ElasticSearch 基础(四)之 常用 API 测试
目录
- 前言
- 一、查看(Cat) API
-
- 1、查看节点信息
- 2、查看各节点机器存储信息
- 3、查询索引信息
- 4、查询分片信息
- 5、查询集群健康状态
- 6、查询集群所有的别名索引
- 7、查询主节点信息
- 8、查询文档数量
- 二、集群(Cluster) API
-
- 1、集群健康
- 2、集群状态
- 3、节点信息
- 三、索引(Index) API
-
- 1、索引是否存在
- 2、创建索引
-
- 2.1、aliases
- 2.2、mappings
- 2.3、settings
- 3、查看索引
- 4、删除索引
- 四、文档(Document) API
-
- 1、文档是否存在
- 2、索引文档
- 3、获取文档
-
- 3.1、元数据
- 4、修改文档
-
- 4.1、局部更新
- 4.2、全量更新
- 5、删除文档
- 五、搜索(Search) API
-
- 1、Query参数查询 与 请求体查询
- 2、单条件筛选
-
- 2.1、匹配关键字
-
- 2.1.1、短语模糊匹配
- 2.1.2、短语精确匹配
- 2.1.3、关键词精确匹配
- 2.1.4、多字段查询
- 2.1.5、前缀查询
- 2.1.6、通配符查询
- 2.2、范围查询
-
- 2.2.1、数字范围
- 2.2.2、日期范围
- 2.3、多id查询
- 3、多条件筛选
-
- 3.1、布尔查询
- 4、指定字段
- 5、高亮查询
-
-
- 5.1、默认高亮显示
- 5.2、自定义高亮html标签
-
- 6、排序
- 7、分页
- 六、批量操作(Mget、Bulk) API
-
- 1、批量查询
-
- 1.1、同一个索引
- 1.2、不同索引
- 2、批量修改
- 七、离线文档下载
前言
本文示例以 ElasticSearch 8.6.2 版本演示,更详细的 API 参数及用法请参考官方文档。测试命令我用的是 Kibana,在输入时会有命令和语法错误提示,可直接复制 CURL 格式、格式化、查看文档,点击导航栏上面的 help,也提供了一些快捷方式,方便学习。
API 测试参考:
Elasticsearch 请求示例
Elasticsearch 8.6 - REST APIs
elasticsearh中查询类型
一、查看(Cat) API
ES cat 命令是监控 ES 的节点,内存,索引,分片,集群状态等一些基本信息。
GET /_cat/<some>
路径参数:
<some>
(必需,字符串)节点,内存,索引,分片,集群状态等一些基本信息
请求参数:
v: 显示详细的查询结果。
help: 帮助了解cat 相关指令支持哪些功能,返回参数第一列显示完整的名称,第二列显示缩写,第三列提供了关于这个参数的简介。
h: 指定字段输出。
1、查看节点信息
GET /_cat/nodes?v
ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role master name
127.0.0.1 22 97 4 0.00 0.03 0.05 cdfhilmrstw * VM-0-12-centos
IP:(默认)IP 地址
heap.percent:(默认)最大配置堆数
ram.percent:(默认)已用内存总百分比
返回结果:堆内存,内存,cpu百分比, 最近1,5,15分钟 节点的负载,显示主节点( * 标记主节点),节点名等信息。
2、查看各节点机器存储信息
GET /_cat/allocation?v
shards disk.indices disk.used disk.avail disk.total disk.percent host ip node
12 53.3mb 13.7gb 35.2gb 49gb 28 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
1 UNASSIGNED
返回结果:节点分片数,索引占用磁盘大小,磁盘已使用容量大小,磁盘可用容量大小,磁盘总容量大小,磁盘使用率等节点信息。
3、查询索引信息
GET /_cat/indices?v
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
yellow open test Ygi2jIdzTsOgn2Aw9KFeVg 1 1 3 1 15.7kb 15.7kb
返回结果:索引的健康状态,索引名,索引主分片,副本大小,文档数,被删除文档数,索引主分片,副本 总占用存储空间。
4、查询分片信息
GET /_cat/shards?v
index shard prirep state docs store ip node
.apm-agent-configuration 0 p STARTED 0 225b 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.kibana_security_session_1 0 p STARTED 5 31.2kb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.security-7 0 p STARTED 113 329.5kb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.geoip_databases 0 p STARTED 41 42.3mb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
test 0 p STARTED 3 15.7kb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
test 0 r UNASSIGNED
.apm-custom-link 0 p STARTED 0 225b 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.kibana_task_manager_8.6.2_001 0 p STARTED 27 7.8mb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.kibana_8.6.2_001 0 p STARTED 1135 2.7mb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.security-profile-8 0 p STARTED 1 8.5kb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.kibana-event-log-8.6.2-000001 0 p STARTED 22 32.6kb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.ds-.logs-deprecation.elasticsearch-default-2023.02.21-000001 0 p STARTED 2 23.6kb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
.ds-ilm-history-5-2023.02.21-000001 0 p STARTED 9 28.3kb 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
返回结果:索引名称,分片序号,主副分片标志,该分片存储空间,分片存储的文档数,分片所属节点ip,节点名。
5、查询集群健康状态
