执行环境:Google Colab
!pip install basemap
import os
import json
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
!git clone https://github.com/JeffereyWu/flood-dataset.git
%set_env LOCAL_DATA_DIR=/content/flood-dataset
image_dir=os.path.join(os.getenv('LOCAL_DATA_DIR'), 'images')
mask_dir=os.path.join(os.getenv('LOCAL_DATA_DIR'), 'masks')
- 创建图像和掩码文件夹的完整路径,帮助程序在后续的操作中定位和访问这些文件夹中的数据。
统计每个地区的图像数量
def count_num_images(file_dir):
"""
This function returns a dictionary representing the count of images for each region as the key.
"""
file_list=os.listdir(file_dir)
region_count={}
for file_name in file_list:
region=file_name.split('_')[0]
if (len(file_name.split('.'))==2) and (region in region_count):
region_count[region]+=1
elif len(file_name.split('.'))==2:
region_count[region]=1
return region_count
- 首先使用 _ 符号分割文件名,以获取地区的名称。
- 然后,检查文件名是否包含扩展名(扩展名由一个点 . 分隔),如果包含扩展名并且地区在 region_count 字典中已经存在,那么就增加该地区的图像数量;
- 如果扩展名存在但地区不在字典中,就将该地区的图像数量初始化为1。
- 文件目录如下图所示:

统计不同地区的图像和掩码数量
images_count=count_num_images(os.path.join(image_dir, 'all_images'))
masks_count=count_num_images(os.path.join(mask_dir, 'all_masks'))
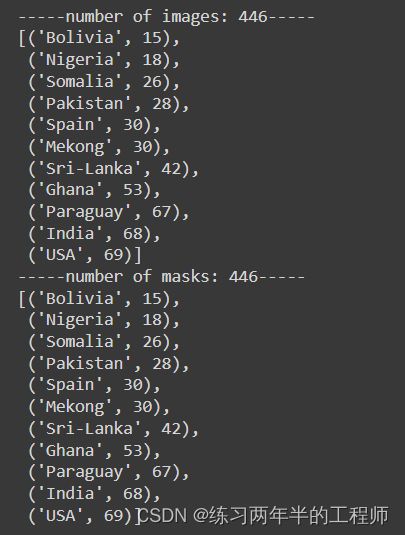
print(f'-----number of images: {sum(images_count.values())}-----')
display(sorted(images_count.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]))
print(f'-----number of masks: {sum(masks_count.values())}-----')
display(sorted(masks_count.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]))
- 使用 sorted 函数,以字典项的value(图像数量)作为排序的关键,然后调用 display 函数将排序后的结果显示出来。
输出为:
从目录文件中提取图像的边界坐标
def get_coordinates(catalog_dir):
"""
This function returns a list of boundaries for every image as [[lon, lat], [lon, lat], [lon, lat], etc.] in the catalog.
"""
catalog_list=os.listdir(catalog_dir)
all_coordinates=[]
for catalog in catalog_list:
if len(catalog.split('.'))==1:
catalog_path=f'{catalog_dir}/{catalog}/{catalog}.json'
with open(catalog_path) as f:
catalog_json=json.load(f)
coordinates_list=catalog_json['geometry']['coordinates'][0]
lon=[coordinates[0] for coordinates in coordinates_list]
all_coordinates.append(lon)
lat=[coordinates[1] for coordinates in coordinates_list]
all_coordinates.append(lat)
return all_coordinates
- 检查文件名是否包含扩展名,以确定它是否是一个目录。如果是目录,构建目录文件的路径并尝试读取该目录文件。
- 一旦成功读取目录文件,解析文件中的坐标信息。具体来说,从 JSON 文件中提取了坐标信息,然后将经度(lon)和纬度(lat)分别提取出来,并将它们添加到 all_coordinates 列表中。
- JSON文件的内容如下:

通过将图像的坐标信息映射到地图上,以便用户更好地理解图像在地理空间上的分布
image_catalog_dir=os.path.join(os.getenv('LOCAL_DATA_DIR'), 'catalog', 'sen1floods11_hand_labeled_source')
image_coordinates_list=get_coordinates(image_catalog_dir)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
m=Basemap(projection='merc', llcrnrlat=-80, urcrnrlat=80, llcrnrlon=-180, urcrnrlon=180)
m.bluemarble(scale=0.2)
m.drawcoastlines(color='white', linewidth=0.2)
m.drawparallels(range(-90, 90, 10), labels=[0, 1, 0, 0], color='white', textcolor='black')
m.drawmeridians(range(-180, 180, 10), labels=[0, 0, 0, 1], color='white', textcolor='black', rotation=90)
image_lon=[image_coordinates_list[x] for x in range(len(image_coordinates_list)) if x%2==0]
image_lon=np.concatenate(image_lon).ravel()
image_lat=[image_coordinates_list[x] for x in range(len(image_coordinates_list)) if x%2==1]
image_lat=np.concatenate(image_lat).ravel()
x, y=m(image_lon, image_lat)
plt.scatter(x, y, s=10, marker='o', color='Red')
plt.title('Data Distribution')
plt.show()
- 创建一个 Basemap 对象,定义地图的投影方式(mercator 投影)和地图的范围(经度和纬度的范围)。Mercator 投影的主要特点是将地球上的经纬度坐标映射到平面上,使得经线和纬线在地图上呈直线。
从目录文件中获取图像的范围
def get_extent(file_path):
"""
This function returns the extent as [left, right, bottom, top] for a given image.
"""
with open(file_path) as f:
catalog_json=json.load(f)
coordinates=catalog_json['geometry']['coordinates'][0]
coordinates=np.array(coordinates)
left=np.min(coordinates[:, 0])
right=np.max(coordinates[:, 0])
bottom=np.min(coordinates[:, 1])
top=np.max(coordinates[:, 1])
return left, right, bottom, top
- 从坐标数组中提取了最小经度、最大经度、最小纬度和最大纬度。这四个值分别表示图像的左、右、底和顶边界。
根据指定的地区以及图像或掩码类型,绘制相应的图像或掩码
def tiles_by_region(region_name, plot_type='images'):
catalog_dir=os.path.join(os.getenv('LOCAL_DATA_DIR'), 'catalog', 'sen1floods11_hand_labeled_source')
if plot_type=='images':
dir=os.path.join(image_dir, 'all_images')
cmap='viridis'
elif plot_type=='masks':
dir=os.path.join(mask_dir, 'all_masks')
cmap='gray'
else:
raise Exception('Bad Plot Type')
x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max=181, -181, 91, -91
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(15, 15))
ax=plt.subplot(111)
file_list=os.listdir(dir)
for each_file in file_list:
if (each_file.split('.')[-1]=='png') & (each_file.split('_')[0]==region_name):
extent=get_extent(f"{catalog_dir}/{each_file.split('.')[0]}/{each_file.split('.')[0]}.json")
x_min, x_max=min(extent[0], x_min), max(extent[1], x_max)
y_min, y_max=min(extent[2], y_min), max(extent[3], y_max)
image=mpimg.imread(f'{dir}/{each_file}')
plt.imshow(image, extent=extent, cmap=cmap)
ax.set_xlim([x_min, x_max])
ax.set_ylim([y_min, y_max])
plt.show()
tiles_by_region(region_name='Spain', plot_type='images')


