Docker版Grafana整合InfluxDB看这一篇就够了(2020全网最详细教程)
本文分为4段为您详细讲解Docker版Grafana集成influxdb监控数据
文章目录
-
- docker安装
-
-
- 卸载
- 安装
- 国内镜像配置
-
- Docker整合influxDB
-
- influxDB介绍
- influxDB安装
- influxDB配置
- 数据插入
- 客户端工具
- 常用InfluxQL
- 代码批量插入
-
- pom.xml
- application.yml
- Java代码
- Docker安装Grafana整合influxDB
-
- Grafana介绍
- Grafana安装
- 配置influxDB数据源
- 创建Dashboard
- 数据集成测试
docker安装
卸载
如果之前安装过Docker需要卸载可以参照如下命令
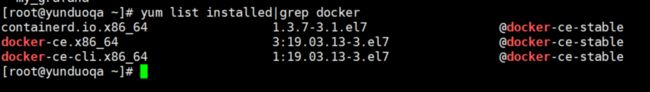
# 列出当前docker相关的安装包
$ yum list installed|grep docker
containerd.io.x86_64 1.3.7-3.1.el7 @docker-ce-stable
docker-ce.x86_64 3:19.03.13-3.el7 @docker-ce-stable
docker-ce-cli.x86_64 1:19.03.13-3.el7 @docker-ce-stable
# 卸载对应的包
$ yum -y remove containerd.io.x86_64
$ yum -y remove docker-ce.x86_64
$ yum -y remove docker-ce-cli.x86_64
安装
注意:且Docker 要求操作系统必须为64位,且centos内核版本为3.1及以上
-
查看系统内核
$ uname -r 3.10.0-1062.el7.x86_6 # 我这里高于3.1 -
保证yum包是最新
# 使用root执行,更新到最新 $ yum update -
列出可安装的docker包
# 列出可以按照的docker包 $ yum list docker-ce --showduplicates | sort -r -
安装
-
指定版本安装
$ yum list docker-ce.x86_64 --showduplicates | sort -r -
直接安装最新版
$ yum install docker-ce -y
-
-
查看当前版本
$ docker version Client: Docker Engine - Community Version: 19.03.13 API version: 1.40 Go version: go1.13.15 Git commit: 4484c46d9d Built: Wed Sep 16 17:03:45 2020 OS/Arch: linux/amd64 Experimental: false Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running? # 此处需要重启 -
不能连接到
Docker daemon异常装完后使用docker命令后会提示异常 Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running? 需要重启下docker -
重启
$ service docker restart -
配置开机启动
$ systemctl enable docker
国内镜像配置
-
找到
/etc/docker目录下的daemon.json文件进行编辑,输入如下内容{ "registry-mirrors": ["https://9cpn8tt6.mirror.aliyuncs.com"] } -
如果没有该文件,可自行创建,也可以使用如下命令
tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF' { "registry-mirrors": ["https://9cpn8tt6.mirror.aliyuncs.com"] } EOF -
重启
docker
Docker整合influxDB
前面我们已经学习了Docker的安装和相关命令,接下来,我们只讲解influxdb的内容
InfluxDB是一个由InfluxData开发的开源时序型数据。它由Go写成,着力于高性能地查询与存储时序型数据。InfluxDB被广泛应用于存储系统的监控数据,IoT行业的实时数据等场景。
influxDB介绍
InfluxDB(时序数据库),常用的一种使用场景:监控数据统计。每毫秒记录一下电脑内存的使用情况,然后就可以根据统计的数据,利用图形化界面(InfluxDB V1一般配合Grafana)制作内存使用情况的折线图;
可以理解为按时间记录一些数据(常用的监控数据、埋点统计数据等),然后制作图表做统计;
与传统数据库中的名词做比较
| influxDB中的名词 | 传统数据库中的概念 |
|---|---|
| database | 数据库 |
| measurement | 数据库中的表 |
| points | 表里面的一行数据 |
InfluxDB中独有的一些概念
Point由时间戳(time)、数据(field)、标签(tags)组成。
| Point属性 | 传统数据库中的概念 |
|---|---|
| time | 每个数据记录时间,是数据库中的主索引(会自动生成) |
| fields | 各种记录值(没有索引的属性)也就是记录的值:温度, 湿度 |
| tags | 各种有索引的属性:地区,海拔 |
influxDB安装
-
拉取最新版镜像
# 拉取最新版镜像 $ docker pull influxdb # 查看镜像 $ docker images✨ -
使用镜像创建容器
# 使用镜像创建容器 $ docker run -d -p 8083:8083 -p 8086:8086 --name myinfluxdb influxdb -d 让容器在后台运行 -p 8083:8083 将容器的 8083 端口映射到主机的 8083 端口 –-name 容器的名字,随便取,但是必须唯一 -
开放防火墙端口
$ firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8083/tcp --permanent $ firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=8086/tcp --permanent $ firewall-cmd --reload -
停止容器
$ docker stop myinfluxdb -
