springboot整合AOP实现操作日志记录功能
什么是AOP?
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。AOP能够在方法的前置,中置,后置中插入逻辑代码,将逻辑独立于业务代码之外,一处编写,多处使用。
重点名词
切面(ASPECT):横切关注点 被模块化 的特殊对象。即,它是一个类。
通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作。即,它是类中的一个方法。
目标(Target):被通知对象。
代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
切入点(PointCut):切面通知执行的 “地点”的定义。
连接点(JointPoint):与切入点匹配的执行点。
支持 5 种类型的通知注解:
@Before: 前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行,前置通知不会影响连接点的执行,除非此处抛出异常
@After: 后置通知, 在连接点正常执行完成后执行,如果连接点抛出异常,则不会执行
@AfterRunning: 返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行
@AfterThrowing: 异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后执行
@Around: 环绕通知, 围绕着方法执行,比如一个方法调用的前后。这是最强大的通知类型,能在方法调用前后自定义一些操作。
Spring AOP作用
1.拦截器
2.事务
3.日志记录
4.权限验证
5.等等
使用Spring AOP
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
dependency>
由于代码中有JSON相关的操作,还需导入(可自行选择,若不加,需在代码中删除相关操作)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.47version>
dependency>
创建自定义注解类Log
在需要日志记录的接口方法(controller)增加该注解。当调用该接口时,变会进行对应的逻辑处理。
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Log {
/**模块*/
String module() default "";
/**描述*/
String description() default "";
}
创建LogAspect类
注意:不是所有的通知都需要,可按照需要进行相应的删减
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class LogAspect{
//切入点。表示在标有@Log注解的方法中进行切入,com.example.demo.log.Log为Log类所在的路径,需自行修改
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.demo.log.Log)") //
public void logPointCut(){}
//环绕通知, 围绕着方法执行
@Around("logPointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
//在pjp.proceed()之前会运行的逻辑任务,相当于@Before
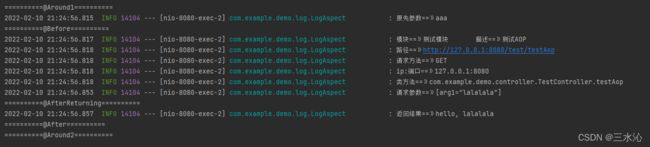
System.out.println("==========@Around1==========");
//如果写了@Around标注的方法,只有返回了obj,才会开始往下运行,依次调用@Before,@After等方法,@AfterReturning的response才获取返回的结果,否则为null
//pjp.proceed()括号中为调用对应接口时填入的参数,如果不填写,则默认原来的参数,(可以在此修改参数)
//获取参数
Object[] objects = pjp.getArgs();
log.info("原先参数==》" + objects[0].toString());
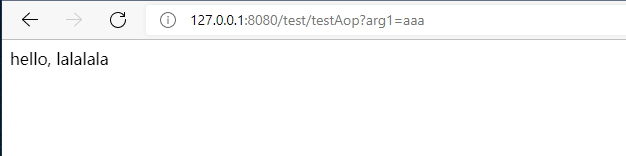
objects[0] = "lalalala";
Object obj=pjp.proceed(objects);
//在pjp.proceed()之后会运行的逻辑任务,类似于@After
System.out.println("==========@Around2==========");
return obj;
}
//前置通知, 在方法执行之前执行
@Before("logPointCut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("==========@Before==========");
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Method method = currentMethod(joinPoint,methodName);
Log logInfo = method.getAnnotation(Log.class);
//@Log中的module内容
String module = logInfo.module();
//@Log中的description内容
String description = logInfo.description();
//@Log中的module字段
log.info("模块==》" + module + " " + "描述==》" + description);
// =====接收到请求,记录请求内容=====
//获取请求的request信息
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
// 记录下请求内容
//路径
log.info("路径==》" + request.getRequestURL().toString());
//请求方法
log.info("请求方法==》" + request.getMethod());
//ip和端口
log.info("ip:端口==》" + request.getRemoteAddr() + ":" + request.getServerPort());
//类方法
log.info("类方法==》" + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
//请求参数
StringBuilder requestLog = new StringBuilder();
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
String[] paramNames = ((MethodSignature) signature).getParameterNames();
Object[] paramValues = joinPoint.getArgs();
int paramLength = null == paramNames ? 0 : paramNames.length;
if (paramLength == 0) {
requestLog.append("{}");
} else {
requestLog.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < paramLength - 1; i++) {
requestLog.append(paramNames[i]).append("=").append(JSON.toJSONString(paramValues[i])).append(",");
}
requestLog.append(paramNames[paramLength - 1]).append("=").append(JSON.toJSONString(paramValues[paramLength - 1])).append("]");
}
log.info("请求参数==》" + requestLog);
}
//后置通知, 在连接点正常执行完成后执行
@After("logPointCut()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("==========@After==========");
}
//异常通知, 在方法抛出异常之后执行
@AfterThrowing("logPointCut()")
public void beferException() {
System.out.println("==========@AfterThrowing==========");
}
//返回通知, 在方法返回结果之后执行
//returning = "response",response为接口返回的结果
@AfterReturning(returning = "response", pointcut = "logPointCut()")
public void doAfter(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object response) throws Exception {
System.out.println("==========@AfterReturning==========");
log.info("返回结果==》" + response.toString());
}
/**
* 获取当前执行的方法
*
* @param joinPoint 连接点
* @param methodName 方法名称
* @return 方法
*/
private Method currentMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, String methodName) {
/**
* 获取目标类的所有方法,找到当前要执行的方法
*/
Method[] methods = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getMethods();
Method resultMethod = null;
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.getName().equals(methodName)) {
resultMethod = method;
break;
}
}
return resultMethod;
}
}
测试Spring AOP
创建TestController类
在需要记录的接口方法上添加类似@Log(module = “测试模块”, description = “测试AOP”)的注解
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
@Log(module = "测试模块", description = "测试AOP")
@GetMapping("/testAop")
public String testAop(String arg1){
return "hello, " + arg1;
}
}