GET /_cat/health?v
epoch timestamp cluster status node.total node.data shards pri relo init unassign pending_tasks max_task_wait_time active_shards_percent
1677579030 10:10:30 elasticsearch yellow 1 1 12 12 0 0 1 0 - 92.3%
返回结果:集群名称,集群状态,节点数,数据节点数,分片数,主分片数,激活的分片百分比(active_shards_percent)。
6、查询集群所有的别名索引
GET /_cat/aliases?v
alias index filter routing.index routing.search is_write_index
.security .security-7 - - - -
.kibana .kibana_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.kibana_8.6.2 .kibana_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.kibana_task_manager .kibana_task_manager_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.kibana_task_manager_8.6.2 .kibana_task_manager_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.security-profile .security-profile-8 - - - -
.kibana_security_session .kibana_security_session_1 - - - -
.kibana-event-log-8.6.2 .kibana-event-log-8.6.2-000001 - - - true
7、查询主节点信息
GET /_cat/master?v
id host ip node
VZje5HgCRDerg5Fp6bWDUA 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 VM-0-12-centos
8、查询文档数量
快速查询当前整个集群或者指定索引的document的数量(不包括删除的但是还没有清理掉的document)。
GET /_cat/master?v
epoch timestamp count
1677579205 10:13:25 3
二、集群(Cluster) API
1、集群健康
获取集群的健康状态有两种方式:
语法:
GET /_cluster/health/<target>
路径参数:
<target>
(可选,字符串) 用于限制的数据流、索引和索引别名的逗号分隔列表 请求。支持通配符表达式 ()。*
要定位集群中的所有数据流和索引,请省略此参数或使用 或 。_all*
测试:
//请求:
GET /_cluster/health
//返回:
{
"cluster_name": "elasticsearch", # 集群名,默认elasticsearch
"status": "green", # 集群状态
"timed_out": false, # 是否超时
"number_of_nodes": 1, # 节点数量
"number_of_data_nodes": 1, # 数据节点数量
"active_primary_shards": 11, # 活动主分片的数量
"active_shards": 11, # 活动主分片和副本分片的总数
"relocating_shards": 0, # 正在重新定位的分片数
"initializing_shards": 0, # 正在初始化的分片数
"unassigned_shards": 0, # 未分配的分片数
"delayed_unassigned_shards": 0, # 分配延迟的分片数量 超时设置
"number_of_pending_tasks": 0, # 尚未更改的群集级别更改数 执行
"number_of_in_flight_fetch": 0, # 未完成的读取数
"task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis": 0, # 自最早启动任务以来以毫秒为单位表示的时间 正在等待执行
"active_shards_percent_as_number": 100 # 集群中活动分片的比率,以百分比表示
}
文档:cluster-health-api
2、集群状态
返回用于调试或诊断问题的集群内部状态的信息。
语法:
GET /_cluster/state/<metrics>/<target>
路径参数:
<metrics>
(可选,字符串)以下选项的逗号分隔列表:
_all
显示所有指标。
blocks
显示响应的一部分。blocks
master_node
显示响应的一部分。master_node
metadata
显示响应的一部分。如果提供逗号分隔 索引列表,返回的输出将仅包含这些索引的元数据 指标。metadata
nodes
显示响应的一部分。nodes
routing_nodes
显示响应的一部分。routing_nodes
routing_table
显示响应的一部分。如果您提供逗号 分离的索引列表,返回的输出将仅包含 这些索引的路由表。routing_table
version
显示群集状态版本。
<target>
(可选,字符串)数据流、索引和别名的逗号分隔列表 用于限制请求。支持通配符 ()。以所有数据流为目标 和索引,省略此参数或使用或 .**_all
测试:
//请求:
GET /_cluster/state
//返回:
{
"cluster_name": "elasticsearch", # 集群名
"cluster_uuid": "MtNAAgvNQhmc1W3u9ytePQ", # 集群ID
"version": 109, # state命令版本
"state_uuid": "M9oKz-6PTY2KWOkLDo8MkQ", # state ID
"master_node": "VZje5HgCRDerg5Fp6bWDUA", # 主节点ID
"blocks": {}, # 系统限制信息,响应的blocks部分
"nodes": {...}, # 节点信息
"metadata": {...} # 元数据信息,响应的metadata部分。如果提供了路径参数index,则只返回指定索引的metadata信息
}
//请求:
GET /_cluster/state/nodes
//返回:
{
"cluster_name": "elasticsearch", # 集群名
"cluster_uuid": "MtNAAgvNQhmc1W3u9ytePQ", # 集群ID
"nodes": { # 节点信息
"VZje5HgCRDerg5Fp6bWDUA": { # 节点ID
"name": "VM-0-12-centos", # 节点名
"ephemeral_id": "_6rakwKVQE62G5O0i9ohyw", # 临时ID
"transport_address": "127.0.0.1:9300", # 节点之间的通讯地址
"external_id": "VM-0-12-centos", # 对外显示的节点名
"attributes": { # 属性
