SpringBoot 学习(六)Shiro
6. Shiro
6.1 简介
6.1.1 什么是Shiro
- Apache Shiro 是一个 Java 的安全权限框架。
- Shiro 可以应用在 JavaSE 和 JavaEE 环境中。
- Shiro 可以完成认证、授权、加密、会话管理、web 集成、缓存等。
- 下载地址:http://shiro.apache.org/
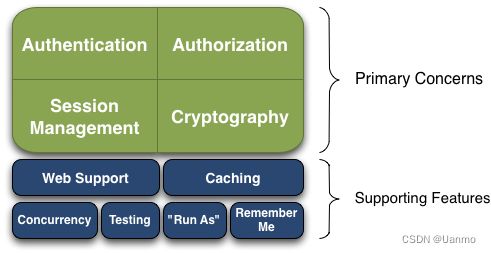
6.1.2 能力
- Authentication:身份认证、登录,验证用户身份。
- Authorization:授权,即权限验证。
- Session Manager:会话管理,在用户登录后且没有退出之前,用户所有的信息都在此次对话中;会话可以应用在 JavaSE 和 JavaWeb 环境中。
- Cryptography:加密,保护数据安全性,如密码加密。
- Web Support:Web 支持,使 Web环境的集成更加容易。
- Caching:缓存。
- Concurrency:Shiro 支持多线程应用的并发验证,即在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能将权限传播过去。
- Testing:测试支持。
- Run As:允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份访问。
- Remember me:记住用户名和密码。
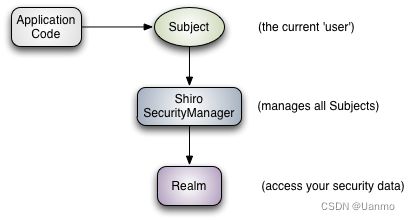
6.1.3 外部架构
-
Shiro有三大核心组件,即Subject、SecurityManager和Realm
-
Subject: 认证主体。应用代码直接交互的对象是 Subject,Subject 代表了当前的用户。包含 Principals 和Credentials 两个信息。
-
Pricipals: 代表身份。可以是用户名、邮件、手机号码等等,用来标识一个登陆主题的身份。
-
Credentials: 代表凭证。常见的有密码、数字证书等等。
-
-
SecurityManager: 为安全管理员。是 Shiro 架构的核心。与 Subject 的所有交互都会委托给 SecurityManager, Subject 相当于是一个门面,而 SecurityManager 才是真正的执行者。它负责与 Shiro 的其他组件进行交互。
-
**Realm:**是一个域。充当了 Shiro 与应用安全数据间的“桥梁”。Shiro 从 Realm 中获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说 SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从 Realm 中获取相应的用户进行比较,来确定用户的身份是否合法;也需要从 Realm 得到用户相应的角色、权限,进行验证用户的操作是否能过进行,可以把Realm 看成 DataSource,即安全数据源。
-
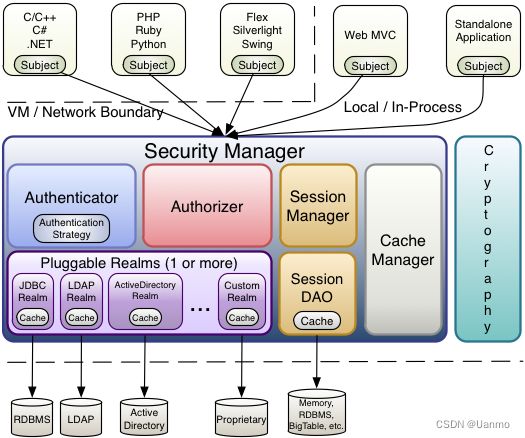
6.1.4 外部架构
- Subject: 主体,主体可以是任何可以与应用交互的“用户”
- SecurityManager: 是Shiro的核心,所有具体的交互都需通过SecurityManager进行,它管理所有的Subject,且负责进行认证授权,会话,及缓存的管理。
- **Authenticator:**负责主体认证。当用户尝试登录时,该逻辑被Authenticatior执行。Authenticator知道如何与一个或多个Realm协调来存储相关的用户。从Realm中获得的数据被用来验证用户的身份来保证用户确实是他们所说的他们是谁。
- Autentication Strategy:如果不止一个Realm被配置,其会协调这些Realm来决定身份认证尝试成功或失败下的条件(比如,如果一个Realm成功,而其他的失败,是否该尝试成功?)