移除容器
# 移除的容器必须是已经停止的 $ docker rm myinfluxdb -
查看容器列表
# 只查看正在运行的 $ docker ps # 查看所有的 $ docker ps -a -
进入容器内部
# 该容器必须已经运行,才能进入 $ docker exec -it myinfluxdb /bin/bash
influxDB配置
使用名进入到myinfluxdb容器内部后,我们来做一点小小的配置
-
进入
influxdb命令交互模式,类似于mysql的命令行# 直接输入influx $ influx Connected to http://localhost:8086 version 1.8.3 InfluxDB shell version: 1.8.3 > # 如果上述报错,采用下面这种方式,输入/usr/bin/influx $ /usr/bin/influx -
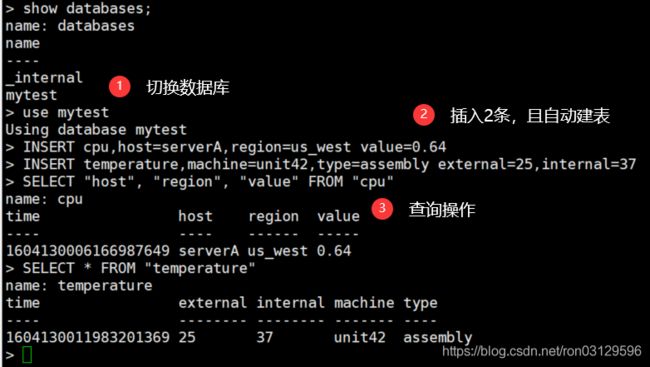
添加数据库
# 查看现有数据库 > show databases; name: databases name ---- _internal # 创建数据库 > create database mytest # 再次查看你会发现有2个库了 > show databases; name: databases name ---- _internal mytest # 使用数据库 > use mytest # 查看用户 > show users; user admin ---- ----- -
创建一个用户
> CREATE USER "master" WITH PASSWORD 'abcd1234' WITH ALL PRIVILEGES > exit 退出 -
influxdb默认没有校验权限,修改influxdb.conf文件# 在当前容器内执行 $ vim /etc/influxdb/influxdb.conf # 此时你会发现vim命令不存在 bash: vim: command not found -
安装vim命令
# 在当前容器类执行(此步骤时间会比较长) $ apt-get update $ apt-get install vim -
再次修改
influxdb.conf文件# 修改[http]处的auth-enabled属性为true [http] ... auth-enabled = true注意有的版本配置文件非常简单,只有如下几个配置:
[meta] dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/meta" [data] dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/data" engine = "tsm1" wal-dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/wal"我这边修改完后的配置文件全内容如下:
[meta] dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/meta" [data] dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/data" engine = "tsm1" wal-dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/wal" [http] enabled = true bind-address = ":8086" auth-enabled = true # ✨ 此处默认是关闭的需要开启,因为前面我们配置的用户名密码,所以需要开启 log-enabled = true write-tracing = false pprof-enabled = false https-enabled = false退出容器,重新启动注意不要改错,改错了,容器就无法再起来了
$ docker restart其实最详细的配置文件如下:**
### Welcome to the InfluxDB configuration file. # Once every 24 hours InfluxDB will report usage data to usage.influxdata.com # The data includes a random ID, os, arch, version, the number of series and other # usage data. No data from user databases is ever transmitted. # Change this option to true to disable reporting. reporting-disabled = false # we'll try to get the hostname automatically, but if it the os returns something # that isn't resolvable by other servers in the cluster, use this option to # manually set the hostname # hostname = "localhost" ### ### [meta] ### ### Controls the parameters for the Raft consensus group that stores metadata ### about the InfluxDB cluster. ### [meta] # Where the metadata/raft database is stored dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/meta" retention-autocreate = true # If log messages are printed for the meta service logging-enabled = true pprof-enabled = false # The default duration for leases. lease-duration = "1m0s" ### ### [data] ### ### Controls where the actual shard data for InfluxDB lives and how it is ### flushed from the WAL. "dir" may need to be changed to a suitable place ### for