"ml.max_jvm_size": "1048576000", # JVM 最大内存
"ml.allocated_processors": "1", # 分配的处理器数
"ml.machine_memory": "2095960064", # 内存大小
"xpack.installed": "true", # xpack 认证
"ml.allocated_processors_double": "1.0" # 分配的处理器_双重
},
"roles": [ # 节点角色,默认全部角色
"data", # 数据节点
"data_cold", # 冷数据节点
"data_content", # 内容数据节点
"data_frozen", # 冻结数据节点
"data_hot", # 热数据节点
"data_warm", # 暖数据节点
"ingest", # 预处理节点
"master", # 主节点
"ml", # 机器学习节点
"remote_cluster_client", # 跨集群客户端节点
"transform" # 转换节点
]
}
}
}
3、节点信息
返回群集节点信息。
GET /_nodes
GET /_nodes/<node_id>
GET /_nodes/<metric>
GET /_nodes/<node_id>/<metric>
路径参数:
<metric>
(可选,字符串) 将返回的信息限制为特定指标。支持 逗号分隔的列表,例如 。http,ingest
的有效值<metric>
aggregations
有关可用聚合类型的信息。
http
有关此节点的 HTTP 接口的信息。
indices
与索引相关的节点级配置:
total_indexing_buffer:此节点上索引缓冲区的最大大小。
ingest
有关引入管道和处理器的信息。
jvm
JVM 信息,包括其名称、版本和配置。
os
操作系统信息,包括其名称和版本。
plugins
有关每个节点安装的插件和模块的详细信息。以下 每个插件和模块都有可用的信息:
name:插件名称
version:插件构建的 Elasticsearch 版本
description:插件用途的简短描述
classname:插件入口点的完全限定类名
has_native_controller:插件是否具有本机控制器 过程
process
进程信息,包括数字进程 ID。
settings
列出文件中定义的所有正在使用的节点设置。elasticsearch.yml
thread_pool
有关每个线程池的配置的信息。
transport
有关节点的传输接口的信息。
如果您使用此 API 的完整形式,那么您 还可以请求指标以检索所有指标,或者您可以请求 用于抑制所有指标并仅检索 节点。GET /_nodes/<node_id>/<metric>_all_none
<node_id>
(可选,字符串)以逗号分隔的节点 ID 或名称列表,用于限制 返回的信息。
测试:
//请求:
GET /_nodes
//返回:
{
"_nodes": { # 节点数量信息
"total": 1, # 节点数量
"successful": 1, # 正常节点数量
"failed": 0 # 错误节点数量
},
"cluster_name": "elasticsearch", # 集群名
"nodes": { # 节点信息
"VZje5HgCRDerg5Fp6bWDUA": {
"name": "VM-0-12-centos",
"transport_address": "127.0.0.1:9300",
"host": "127.0.0.1",
"ip": "127.0.0.1",
"version": "8.6.2",
"build_flavor": "default",
"build_type": "tar",
"build_hash": "2d58d0f136141f03239816a4e360a8d17b6d8f29",
"total_indexing_buffer": 104857600,
"roles": [ # 节点角色,没有设置默认所有角色
"data", # 数据节点
"data_cold", # 冷数据节点
"data_content", # 内容数据节点
"data_frozen", # 冻结数据节点
"data_hot", # 热数据节点
"data_warm", # 暖数据节点
"ingest", # 预处理节点
"master", # 主节点
"ml", # 机器学习节点
"remote_cluster_client", # 跨集群客户端节点
"transform" # 转换节点
],
"attributes": {...}, # 节点属性
"settings": {...}, # 节点设置
"os": {...}, # 操作系统信息
"process": {...}, # 进程信息
"jvm": {...}, # JVM 信息
"thread_pool": {...}, # 线程池配置信息
"transport": {...}, # 节点传输接口信息
"http": {...}, # 节点 HTTP 接口信息
"plugins": {...}, # 节点安装的插件和模块的详细信息
"modules": {...}, # 节点的模块信息
"ingest": {...}, # 有关引入管道和处理器的信息
"aggregations": {...} # 有关可用聚合类型的信息
}
}
}
三、索引(Index) API
1、索引是否存在
语法:
HEAD <index>
测试:
//请求:
HEAD test
//存在返回:
200 - OK
//不存在返回:
{
"statusCode": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"message": "404 - Not Found"
}
2、创建索引
没有索引前,第一次创建文档的时候也会创建索引。
语法:
PUT <index>
{
"aliases": {}, # 别名
"mappings": {}, # 映射
"settings": {}, # 配置
}
路径参数:
<index>
(必需,字符串)要创建的索引的名称。
请求体:
<aliases>
(可选,对象的对象)索引的别名。
<mappings>
(可选,映射对象)索引中字段的映射。如果 指定时,此映射可以包括:
字段名称
字段数据类型
映射参数
请参阅 映射:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.6/mapping.html。
<settings>
(可选,索引设置对象)配置 索引的选项。
请参阅索引设置:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.6/index-modules.html#index-modules-settings。
索引名称必须满足以下条件:
- 仅小写
- 不能包含
\,/,*,?,",<,>,|,,,# - 7.0 之前的索引可能包含
:,但该冒号已弃用,在 7.0+ 中不受支持 - 不能以
_,-,+开头 - 不能是
.或.. - 不能超过 255 字节(请注意它是字节,因此多字节字符将更快地计入 255 限制)
- 以
.开头的名称已被弃用,隐藏索引和插件管理的内部索引除外.
测试:
//请求:
PUT test
//返回:
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "test"
}
//请求:
GET test
//返回:
{
