Java并发编程——线程池
一、池化技术
程序运行的本质是占用系统资源,而池化技术可以优化资源的使用。
池化技术:事先准备好一些资源,有人要用,就来拿,用还之后还给线程池(生活类似场景:共享充电宝)
线程池的好处:
1.降低资源的消耗
2.提高响应的速度
3.方便管理(线程复用、控制最大并发数、管理线程)
二、线程池(三大方法)
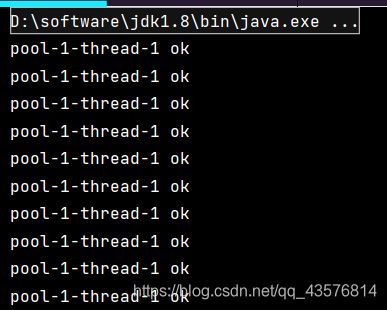
1.newSingleThreadExecutor()
newSingleThreadExecutor()方法创建一次执行单个任务的执行程序。
//Executors
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();//单个线程
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用线程池创建线程
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok");
});
}
}finally{
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
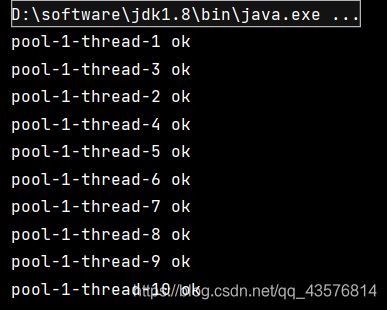
2.newFixedThreadPool()
newFixedThreadPool()创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
//Executors
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);//创建一个固定大小的线程池
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用线程池创建线程
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok");
});
}
}finally{
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
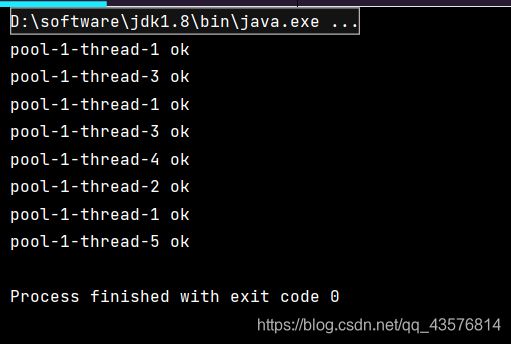
3.newCachedThreadPool()
newSingleThreadExecutor()创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行
//Executors
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//创建一个可伸缩的线程池
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用线程池创建线程
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok");
});
}
}finally{
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
三、七大参数
底层源码
newSingleThreadExecutor()

newFixedThreadPool()
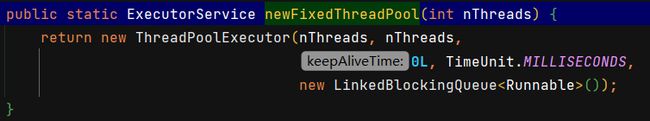
newCachedThreadPool()
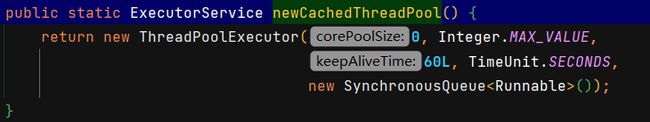
本质:ThreadPoolExecutor()

corePoolSize:核心线程池大小
maximumPoolSize:最大核心线程池大小
keepAliveTime:超时后没有被调用就会释放
TimeUnit:超时单位
BlockingQueue:阻塞队列
ThreadFactory:线程工厂,创建线程
RejectedExecutionHandler:拒绝策略
四、四种拒绝策略
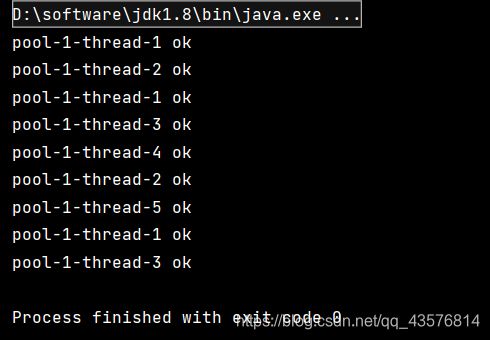
1.AbortPolicy():
如果超过最大承载数,报异常
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2,
5,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
//最大承载:maximumPoolSize+Deque
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用线程池创建线程
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok");
});
}
}finally{
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
2.CallerRunsPolicy()
在任务被拒绝添加后,会用调用execute函数的上层线程去执行被拒绝的任务。哪来的回哪去。
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2,
5,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//最大承载:maximumPoolSize+Deque
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用线程池创建线程
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok");
});
}
}finally{
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
3.DiscardPolicy()
如果超过最大承载数,让被线程池拒绝的任务直接抛弃,不会抛异常也不会执行。
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2,
5,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy());
//最大承载:maximumPoolSize+Deque
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用线程池创建线程
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok");
});
}
}finally{
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
4.DiscardOldestPolicy()
当任务被拒绝添加时,会抛弃任务队列中最旧的任务也就是最先加入队列的,再把这个新任务添加进去。
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2,
5,
3,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
//最大承载:maximumPoolSize+Deque
try{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//使用线程池创建线程
threadPool.execute(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ok");
});
}
}finally{
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
五、CPU密集型
获取CPU核数
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
几核CPU,maximumPoolSize就是几,可以保持CPU效率最高。
六、IO密集型
判断程序中十分耗IO的线程,maximumPoolSize一般设置为他的两倍。