二叉树相关的简单递归oj
二叉树相关的简单递归oj
- 前言
- 题目
-
- 二叉树的前序遍历
- 相同的树判断
- 单值二叉树
- 对称二叉树
- 另一棵树的子树
- 创建二叉树并遍历
前言
这篇博客主要是博主感觉对二叉树oj题目不太熟悉,随便整理的一下题目和解答,方便复习,所以讲题部分主要以我自己以及为我以后便于复习的简便语言来描述,看官可以当作的题目随便刷一下,如果看不懂可以自己画一下递归展开图。
题目
二叉树的前序遍历
oj链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/


这道题并不难,难的是给了个参数returnSize
其实这里就是要求,以前序遍历的排列方式,将二叉树的值放入至一个数组中,并且返回数组大小就好。
int CountTreeNode(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
return 1+CountTreeNode(root->right)+CountTreeNode(root->left);
}
void printTN(struct TreeNode* root,int* i,int* a)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
a[(*i)]=root->val;
(*i)++;
printTN(root->left,i,a);
printTN(root->right,i,a);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize=CountTreeNode(root);
int* ptr=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
int i=0;
printTN(root,&i,ptr);
return ptr;
}
相似的还有前序遍历,后序遍历,这里就不放出来了。
相同的树判断
oj链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/
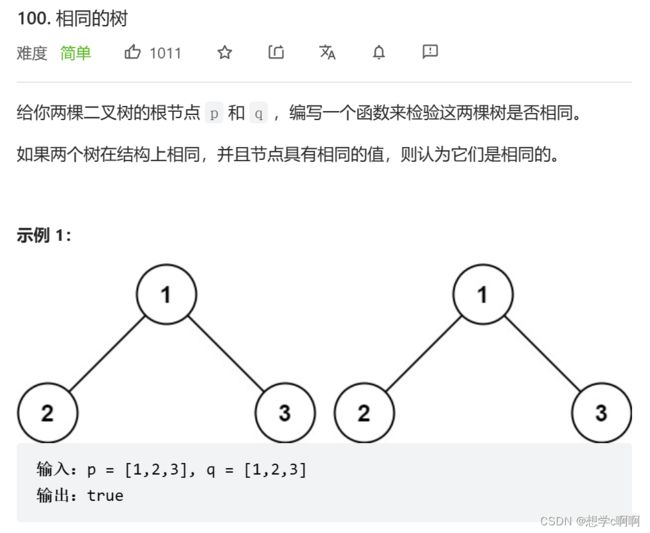
这个题目不要用遍历的角度去看,虽然实现角度确实是遍历,但是为了方便理解还是用分治方法去思考
让q和p一起去递归,一起走q和p的左子树比较,然后走右子树的比较,如果一样,返回他们对应的布尔值,不一样就返回false。
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)
return false;
if(q->val!=p->val)
return false;
return (isSameTree(q->left,p->left)&&isSameTree(q->right,p->right));
}
单值二叉树
oj链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/univalued-binary-tree/

这道题让根值与左子树以及右子树的值比较就好,同时要判断左子树和右子树是否为空,然后同时比较返回左子树和右子树的比较值就好。
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if((root->left)!=NULL&&root->val!=root->left->val)
return false;
if((root->right)!=NULL&&root->val!=root->right->val)
return false;
return (isUnivalTree(root->left)&&isUnivalTree(root->right));
}
对称二叉树
oj链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/

这道题很简单
bool issame(struct TreeNode* left,struct TreeNode* right)
{
if(left==NULL&&right==NULL)
return true;
if(left==NULL||right==NULL)
return false;
if(left->val!=right->val)
return false;
return (issame(left->left,right->right)&&issame(left->right,right->left));
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return issame(root->left,root->right);
}
另一棵树的子树
oj链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/

这道题递归套递归就好
bool sameTreeNode(struct TreeNode* root,struct TreeNode* subRoot)
{
if(root==NULL&&subRoot==NULL)
return true;
if(root==NULL||subRoot==NULL)
return false;
if(root->val!=subRoot->val)
return false;
return (sameTreeNode(root->left,subRoot->left)
&&sameTreeNode(root->right,subRoot->right));
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)
{
if(root==NULL)
return false;
if(sameTreeNode(root,subRoot))
return true;
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)
|| isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
创建二叉树并遍历
oj链:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/4b91205483694f449f94c179883c1fef?tpId=60&&tqId=29483&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/tsing-kaoyan/question-ranking
这道题就稍微创建有点难,但而不至于到较难
#include