"test": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {},
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "test",
"creation_date": "1677306509277",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "tXKSzCSUQNWxnDhqeBrLeA",
"version": {
"created": "8060299"
}
}
}
}
}
创建索引时有三个重要的参数:aliases,mappings,settings:
2.1、aliases
ES 的 aliases(别名) 就类似数据库的视图,我们为索引 test 创建一个别名 test_alias,这样我们对 test_alias 的操作就像对 test 的操作一样。
//请求:
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "test",
"alias": "test_alias"
}
}
]
}
//返回:
{
"acknowledged": true
}
//请求:
GET _cat/aliases
//返回:
alias index filter routing.index routing.search is_write_index
.security .security-7 - - - -
test_alias test - - - -
.kibana .kibana_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.kibana_8.6.2 .kibana_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.kibana_task_manager .kibana_task_manager_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.kibana_task_manager_8.6.2 .kibana_task_manager_8.6.2_001 - - - -
.kibana_security_session .kibana_security_session_1 - - - -
.security-profile .security-profile-8 - - - -
.kibana-event-log-8.6.2 .kibana-event-log-8.6.2-000001 - - - true
别名不仅仅可以关联一个索引,它能聚合多个索引。也对于同一个index,给不同人看到不同的数据,假设 test 有个字段是 team,team 字段记录了该数据是哪个人添加的,设置别名可以使不同人之间的 team 数据是不可见的。
可参考:Elasticsearch基础11——索引之别名使用。
2.2、mappings
ES 的 mappings(映射) 相当于数据库中的表结构,对表的字段类型长度索引做设置,而在 ES 中 映射是定义一个文档和它所包含的字段如何被存储和索引的过程,分为 自动映射(Dynamic mapping) 和 显式映射(Explicit mapping)。
动态映射:
- 动态映射允许您试验 并在刚开始时探索数据。Elasticsearch 添加了新字段 自动,只需为文档编制索引即可。您可以将字段添加到顶级 映射,以及内部对象和嵌套字段。
- 使用动态模板定义自定义映射,这些映射是 应用于基于匹配条件动态添加的字段。
显式映射:
显式映射允许您精确选择如何 定义映射定义,例如:
- 哪些字符串字段应被视为全文字段。
- 哪些字段包含数字、日期或地理位置。
- 日期值的格式。
- 用于控制动态添加字段映射的自定义规则。
使用运行时字段进行架构更改,而无需 重新索引。可以将运行时字段与索引字段结合使用,以 平衡资源使用情况和性能。您的索引会更小,但 搜索性能较慢。
在ElasticSearch中一旦创建了映射是不被允许进行修改的,因为对于数据存储、分析、检索,都是按照mapping 中的配置进行的,如果前期 根据 mapping存储好了之后,又对 mapping 进行更改,那么就会导致前面存储的数据和后面的检索策略后面的存储 数据不一致的情况,导致检索行为不准确。 只能在创建index 的时候手动配置 mapping,或者新增 fieId mapping。
测试:
给索引test 设置映射,id:long,name:keyword。
//请求:
POST test/_doc/_mapping
{
"properties":{
"id":{
"type":"long"
},
"name":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "_mapping",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created", # 创建成功
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}
//请求:
GET test/_mapping
//返回:
{
"test": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
2.3、settings
索引的配置项可以分为 静态配置 与 动态配置,所谓的静态配置即索引创建后不能修改。
index.number_of_shards:索引分片的数量。在ES层面可以通过es.index.max_number_of_shards属性设置索引最大的分片数,默认为1024,index.number_of_shards的默认值为Math.min(es.index.max_number_of_shards,5),故通常默认值为5。index.shard.check_on_startup:分片在打开之前是否应该检查该分片是否损坏。当检测到损坏时,它将阻止分片被打开。可选值:false:不检测;checksum:只检查物理结构;true:检查物理和逻辑损坏,相对比较耗CPU;fix:类同与false,7.0版本后将废弃。默认值:false。index.codec:数据存储的压缩算法,默认值为LZ4,可选择值best_compression ,比LZ4可以获得更好的压缩比(即占据较小的磁盘空间,但存储性能比LZ4低)。index.routing_partition_size:路由分区数,如果设置了该参数,其路由算法为:(hash(_routing) + hash(_id) % - index.routing_parttion_size ) % number_of_shards。如果该值不设置,则路由算法为 hash(_routing) % number_of_shardings,_routing默认值为_id。
更多配置这里不多说,可参考https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1443568。
//请求:
GET /test/_settings
//返回:
{
"test": {
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "test",
"creation_date": "1677313859733",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "SWZ28NdRRsCgcgWlyjmePQ",
"version": {
