统计第一个只出现两次的字符
方法一:在一个一维数组里面查询:
最直接的方法是从头到尾遍历这个字符数组的字符,当访问这个字符时,拿这个字符和后面的每个字符匹配,如果下次又找到一个字符再次出现,就表明是出现两次的字符,如果字符与n个字符,每个字符可能都会与后面的比较,这种思路的时间复杂度较高,O(N^2)
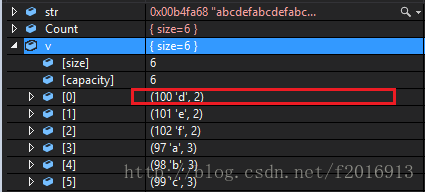
方法二:map加上排序;
思路是:将字符作为,键值,将出现的次数作为实值,那么如歌保证第一个出现的次数是两次我们需要加上仿函数来统计次数的高低.
map的底层是红黑树,而红黑树的查找时间复杂度是O(NlgN),结构比较复杂.
#includesecond;
}
};
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Compare());
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
} 
方法三:用直接定址的哈希
思路:哈希表的key值用来存放每个字符,而value值用来存放每个字符出现的次数.同时我们还需要从头到尾遍历这个字符串两次,
第一次遍历字符串时,每遍历一个字符就在哈希表所对应的项的次数加1,第二次遍历时就可以统计每个字符出现的次数,当找到次数为2时,就表明是第一次出现的字符.
时间复杂度是O(N),空间复杂度是O(1);
char FindFistTwice(char *String)
{
assert(String);
char HashTable[256] = { 0 };
int len = strlen(str);
char *pHashKey = String;
//第一次遍历将每个字符出现的次数,放到哈希表中
while (*(pHashKey) != '\0')
{
HashTable[*(pHashKey++)]++;
}
//第二次遍历找到第一个只出现两次的字符
while (*pHashKey != '\0')
{
if (HashTable[*pHashKey] == 2)
return *pHashKey;
++pHashKey;
}
return '\0';
}
int main()
{
char HashTable[] = "abcdefabcdefabc";
//char HashTable[] = "abcdefabcdefgbc";
cout << FindFistTwice(HashTable)<< endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}![]()
关于哈希表在前面我们已经介绍:http://blog.csdn.net/f2016913/article/details/70849292
同时map和set:http://blog.csdn.net/f2016913/article/details/70224249
通过前面的介绍:
总结:第一种按字符去匹配,时间复杂度较高O(N^2)
第二种:map来统计次数,同时加上sort排序,时间复杂度是O(NlgN)
第三种:直接定址的哈希:时间复杂度是O(N),空间复杂度是O(1)