your system, but the WAL settings are an advanced configuration. The ### defaults should work for most systems. ### [data] # Controls if this node holds time series data shards in the cluster enabled = true dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/data" # These are the WAL settings for the storage engine >= 0.9.3 wal-dir = "/var/lib/influxdb/wal" wal-logging-enabled = true # Trace logging provides more verbose output around the tsm engine. Turning # this on can provide more useful output for debugging tsm engine issues. # trace-logging-enabled = false # Whether queries should be logged before execution. Very useful for troubleshooting, but will # log any sensitive data contained within a query. # query-log-enabled = true # Settings for the TSM engine # CacheMaxMemorySize is the maximum size a shard's cache can # reach before it starts rejecting writes. # cache-max-memory-size = 524288000 # CacheSnapshotMemorySize is the size at which the engine will # snapshot the cache and write it to a TSM file, freeing up memory # cache-snapshot-memory-size = 26214400 # CacheSnapshotWriteColdDuration is the length of time at # which the engine will snapshot the cache and write it to # a new TSM file if the shard hasn't received writes or deletes # cache-snapshot-write-cold-duration = "1h" # MinCompactionFileCount is the minimum number of TSM files # that need to exist before a compaction cycle will run # compact-min-file-count = 3 # CompactFullWriteColdDuration is the duration at which the engine # will compact all TSM files in a shard if it hasn't received a # write or delete # compact-full-write-cold-duration = "24h" # MaxPointsPerBlock is the maximum number of points in an encoded # block in a TSM file. Larger numbers may yield better compression # but could incur a performance penalty when querying # max-points-per-block = 1000 ### ### [coordinator] ### ### Controls the clustering service configuration. ### [coordinator] write-timeout = "10s" max-concurrent-queries = 0 query-timeout = "0" log-queries-after = "0" max-select-point = 0 max-select-series = 0 max-select-buckets = 0 ### ### [retention] ### ### Controls the enforcement of retention policies for evicting old data. ### [retention] enabled = true check-interval = "30m" ### ### [shard-precreation] ### ### Controls the precreation of shards, so they are available before data arrives. ### Only shards that, after creation, will have both a start- and end-time in the ### future, will ever be created. Shards are never precreated that would be wholly ### or partially in the past. [shard-precreation] enabled = true check-interval = "10m" advance-period = "30m" ### ### Controls the system self-monitoring, statistics and diagnostics. ### ### The internal database for monitoring data is created automatically if ### if it does not already exist. The target retention within this database ### is called 'monitor' and is also created with a retention