C for Graphic:Ugui CanvasRenderer Effect
前几天没想准备做点ugui效果就又找到unity的bug了,那就是和上一篇相关,我想对ugui line制作一些简单的动效,结果发现uivertex的uv字段不生效,同时发现FillMesh函数也无效,那么对我来说Graphic.OnPopulateMesh就没用了,我得想别的办法。
下面来详细说明一下我碰到的问题:
我想给绘制的line加上shader动效,所以需要uv0参数,我按照如下图计算出uv0:

代码如下:
/// 我为了测试,把uv0-3都赋值了,顺便做了个uv sample shader,如下:
Shader "Ugui/UguiUVSampleShader"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_MainColor("Main Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Transparent" "Queue"="Transparent" }
LOD 100
Pass
{
Cull OFF
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
float4 _MainColor;
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
fixed4 col = tex2D(_MainTex, i.uv);
return col;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
结果???没效果?如图:
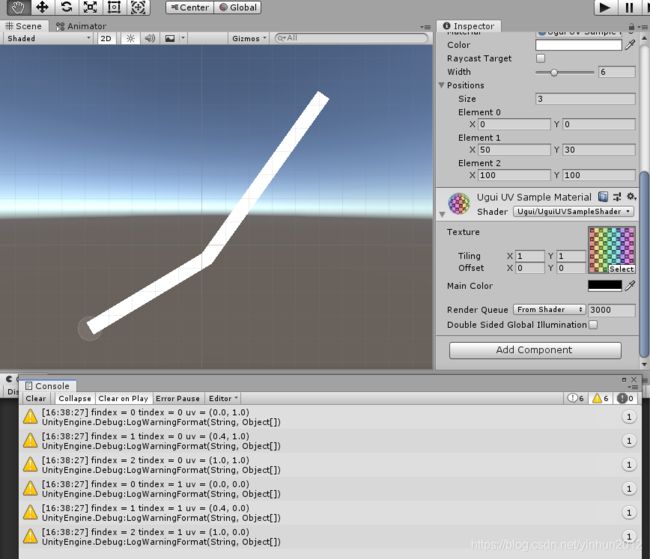
我顺便试了下color属性,发现有效果:
vertex.color = Color.green;
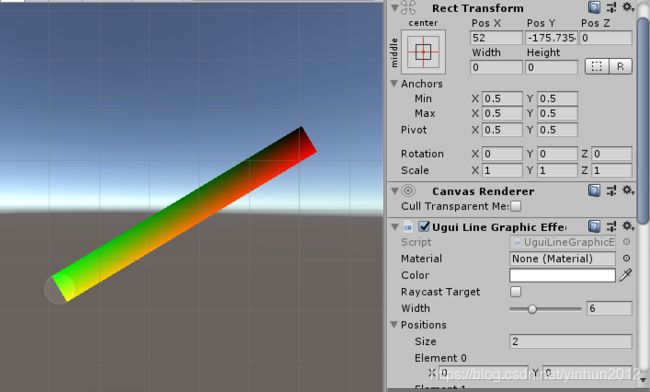
我给上面四个顶点赋值了不同的颜色,就正常渲染了,但是,这并不满足我的需求,用c#写动效,效率不见得ok。
同时我测试了一下FillMesh方式,如下:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class UguiMeshGraphic : Graphic
{
protected override void OnPopulateMesh(VertexHelper vh)
{
//base.OnPopulateMesh(vh);
vh.Clear();
Mesh mesh = new Mesh();
mesh.vertices = new Vector3[] { new Vector3(0, 0), new Vector3(0, 100), new Vector3(100, 100), new Vector3(100, 0) };
mesh.uv = new Vector2[] { new Vector2(0, 0), new Vector2(0, 1), new Vector2(1, 1), new Vector2(1, 0) };
mesh.triangles = new int[]
{
0,1,2,
