表达(旋转矩阵R+平移向量t)
三、自己动手实现手眼标定及验证¶
// Created by poplar on 19-7-25.
#include
#include
#include
#include "boost/filesystem.hpp" // includes all needed Boost.Filesystem declarations
#include
#include
#include "tinyxml/tinyxml2.h"
#include
2D与3D融合实践¶
根据模板抓取指定物体:
制作模板,并计算取得相机到模板的变换矩阵T1,根据实时相机中拍到的物体进行模板匹配,得到变换矩阵T0,最后和相机的外参矩阵Tc进行矩阵相乘,得到目标在世界坐标系的表示,从而进行抓取操作。
一、制作模板:求T1¶
-
Kinect相机拍照(得到RGB图和深度图)
01_PhotoCapture.cpp
-
检测抓取位置(u,v),根据内参及深度信息得到三个空间中的点坐标
02_PointLocator.cpp
03_TemplateMaker.cpp
-
构建坐标系得到旋转矩阵T1,转成RPY进行抓取测试
04_TestGrabTemplate.cpp
-
生成点云图用于模板匹配(进行直通滤波及降采样)
05_CreatePclCloud.cpp 验证变换矩阵
06_TemplateCloudFilter.cpp 生成剪切后的模板
- 实时的拍照得到RGB和深度图
- 合成目标点云图
- 通过直通滤波框定范围(得到感兴趣区域)
- 将感兴趣区域进行降采样(提高模板匹配效率)
二、使用模板:求T0¶
准备好切割后的点云template.pcd以及对应的变换矩阵T1(可以有多个)
-
Kinect相机拍照(得到RGB图和深度图)
01_PhotoCapture.cpp
-
生成目标点云图
07_TargetCloudFilter.cpp
-
进行模板与目标点云图匹配(统一进行直通滤波及降采样),得到变换矩阵T0
08_TemplateAlignment.cpp
三、进行抓取测试¶
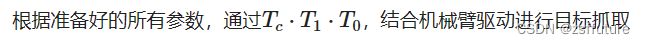
09_TestGrabTarget.cpp√
T0 为目标在模板坐标系的表达 T1 为模板在相机坐标系的表达 Tc 为相机在基坐标系的表达
待优化事宜¶
- 安全位置判定
- 将盒子抓取到指定位置放置
- 不间断抓取多个盒子
- 准备多个模板,提高模板匹配姿态识别度
- 设置间隔,实时进行模板匹配
- 设置目标位置抓取动态延时
- 自动避障
- 其他
自己封装内外参标定工具¶