- **Authorizer:**负责在应用程序中决定用户的访问控制。它是一种最终判定用户是否被允许做某事的机制。与Authenticator相似,Authorizer也知道如何协调多个后台数据源来访问角色恶化权限信息。Authorizer使用该信息来准确度的决定用户是否被允许执行给定的动作。
- SessionManager:知道如何去创建及管理用户Session生命周期来为所有环境下的用户提供一个强健的session体验。
- SessionDAO:代表SessionManager执行Session持久化操作。允许数据存储被插入到会员管理的基础之中。
- CacheManager:创建并管理其他Shiro组件使用的Cache实例声明周期。因为Shiro能访问许多后台数据源,由于身份验证、授权和会话管理,缓存在框架中一直是一流 的架构功能,用来在通过还是使用这些数据源时提高性能。
- Cryptograhy:是对企业安全框架的一个自然的补充。密码模块,shrio提高了一些常见的加密组件用于密码加密,解密等。
6.2 快速开始
(1) 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4jartifactId>
<version>1.7.21version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4jgroupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12artifactId>
<version>1.7.21version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
dependencies>
(2) 配置文件
# resources/log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m %n
# General Apache libraries
log4j.logger.org.apache=WARN
# Spring
log4j.logger.org.springframework=WARN
# Default Shiro logging
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro=INFO
# Disable verbose logging
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.util.ThreadContext=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCache=WARN
# resources/shiro.ini
[users]
# user 'root' with password 'secret' and the 'admin' role
root = secret, admin
# user 'guest' with the password 'guest' and the 'guest' role
guest = guest, guest
# user 'presidentskroob' with password '12345' ("That's the same combination on
# my luggage!!!" ;)), and role 'president'
presidentskroob = 12345, president
# user 'darkhelmet' with password 'ludicrousspeed' and roles 'darklord' and 'schwartz'
darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz
# user 'lonestarr' with password 'vespa' and roles 'goodguy' and 'schwartz'
lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Roles with assigned permissions
#
# Each line conforms to the format defined in the
# org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setRoleDefinitions JavaDoc
# -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
[roles]
# 'admin' role has all permissions, indicated by the wildcard '*'
admin = *
# The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber:
schwartz = lightsaber:*
# The 'goodguy' role is allowed to 'drive' (action) the winnebago (type) with
# license plate 'eagle5' (instance specific id)
goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5
(3) 测试
// java/Quickstart.java
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* Simple Quickstart application showing how to use Shiro's API.
*
* @since 0.9 RC2
*/
public class Quickstart {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Quickstart.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The easiest way to create a Shiro SecurityManager with configured
// realms, users, roles and permissions is to use the simple INI config.
// We'll do that by using a factory that can ingest a .ini file and
// return a SecurityManager instance:
// Use the shiro.ini file at the root of the classpath
// (file: and url: prefixes load from files and urls respectively):
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
// for this simple example quickstart, make the SecurityManager
// accessible as a JVM singleton. Most applications wouldn't do this
// and instead rely on their container configuration or web.xml for
// webapps. That is outside the scope of this simple quickstart, so
// we'll just do the bare minimum so you can continue to get a feel
// for things.
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// Now that a simple Shiro environment is set up, let's see what you can do:
// get the currently executing user:
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// let's login the current user so we can check against roles and permissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
//unexpected condition? error?
}
}
//say who they are:
//print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully.");
//test a role:
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
}
//test a typed permission (not instance-level)
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
}
//a (very powerful) Instance Level permission:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " +
"Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");
}
//all done - log out!