0,2,3,
};
vh.FillMesh(mesh);
}
}
结果???别说uv sample了,连网格都构建不出来,如下:

好吧,unity2018.4.12f1 personal版本,不知道是不是版本问题(或是我的问题),我也没兴趣切换别的版本测试了(有兴趣的同学可以试试),毕竟如果这是个随机的bug,那就算我以后切换了版本还是可能遇到问题。这样的话,UnityEngine.UI.Graphic.OnPopulateMesh,我们就可以放弃了,另想他法。
还好CanvasRenderer这个组件照样能满足我们的ugui渲染需求,下面测试一下:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class UguiTestMeshRender : MonoBehaviour
{
public Material mat;
private void Start()
{
Mesh mesh = new Mesh();
mesh.vertices = new Vector3[] { new Vector3(0, 0), new Vector3(0, 100), new Vector3(100, 100), new Vector3(100, 0) };
mesh.uv = new Vector2[] { new Vector2(0, 0), new Vector2(0, 1), new Vector2(1, 1), new Vector2(1, 0) };
mesh.triangles = new int[]
{
0,1,2,
0,2,3,
};
CanvasRenderer crender = GetComponent<CanvasRenderer>();
crender.SetMaterial(mat, null);
crender.SetMesh(mesh);
}
}
Good,需要的效果直接就出来了:

那么,接下来我们改版c#代码:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class UguiLineRenderer : MonoBehaviour
{
[Range(0, 20)]
public float width = 10f;
public Vector2[] positions;
public Material mat;
private float[] lengths;
public bool isUpdate = false;
private CanvasRenderer canvasRender;
void Start()
{
canvasRender = GetComponent<CanvasRenderer>();
}
void Update()
{
if (isUpdate)
{
DrawUpdate();
isUpdate = false;
}
}
/// 效果如下:
这样的话,uv0就生效了,那么接下来我们写两个effect shader,比如虚线:
Shader "Ugui/UguiDottedLineShader"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_MainColor("Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_Pow("Pow",Range(0,1000)) = 200