"created": "8060299"
}
}
}
}
}
3、查看索引
语法:
GET /<index> # 查看指定索引信息
GET _cat/indices # 查看所有索引
测试:
//请求:
GET /test
//返回:
{
"test": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {},
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "test",
"creation_date": "1677306509277",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "tXKSzCSUQNWxnDhqeBrLeA",
"version": {
"created": "8060299"
}
}
}
}
}
//请求:
GET _cat/indices?v
//返回:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
yellow open test tXKSzCSUQNWxnDhqeBrLeA 1 1 0 0 225b 225b
4、删除索引
语法:
DELETE <index>
测试:
//请求:
DELETE test
//返回:
{
"acknowledged": true
}
//请求:
GET _cat/indices
//返回:
# 空
四、文档(Document) API
1、文档是否存在
语法:
HEAD <index>/_doc/<_id>
HEAD <index>/_source/<_id>
路径参数:
<index>
(必需,字符串)包含文档的索引的名称。
<_id>
(必需,字符串)文档的唯一标识符。
测试:
//请求:
HEAD test/_doc/1
//存在返回:
200 - OK
//不存在返回:
{
"statusCode": 404,
"error": "Not Found",
"message": "404 - Not Found"
}
2、索引文档
索引文档就是创建文档,这里的索引表示创建文档这个动作。
语法:
PUT /<target>/_doc/<_id>
POST /<target>/_doc/<_id>
PUT /<target>/_create/<_id>
POST /<target>/_create/<_id>
路径参数:
<target>
(必需,字符串)目标数据流或索引的名称。
<_id>
(可选,字符串)文档的唯一标识符。省略此参数会自动生成文档 ID。
测试:
//请求:
POST test/_doc/1
{
"id":"1",
"name":"张三",
"avatar":"https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age":20
}
//返回:
{
"_index": "test", # 文档所在索引
"_id": "1", # 文档ID,这是ES 的文档ID 和 源数据中的id关联需要业务维护
"_version": 1, # 版本
"result": "created", # 执行结果 - 成功
"_shards": { # 分片
"total": 2, # 分片总数 - 一主一副
"successful": 1, # 正常运行的分片数量,因为是单机,主副分片在一起,只会使用主分片
"failed": 0 # 失败数量,副分片没用到并不是运行失败,主副分片本就是为了数据冗余而存在的,单机的话副分片就用不到了,宕机一起死
},
"_seq_no": 1, # _seq_no是严格递增的顺序号,每个文档一个,Shard级别严格递增,保证后写入的Doc的_seq_no大于先写入的Doc的_seq_no。任何类型的写操作,包括index、create、update和Delete,都会生成一个_seq_no。
"_primary_term": 1 # _primary_term主要是用来恢复数据时处理当多个文档的_seq_no一样时的冲突,比如当一个shard宕机了,raplica需要用到最新的数据,就会根据_primary_term和_seq_no这两个值来拿到最新的document
}
//测试:
POST test/_doc
{
"id":"2",
"name":"李四",
"avatar":"https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age":22
}
//返回:
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "Ra20kIYBD3T716opayt9", # 自动生成的文档ID
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1
}
测试:
- 如果没有还没有创建索引
test2,那么在第一次创建文档的时候会自动创建test2。
//请求:
GET _cat/indices
//返回:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
yellow open test SWZ28NdRRsCgcgWlyjmePQ 1 1 1 0 5.4kb 5.4kb
//请求:
POST test2/_doc/1
{
"id":"1",
"name":"张三",
"avatar":"https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age":20
}
//返回:
{
"_index": "test2",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1
}
//请求:
GET _cat/indices
//返回:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
yellow open test2 ssrY7_QvQHCEHyxbYIW2FQ 1 1 1 0 6.5kb 6.5kb
yellow open test SWZ28NdRRsCgcgWlyjmePQ 1 1 1 0 5.4kb 5.4kb
3、获取文档
语法:
# 获取索引下所有文档
GET /<index>/_search
# 获取指定文档
GET <index>/_doc/<_id>
GET <index>/_source/<_id>
路径参数:
<index>
(必需,字符串)包含文档的索引的名称。
<_id>
(必需,字符串)文档的唯一标识符。
部分查询参数,详细用法参考官网(https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.6/docs-get.html#docs-get-api-prereqs):
stored_fields
(可选,布尔值)如果 ,则检索存储在 索引而不是文档。默认值为false 。
_source
(可选,字符串)真或假返回字段与否,或 要返回的字段列表。
version
(可选,整数)用于并发控制的显式版本号。 指定的版本必须与文档的当前版本匹配 请求成功。
3.1、元数据
这里关于获取文档返回信息中的参数叫做 元数据:
- _index:文档所属索引的名称。
- _id:文档的唯一标识符。
- _version:文档版本。每次更新文档时递增。
- _seq_no:分配给文档以编制索引的序列号 操作。序列号用于确保文档的较旧版本 不会覆盖较新的版本。请参阅 乐观并发控制。