currentUser.logout();
System.exit(0);
}
}
6.3 springboot 整合 shiro
(1) 导入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId>
<artifactId>shiro-springartifactId>
<version>1.4.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
(2) shiro 配置
// ShiroConfig.java
public class ShiroConfig {
// 创建 ShiroFilterFactoryBean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
return bean;
}
// 创建 DefaultWebSecurityManager
@Bean(name = "securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm) {
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
// 关联 userRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
// 创建 realm 对象,需要自定义类
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm() {
return new UserRealm();
}
}
(3) 自定义 UserRealm
// UserRealm.java
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
// 授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了 => 授权 doGetAuthorizationInfo");
return null;
}
// 认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了 => 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo");
return null;
}
}
(4) 路由控制器
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping({"/", "/index"})
public String toIndex(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "hello, Shiro");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/toAdd")
public String toAdd() {
return "/user/add";
}
@RequestMapping("/toUpdate")
public String toUpdate() {
return "/user/update";
}
}
(5) html 页面
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>首页h1>
<p th:text="${msg}">p>
<hr>
<a th:href="@{/toAdd}">adda> | <a th:href="@{/toUpdate}">Updatea>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Updatetitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>Updateh1>
body>
html>
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Updatetitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>Updateh1>
body>
html>
6.4 登录拦截
(1) shiro 配置
// 添加 Shiro 内置过滤器
/*
anon: 无需认证即可访问
authc: 必须认证才可访问
user: 必须拥有 remember me 功能才可使用
perms: 拥有对某个资源的权限才可访问
role: 拥有某个角色权限才可访问
*/
// 拦截
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 前面的参数为控制器接口名
// filterMap.put("/user/add", "authc");
// filterMap.put("/user/update", "authc");
filterMap.put("/user/*", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
// 设置登录请求
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
(2) 路由控制器
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin() {
return "login";
}
(3) html 页面
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录title>
head>
<body>
<h1>登录h1>
<hr>
<form action="">
<p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username">p>
<p>密码:<input type="text" name="password">p>
<p><input type="submit">p>
form>
body>
html>
6.5 用户认证
(1) 路由控制器
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password, Model model) {
// 获取当前用户
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 封装用户的登录数据
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
try {
subject.login(token); // 执行登录方法
return "index";
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) { // 用户名不存在
model.addAttribute("msg", "用户名错误");
return "login";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) { // 密码错误
model.addAttribute("msg", "密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
(2) html 页面
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<p th:text="${msg}" style="color: red;">p>
<form th:action="@{/login}">
(3) UserRealm 认证
// 认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了 => 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo");
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken)token;
if (!userToken.getUsername().equals(username)) {
return null; // 抛出异常 UnknownAccountException
}
// shiro 密码认证
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("", password, "");
}
6.6 shiro 整合 mybatis
(1) 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.12version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.16.10version>
dependency>
(2) 配置数据源
# application.yml
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 981030
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# SpringBoot 默认不注入以下属性值
# Druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
# 配置统计监控拦截 filters
# stat: 监控统计; log4j: 日志记录; wall: 防御 sql 注入
# 如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.Log4j.Priority
# 则导入 log4j 依赖即可, Maven 地址: https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/Log4j
filters: stat, wall, log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
(3) 配置 mybatis
# application.properties
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.why.pojo
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
(4) 编写实体类
// pojo
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pw;
// 权限格式:user:add
private String perms;
}
(5) 编写 mapper 接口
// mapper
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
public User queryUserByName(String name);
}
(6) 编写 mapper.xml 文件
<mapper namespace="com.why.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="queryUserByName" parameterType="String" resultType="User">
select * from mybatis.user where name = #{name};
select>
mapper>
(7) 编写 service 接口
// service
public interface UserService {
public User queryUserByName(String name);
}
(8) 编写 service 实现类
// service/impl
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public User queryUserByName(String name) {
return userMapper.queryUserByName(name);
}
}
(9) 用户认证
// config/UserRealm
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了 => 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo");
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken)token;
// 连接真实的数据库
User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername());
if (user == null) {
return null; // 抛出异常 UnknownAccountException
}
// shiro 密码认证
// 密码加密 md5 md5盐值加密
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user, user.getPw(), user.getName());
}
(10) 用户授权
// config/UserRealm
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principal) {
System.out.println("执行了 => 授权 doGetAuthorizationInfo");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
// info.addStringPermission("user:add");
// 获取当前用户
User user = (User)principal.getPrimaryPrincipal();
if (user.getPerms() != null) {
info.addStringPermission(user.getPerms());
}
return info;
}
(11) 权限设置
// config/ShiroConfig
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
// 拦截
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 权限设置
// 必须拥有 add 权限的 user 用户才可以访问/user/add路径的控制器
filterMap.put("/user/add", "perms[user:add]");
filterMap.put("/user/update", "perms[user:update]");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
// 设置未授权请求
bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/unauth");
return bean;
}
(12) 添加控制器
// 无授权页面跳转
@RequestMapping("/unauth")
@ResponseBody
public String unauthorized() {
return "未经授权,无法访问";
}
6.7 shiro 整合前端
(1) 引入约束
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:shiro="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
(2) shiro 权限控制
<div shiro:notAuthenticated="">
<a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登录a>
div>
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:add">
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">adda>
div>
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:update">
<a th:href="@{/user/update}">Updatea>
div>