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Transparent" "Queue"="Transparent" }
LOD 100
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
float4 _MainColor;
float _Pow;
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
fixed4 col = _MainColor;
float s = sin(i.uv*_Pow);
if(s<0)
{
discard;
}
return col;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
效果如下:
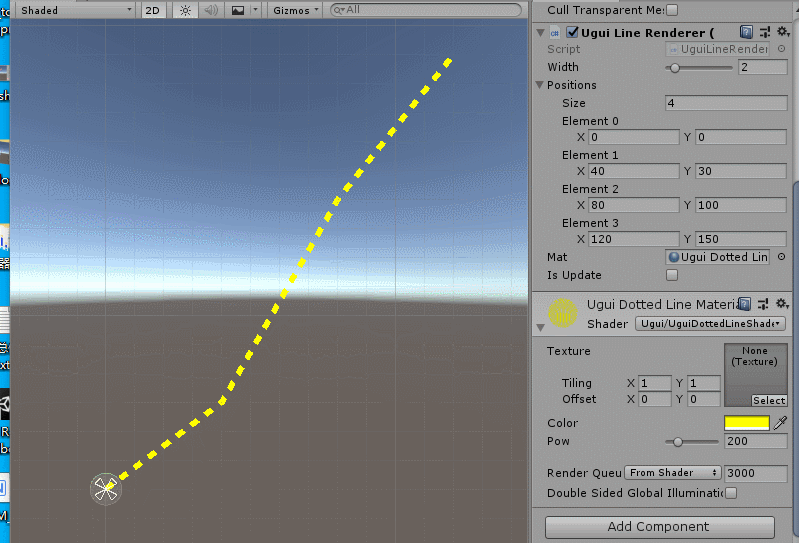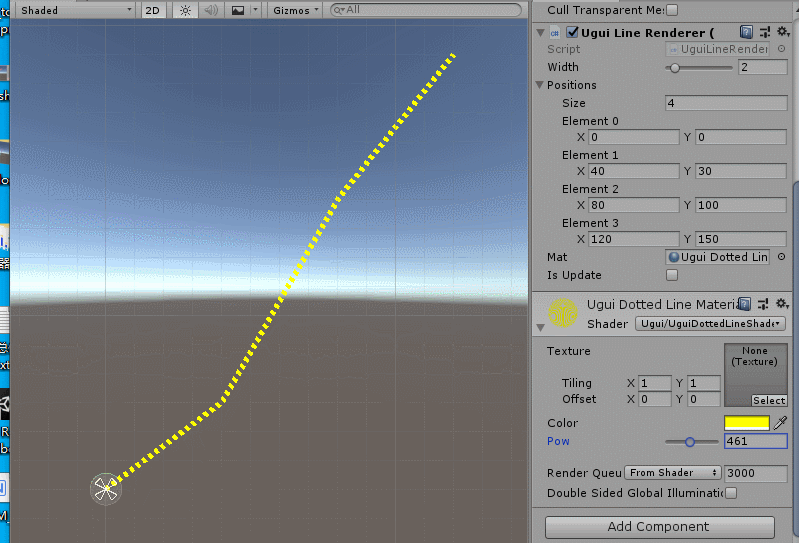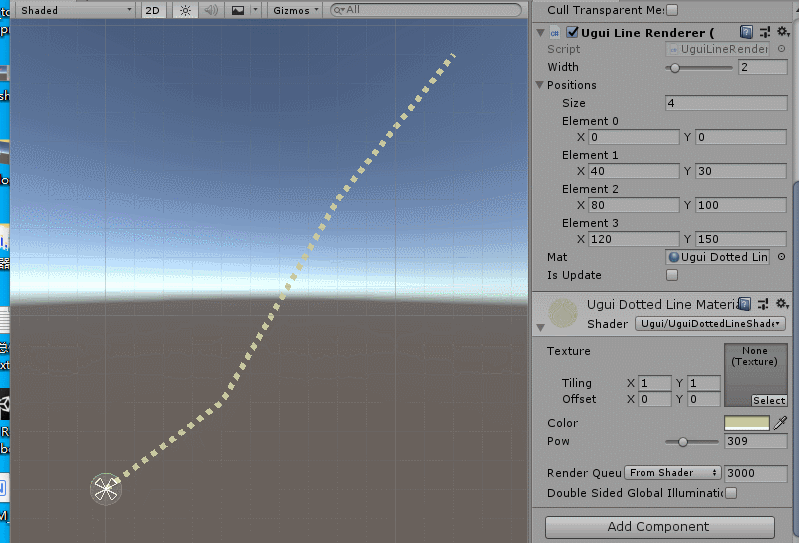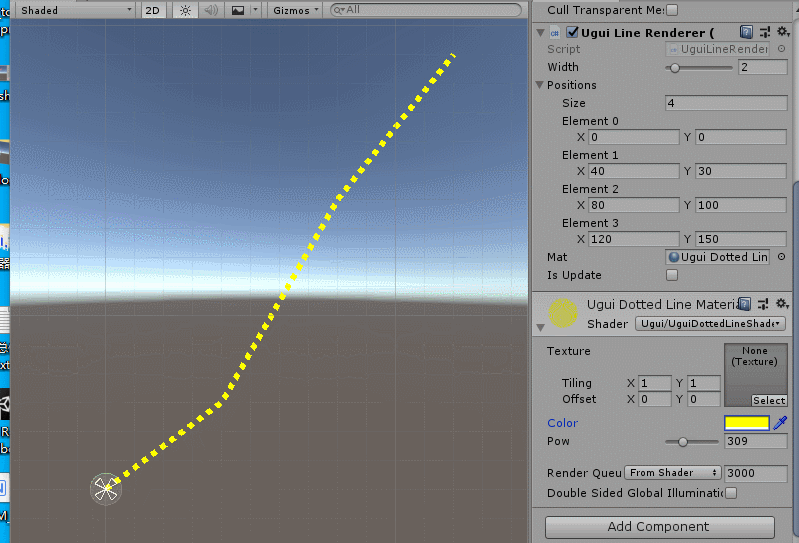
效果原理也简单:就是根据sin(uv.x)进行周期性的discard pixel,就可以做成虚线。
再来一个移动的效果:
Shader "Ugui/UguiLineMotionShader"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
_BgColor("Bg Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_ForeColor("Fore Color",Color) = (1,1,1,1)
_Speed("Speed",Range(0,2)) = 1
_Pow("Pow",Range(0,100)) = 10
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Transparent" "Queue"="Transparent" }
LOD 100
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
float4 _BgColor;
float4 _ForeColor;
float _Speed;
float _Pow;
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
i.uv.x -= _Time.y * _Speed;
float s = sin(i.uv.x * _Pow);
fixed4 col = lerp(_ForeColor,_BgColor,s);
return col;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
效果如下:

原理也比较简单:就是根据uv.x进行偏移,通过sin函数制作周期的波峰,就行了。
好,今天就到这里,以后有时间继续。