period of 7 days ### and a replication factor of 1, if it does not exist. In all cases the ### this retention policy is configured as the default for the database. [monitor] store-enabled = true # Whether to record statistics internally. store-database = "_internal" # The destination database for recorded statistics store-interval = "10s" # The interval at which to record statistics ### ### [admin] ### ### Controls the availability of the built-in, web-based admin interface. If HTTPS is ### enabled for the admin interface, HTTPS must also be enabled on the [http] service. ### [admin] enabled = true bind-address = ":8083" https-enabled = false https-certificate = "/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem" ### ### [http] ### ### Controls how the HTTP endpoints are configured. These are the primary ### mechanism for getting data into and out of InfluxDB. ### [http] enabled = true bind-address = ":8086" auth-enabled = true log-enabled = true write-tracing = false pprof-enabled = false https-enabled = false https-certificate = "/etc/ssl/influxdb.pem" ### Use a separate private key location. # https-private-key = "" max-row-limit = 10000 realm = "InfluxDB" ### ### [subsciber] ### ### Controls the subscriptions, which can be used to fork a copy of all data ### received by the InfluxDB host. ### [subsciber] enabled = true http-timeout = "30s" ### ### [[graphite]] ### ### Controls one or many listeners for Graphite data. ### [[graphite]] enabled = false # database = "graphite" # bind-address = ":2003" # protocol = "tcp" # consistency-level = "one" # These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled # otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Batching # will buffer points in memory if you have many coming in. # batch-size = 5000 # will flush if this many points get buffered # batch-pending = 10 # number of batches that may be pending in memory # batch-timeout = "1s" # will flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit # udp-read-buffer = 0 # UDP Read buffer size, 0 means OS default. UDP listener will fail if set above OS max. ### This string joins multiple matching 'measurement' values providing more control over the final measurement name. # separator = "." ### Default tags that will be added to all metrics. These can be overridden at the template level ### or by tags extracted from metric # tags = ["region=us-east", "zone=1c"] ### Each template line requires a template pattern. It can have an optional ### filter before the template and separated by spaces. It can also have optional extra ### tags following the template. Multiple tags should be separated by commas and no spaces ### similar to the line protocol format. There can be only one default template. # templates = [ # "*.app env.service.resource.measurement", # # Default template # "server.