- _primary_term:为索引操作分配给文档的主要术语。 请参阅 乐观并发控制。
- found:指示文档是否存在:
true或false。 - _source:如果
found是true,则包含以 JSON 格式设置的文档数据。如果_source参数设置为false或stored_fields参数设置为true,则排除。
注意:元数据和源数据不要搞混了,源数据是元数据 _source 下的内容,就是我们存到 ES 中的信息。
测试:
//请求:
GET test/_doc/1
//返回:
{
"_index": "test", # 索引
"_id": "1", # 文档ID
"_version": 1, # 版本号
"_seq_no": 1, # 顺序号 _seq_no和_primary_term 共同用于版本控制
"_primary_term": 1, # 编号
"found": true, # 是否找到
"_source": { # 源数据,存到ES中的数据
"id": "1",
"name": "张三",
"avatar": "https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age": 20
}
}
//请求:
GET test/_source/1
//返回:
{
"id": "1",
"name": "张三",
"avatar": "https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age": 20
}
//请求:
GET /test/_search
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "_mapping",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": "1",
"name": "张三",
"avatar": "https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age": 20
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "Ra20kIYBD3T716opayt9",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": "2",
"name": "李四",
"avatar": "https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age": 22
}
}
]
}
}
4、修改文档
官方提供 Update API 实际上是局部更新,能够编写文档更新脚本。要完全替换现有文档,则使用 索引文档API。
4.1、局部更新
更新API支持传递合并到现有文档中的部分文档。
更新API 还能够编写文档更新脚本,脚本可以更新、删除或跳过修改文档。
语法:
POST /<index>/_update/<_id>
路径参数:
<index>
(必需,字符串)包含文档的索引的名称。
<_id>
(必需,字符串)文档的唯一标识符。
请求体:
doc:修改信息。
script:脚本内容。
测试:
修改源数据:
//请求:
POST /test/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"name":"张三222",
"age":30
}
}
//返回:
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 3,
"_primary_term": 1
}
//请求:
GET test/_source/1
//返回:
{
"id": "1",
"name": "张三222",
"avatar": "https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age": 30
}
执行脚本测试(年龄加10):
//请求:
POST test/_update/1
{
"script" : {
"source": "ctx._source.age+= params.add",
"lang": "painless",
"params" : {
"add" : 10
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 3,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 4,
"_primary_term": 1
}
//请求:
GET test/_source/1
//返回:
{
"id": "1",
"name": "张三222",
"avatar": "https://profile-avatar.csdnimg.cn/21f4a00156854dcab8a86032bf5b9068_weixin_43844718.jpg!0",
"age": 40
}
4.2、全量更新
和新增文档一样,如果请求体变化,会将原有的数据内容覆盖。
测试:
//请求:
POST test/_doc/1
{
"name":"李四"
}
//返回:
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 4,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 10,
"_primary_term": 1
}
5、删除文档
DELETE /<index>/_doc/<_id>
测试:
//请求:
DELETE test/_doc/1
//返回:
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 10,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 11,
"_primary_term": 1
}
//请求:
GET test/_doc/1
//返回:
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"found": false
}
五、搜索(Search) API
Search API 执行搜索查询并返回与查询匹配的搜索命中。可以使用 查询字符串参数 或 请求体 提供搜索查询。
GET /<target>/_search
GET /_search
POST /<target>/_search
POST /_search
路径参数:
<target>
(可选,字符串)以逗号分隔的数据流、索引和别名列表 搜索。支持通配符 ()。省略则搜索所有数据流和索引。
部分查询参数(更多参考: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/8.6/search-search.html):
q:
(可选,字符串)使用Lucene查询字符串语法进行查询。您可以使用q参数来运行查询参数搜索。查询参数搜索不支持完整的Elasticsearch查询DSL,但便于测试。
from:
(可选,整数)起始文档偏移量。需要为非负,默认值为0。默认情况下,使用from和size参数,页面浏览次数不能超过10000次。要浏览更多点击,请使用search_after参数。
size:
(可选,整数)定义要返回的命中数。默认值为 10。默认情况下,使用from和size参数,页面浏览次数不能超过10000次。要浏览更多点击,请使用search_after参数。
sort:
