【前端基础】函数式排列
坐标系变换
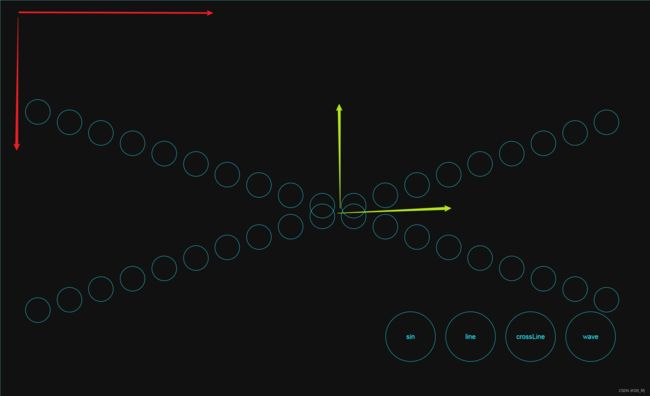
浏览器默认的坐标系,是以左上角为原点,向右为x轴,向下为y轴。
这个坐标系与数学中使用的坐标系不符,为了更方便使用函数来描述页面的布局,需要使用css来对浏览器的坐标系进行变换。
下面的css自定义了--x和--y两个自定义属性,通过clac动态计算的方式,实现了以正中心为原点,向右为x轴,向上为y轴的坐标系。通过--x和--y两个属性来指定坐标。
li {
--dx: 0px;
--dy: 0px;
position: absolute;
top: calc(50% - var(--dy));
left: calc(50% + var(--dx));
}
曲线类
下面定义了一个曲线类,它接收一个三个参数来进行初始化,分别为:
- 描述曲线的函数
- x轴取值范围
- y轴取值范围
还提供了一个getY函数,根据x的值返回对应的y值,如果超出范围则做出一定的处理。
class Curve {
constructor(curveFunc, xRange, yRange) {
this.curveFunc = curveFunc;
this.xRange = xRange;
this.yRange = yRange;
}
getY(x) {
let y = this.curveFunc(x);
if(x < this.xRange[0]) {
y = this.curveFunc(this.xRange[0]);
} else if (x > this.xRange[1]) {
y = this.curveFunc(this.xRange[1]);
}
if(y < this.yRange[0]) {
y = this.yRange[0];
} else if(y > this.yRange[1]) {
y = this.yRange[1];
}
return y;
}
}
layout函数
函数说明
layout函数根据上面定义的曲线类,对DOM元素进行布局。
这个函数接收4个参数。
- 曲线对象
- 要布局的元素数组
- 布局占据的宽度
- 布局占据的高度
实现思路
- 函数首先根据曲线获取函数的定义域和值域的边界点。
- 针具边界点计算出中心点的位置。
- 再根据布局占据的宽高计算出缩放比例。
- 根据定义域范围和布局元素个数计算出步长(元素之间的间隔)。
- 遍历每个元素,设置根据步长和缩放比例计算出每个元素的坐标。
function layout(curve, doms, width, height) {
const [xmin, xmax] = curve.xRange;
const [ymin, ymax] = curve.yRange;
const cx = (xmin + xmax) / 2;
const cy = (ymin + ymax) / 2;
const scaleX = width / (xmax - xmin);
const scaleY = height / (ymin - ymax);
const step = (xmax - xmin) / doms.length;
for(let i = 0; i < doms.length; i++) {
const dom = doms[i];
const x = xmin + i * step;
const y = curve.getY(x);
const dx = (x - cx) * scaleX;
const dy = (y - cy) * scaleY;
dom.style.setProperty('--dx', dx + 'px');
dom.style.setProperty('--dy', dy + 'px');
}
}
layouts映射
根据布局的需求创建不同的曲线对象,并使用layout函数对其进行布局。
const layouts = {
wave() {
const wave = new Curve(x => Math.sin(x), [0, Math.PI * 3], [-1, 1]);
layout(wave, doms, container.clientWidth - 100, container.clientHeight / 2);
},
line() {
const line = new Curve(x => 1, [0, 1], [0, 2]);
layout(line, doms, container.clientWidth - 100, container.clientHeight / 2);
},
corssLine() {
const curve1 = new Curve(x => x, [-1,1], [-1,1]);
const curve2 = new Curve(x => -x, [-1, 1], [-1, 1]);
const midIndex = Math.floor(doms.length / 2);
const doms1 = Array.from(doms).slice(0, midIndex);
const doms2 = Array.from(doms).slice(midIndex);
layout(curve1, doms1, container.clientWidth - 100, container.clientHeight / 2);
layout(curve2, doms2, container.clientWidth - 100, container.clientHeight / 2);
},
corssWave() {
const curve1 = new Curve(x => Math.sin(x), [0, Math.PI * 3], [-1,1]);
const curve2 = new Curve(x => -Math.sin(x), [0, Math.PI * 3], [-1, 1]);
const midIndex = Math.floor(doms.length / 2);
const doms1 = Array.from(doms).slice(0, midIndex);
const doms2 = Array.from(doms).slice(midIndex);
layout(curve1, doms1, container.clientWidth - 100, container.clientHeight / 3);
layout(curve2, doms2, container.clientWidth - 100, container.clientHeight / 3);
}
}
最后遍历按钮实现事件的绑定,不同的按钮对应不同的布局。
const btns = document.querySelectorAll('button');
const events = Object.values(layouts);
btns.forEach((item, index) => {
item.addEventListener('click', events[index]);
})