*", # ] ### ### [collectd] ### ### Controls one or many listeners for collectd data. ### [[collectd]] enabled = false # bind-address = "" # database = "" # typesdb = "" # These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled # otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Batching # will buffer points in memory if you have many coming in. # batch-size = 1000 # will flush if this many points get buffered # batch-pending = 5 # number of batches that may be pending in memory # batch-timeout = "1s" # will flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit # read-buffer = 0 # UDP Read buffer size, 0 means OS default. UDP listener will fail if set above OS max. ### ### [opentsdb] ### ### Controls one or many listeners for OpenTSDB data. ### [[opentsdb]] enabled = false # bind-address = ":4242" # database = "opentsdb" # retention-policy = "" # consistency-level = "one" # tls-enabled = false # certificate= "" # log-point-errors = true # Log an error for every malformed point. # These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled # otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Only points # metrics received over the telnet protocol undergo batching. # batch-size = 1000 # will flush if this many points get buffered # batch-pending = 5 # number of batches that may be pending in memory # batch-timeout = "1s" # will flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit ### ### [[udp]] ### ### Controls the listeners for InfluxDB line protocol data via UDP. ### [[udp]] enabled = false # bind-address = "" # database = "udp" # retention-policy = "" # These next lines control how batching works. You should have this enabled # otherwise you could get dropped metrics or poor performance. Batching # will buffer points in memory if you have many coming in. # batch-size = 1000 # will flush if this many points get buffered # batch-pending = 5 # number of batches that may be pending in memory # batch-timeout = "1s" # will flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit # read-buffer = 0 # UDP Read buffer size, 0 means OS default. UDP listener will fail if set above OS max. # set the expected UDP payload size; lower values tend to yield better performance, default is max UDP size 65536 # udp-payload-size = 65536 ### ### [continuous_queries] ### ### Controls how continuous queries are run within InfluxDB. ### [continuous_queries] log-enabled = true enabled = true # run-interval = "1s" # interval for how often continuous queries will be checked if they need to run -
退出容器,重新启动注意不要改错,改错了,容器就无法再起来了
$ docker restart myinfluxdb -
再次进入容器,并使用命令进行influx操作
root@5f1bb39363e6:/# influx Connected to http://localhost:8086 version 1.8.3 InfluxDB shell version: 1.8.3 > show users ERR: unable to parse authentication credentials Warning: It is possible this error is due to not setting a database. Please set a database with the command "use" . >上述提示权限校验错误,接下来我们exit退出当前influx交互(不要退出容器),再次使用用户密码登录