(可选,字符串)以逗号分隔的<field>:<direction>对列表。
_source:
(可选) (可选)指示为匹配的文档返回哪些源字段。这些字段在命中时返回_搜索响应的源属性。默认为true。请参见源过滤。
true:(布尔值)返回整个文档源。
false:(布尔值)不返回文档源。
<string>:(string)要返回的源字段的逗号分隔列表。支持通配符(*)模式。
timeout:
(可选,时间单位)指定等待每个碎片响应的时间段。如果在超时到期之前没有收到响应,则请求失败并返回错误。默认为无超时。
version:
(可选,布尔值)如果为true,则返回文档版本作为命中的一部分。默认为false。
先准备下数据:
GET test/_search
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": "1",
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": "2",
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": "3",
"name": "王五",
"age": 30,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心"
}
}
]
}
}
1、Query参数查询 与 请求体查询
Query参数查询 测试:
//请求:
GET test/_search?q=name:张三
//返回:
{
"took": 411,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.9616582,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1.9616582,
"_source": {
"id": "1",
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
}
}
]
}
}
//请求:
GET test/_search?q=name:张三&from=0&size=2&_source=name
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.9616582,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1.9616582,
"_source": {
"name": "张三" # _source 限制返回字段
}
}
]
}
}
请求体查询 测试:
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 2,
"_source": ["name", "address"],
"sort": [
{
"id": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": null,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"name": "张三",
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
},
"sort": [
1
]
}
]
}
}
match_all :等同于上面的空查询,没有任何条件,最简单的查询,它匹配所有文档就相当于空搜索,给它们的_score 默认都是1.0,可以通过boost 设置,可以进行一些排序之类的。
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心"
}
}
]
}
}
下面示例都使用请求体测试。
2、单条件筛选
首先我们需要知道 ES 中默认使用分词器为 标准分词器(StandardAnalyzer),标准分词器对于英文 单词分词 ,对于中文 单字分词。
在 ES 的 映射类型(Mapping Type) 中 keyword,date,integer,long,double ,boolean or ip 这些类型不分词,只有 text 类型分词。
2.1、匹配关键字
2.1.1、短语模糊匹配
match :先对搜索词进行分词,分词完毕后再逐个对分词结果进行匹配,因此相比于 term 的精确搜索,match 是分词匹配搜索,相当于模糊匹配,只包含其中一部分关键词就行 。
注意:这里的
match和 下面的match_pharse查询都是属于全文查询,全文查询会给当前的句子进行分词,通常来讲,索引的时候怎么分的词,查询的时候就是用的什么分词器,默认是不用设置的,但是如果有个别场景,也可以自己设置分词器。
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "江南" # 匹配江南,搜索到包含江苏和南通的两条数据
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.6375607,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1.6375607,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.53428984,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
}
}
]
}
}
模糊查询:
在实际的搜索中,我们有时候会打错字,从而导致搜索不到。在 ES 中,我们可以使用 fuzziness 属性 设置 编辑距离 来进行模糊查询,从而达到搜索有错别字的情形。
match 查询具有 fuziness 属性。它可以被设置为 0, 1, 2或 auto。auto 是推荐的选项,它会根据查询词的长度定义距离。在实际的使用中,当我们使用 auto 时,如果字符串的长度大于5,那么 funziness 的值自动设置为2,如果字符串的长度小于2,那么 fuziness 的值自动设置为 0。
编辑距离 是将一个术语转换为另一个术语所需的一个字符更改的次数。 这些更改可以包括:
- 更改字符(box→fox)
- 删除字符(black→lack)
- 插入字符(sic→sick)
- 转置两个相邻字符(act→cat)
准备数据:
POST /test/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"hobby": "football, basketball" # 使用英文测试,中文是分析器处理后是单字,英文是多个字母,更适合测试
}
}
测试:
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": "footbalf" # 当只有一个字母不同,正常匹配搜索不到
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 0,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": null,
"hits": []
}
}
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "footbalf",
"fuzziness": "1" # 编辑距离为 1,football 和 footbalf 只有一个字母不同,这时就可以搜索到。