root@5f1bb39363e6:/# influx -username 'master' -password 'abcd1234' Connected to http://localhost:8086 version 1.8.3 InfluxDB shell version: 1.8.3 > show users user admin ---- ----- master true上述登录成功,并且能够使用
show users语句
先切换到我们创建的mytest数据库
> use mytest
数据插入
由于InfluxDB的无结构(schemeless)特性,我们不需要预先建表,直接use [ database ]后就可以写入数据了。举个栗子。
INSERT cpu,host=serverA,region=us_west value=0.64
INSERT temperature,machine=unit42,type=assembly external=25,internal=37
读数据
SELECT "host", "region", "value" FROM "cpu"
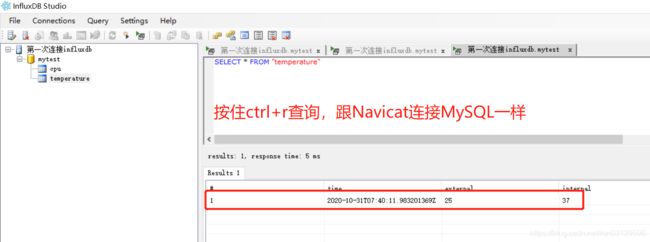
SELECT * FROM "temperature"
-- measurement都可以用正则表示,下面表示读一个db下的所有measurement的数据
SELECT * FROM /.*/
-- 配上where条件
SELECT "region", "value" FROM "cpu" where "host" = "server1"
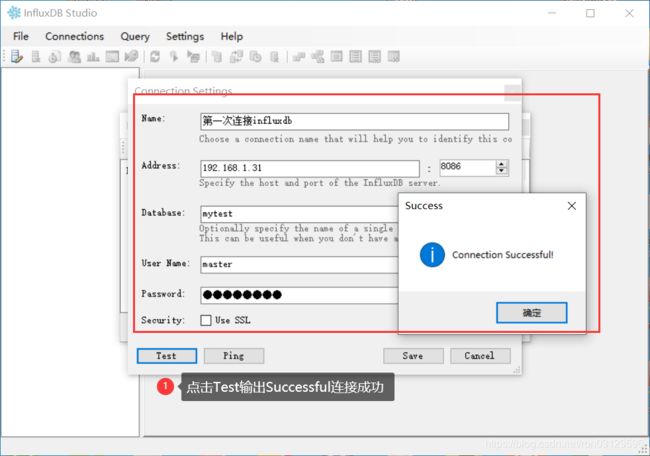
客户端工具
下载地址:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1FBFRc2fPkmDoHDYjdNgntA
提取码:s4ut
常用InfluxQL
-- 查看所有的数据库
show databases;
-- 使用特定的数据库
use database_name;
-- 查看所有的measurement
show measurements;
-- 查询10条数据
select * from measurement_name limit 10;
-- 数据中的时间字段默认显示的是一个纳秒时间戳,改成可读格式
precision rfc3339; -- 之后再查询,时间就是rfc3339标准格式
-- 或可以在连接数据库的时候,直接带该参数
influx -precision rfc3339
-- 查看一个measurement中所有的tag key
show tag keys
-- 查看一个measurement中所有的field key
show field keys
-- 查看一个measurement中所有的保存策略(可以有多个,一个标识为default)
show retention policies;
代码批量插入
新建Java的SpringBoot项目,项目地址GitHub:
pom.xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.it235groupId>
<artifactId>influxdbartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.influxdbgroupId>
<artifactId>influxdb-javaartifactId>
<version>2.15version>
dependency>
dependencies>
application.yml
server:
port: 8010
spring:
influx:
url: http://192.168.1.31:8086
user: master
username: master
password: abcd1234
database: mytest
retention_policy: default
retention_policy_time: 30d
Java代码
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDB;
import org.influxdb.dto.Point;
import org.influxdb.dto.Query;
import org.influxdb.dto.QueryResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author: it235.com
* @Date: 2020-10-10
* @Description: 工具支持类
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class InfluxDBSupport {
/**
* 数据保存策略
*/
@Value("${spring.influx.retentionPolicy:}")
private String retentionPolicy;
/**
* 数据保存策略中数据保存时间
*/
@Value("${spring.influx.retentionPolicyTime:}")
private String retentionPolicyTime;
@Value("${spring.influx.database:}")
private String database;
/**
* InfluxDB实例
*/
@Autowired
private InfluxDB influxDB;
public InfluxDBSupport() {
// autogen默认的数据保存策略
this.retentionPolicy = retentionPolicy == null || "".equals(retentionPolicy) ? "autogen" : retentionPolicy;
this.retentionPolicyTime = retentionPolicyTime == null || "".equals(retentionPolicy) ? "30d" : retentionPolicyTime;
}
/**
* 设置数据保存策略 defalut 策略名 /database 数据库名/ 30d 数据保存时限30天/ 1 副本个数为1/ 结尾DEFAULT
* 表示 设为默认的策略
*/
public void createRetentionPolicy() {
String command = String.format("CREATE RETENTION POLICY \"%s\" ON \"%s\" DURATION %s REPLICATION %s DEFAULT",
retentionPolicy, database, retentionPolicyTime, 1);
this.query(command);
}
/**
* 查询
*
* @param command 查询语句
* @return
*/
public QueryResult query(String command) {
return influxDB.query(new Query(command, database));
}
/**
* 插入
*
* @param measurement 表
* @param tags 标签
* @param fields 字段
*/
public void insert(String measurement, Map<String, String> tags, Map<String, Object> fields) {
Point.Builder builder = Point.measurement(measurement);
// 纳秒时会出现异常信息:partial write: points beyond retention policy dropped=1
// builder.time(System.nanoTime(), TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
builder.time(System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
builder.tag(tags);
builder.fields(fields);
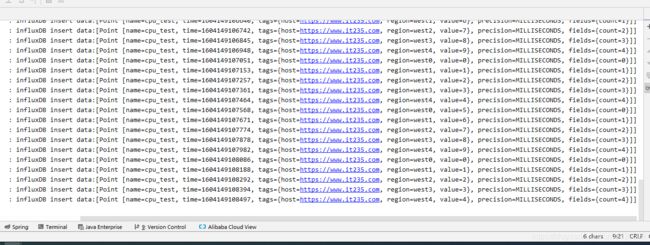
log.info("influxDB insert data:[{}]", builder.build().toString());
influxDB.write(database, "", builder.build());
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.influxdb.dto.QueryResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @Author: it235.com
* @Date: 2020-10-10
* @Description: 启动主程序
*/
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
public class InfluxdbDemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(InfluxdbDemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Autowired
private InfluxDBSupport influxDBSupport;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
//插入测试
insertTest();
//查询测试
//querTest();
}
/**
* 插入测试
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public void insertTest() throws InterruptedException {
Map<String, String> tagsMap = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Object> fieldsMap = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println("influxDB start time :" + System.currentTimeMillis());
int i = 0;
for (; ; ) {
Thread.sleep(100);
tagsMap.put("value", String.valueOf(i % 10));
tagsMap.put("host", "https://www.it235.com");
tagsMap.put("region", "west" + (i % 5));
fieldsMap.put("count", i % 5);
influxDBSupport.insert("cpu_test", tagsMap, fieldsMap);
i++;
}
}
/**
* 查询测试
*/
public void querTest(){
QueryResult rs = influxDBSupport.query("select * from usage");
log.info("query result => {}", rs);
if (!rs.hasError() && !rs.getResults().isEmpty()) {
rs.getResults().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
}
启动程序测试,观看控制台可以看到在批量插入数据,此时也可以去influxdb中去看看
Docker安装Grafana整合influxDB
Grafana介绍
Grafana安装
前面我们已经学习了Docker的安装和相关命令,接下来,我们只讲解Grafana的内容
-
镜像拉取
$ docker pull grafana/grafana $ docker images -
安装配置
$ docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name=it35graf grafana/grafana $ docker ps -a -
开放防火墙端口
$ firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=3000/tcp --permanent $ firewall-cmd --reload -
浏览器访问
http://ip:3000,用户名密码默认:admin
- 到此Grafana安装完成
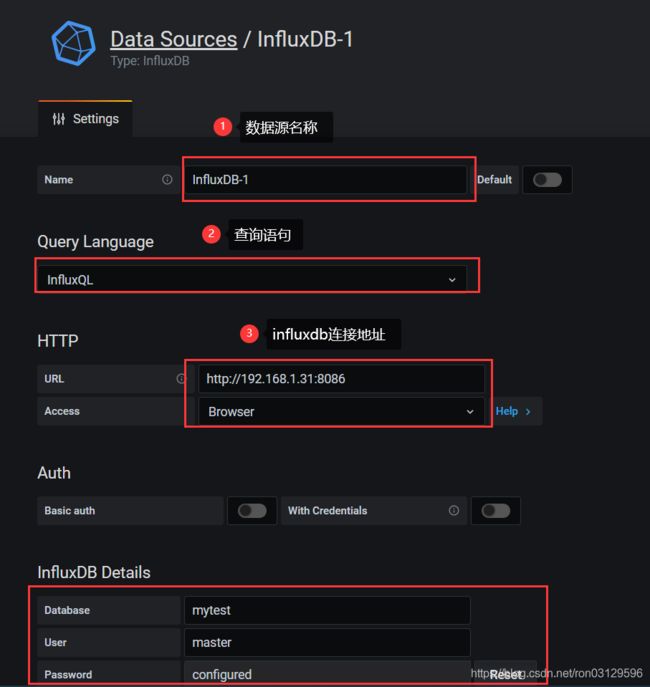
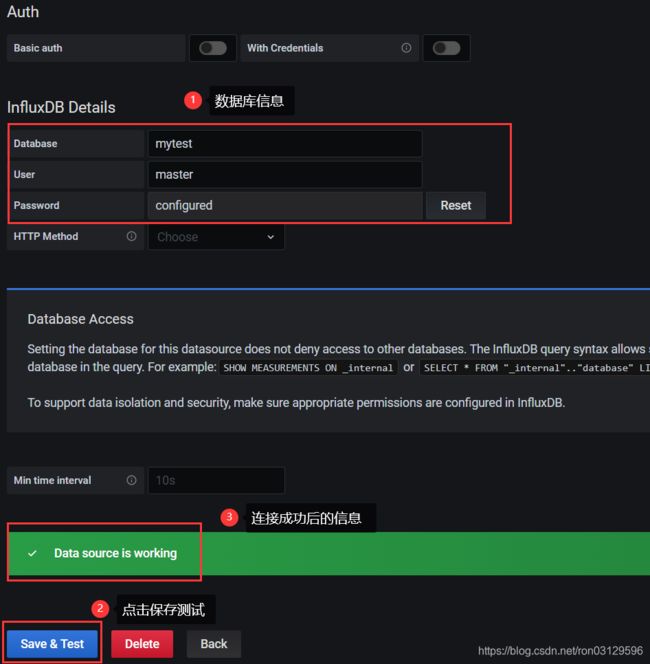
配置influxDB数据源
创建Dashboard
dashboard是Grafana种用于展示呈现的工具,我们可以将influxdb中的数据展示到dashboard中
注意上述选择的表一定是要有数据的,否则看不到效果
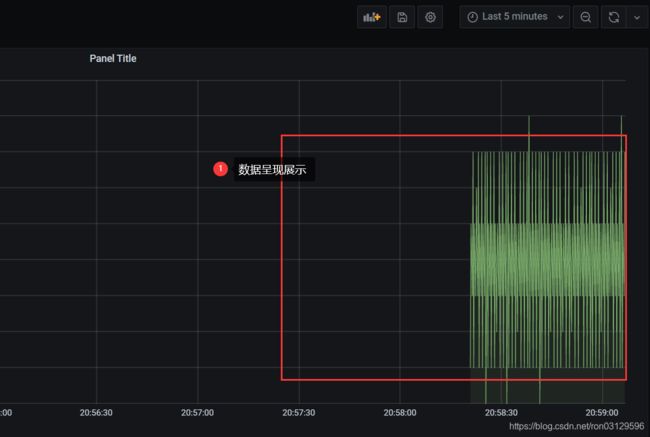
数据集成测试
- 开启代码批量插入程序
- 观看Grafana面板中的效果