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 0.25172183,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.25172183,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01",
"hobby": "football, basketball"
}
}
]
}
}
fuziness 设置是针对每个词语而言的,而不是总的错误的数值,所以可以查询多个单词。
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": {
"query": "footbalf basketbalf",
"fuzziness": "1"
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 11,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 0.51063573,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.51063573,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01",
"hobby": "football, basketball"
}
}
]
}
}
ES 的 fuzzy 查询,功能和上面一样,但是这个只针对一个 term 比较有用。
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"hobby": {
"value": "footbalf",
"fuzziness": "1"
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 0.25172183,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.25172183,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01",
"hobby": "football, basketball"
}
}
]
}
}
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"hobby": {
"value": "footbalf basketbal", # 两个单词就查询不到了
"fuzziness": "1"
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 0,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": null,
"hits": []
}
}
参考:
Elasticsearch:fuzzy 搜索 (模糊搜索)
ES 8.x Doc - 模糊查询
2.1.2、短语精确匹配
match_phrase :短语匹配查询,要求必须全部精确匹配,且顺序必须与指定的短语相同。首先解析查询字符串来产生一个词条列表,然后会搜索所有的词条,但只保留包含了所有搜索词条的文档。match_phrase 还支持词条列表各词项间隔距离多少的设置。
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query":{
"match_phrase": {
"address": "江南" # 未匹配到江南,三条数据地址有包含江苏或南通,但是没有江南
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 0,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": null,
"hits": []
}
}
2.1.3、关键词精确匹配
term :单词或单字精确匹配,只是查分词,不会对查询语句进行分词,所以会区分大小写。
terms :多个 term 的并集。
注意: term查询是基于词项的查询,当使用 term查询时,ES 不会对这个词做任何处理,但是在文本进行分词时,通常都会将大写转为小写,这个时候就会出现查不出来的情况。
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query":{
"term": {
"address": {
"value": "江" # 匹配包含江字的数据,两条
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 0.53428984,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.53428984,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.41070414,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心"
}
}
]
}
}
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query":{
"terms": {
"address": ["江","南"] # terms 就相当于多个 term 的并集
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心"
}
}
]
}
}
2.1.4、多字段查询
multi_match 查询提供了一个简便的方法用来对多个字段执行相同的查询。
更改一下数据:
POST /test/_update/2
{
"doc": {
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园张三家旁边"
}
}
测试:
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "张三",
"fields": ["name","address"]
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 718,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 2.5153382,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 2.5153382,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园张三家旁边",
"time": "2022/01/01"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1.5241971,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01",
"hobby": "football, basketball"
}
}
]
}
}
2.1.5、前缀查询
prefix:查询返回在提供的字段中包含特定前缀的文档。
前缀匹配只适用于 keyword ,是不做分词的且大小写敏感, 因为前缀匹配不涉及索引分词,所以只能匹配 关键字 keyword,因此效率很低,不推荐生产环境使用。
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"address.keyword": "上海" #
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园张三家旁边",
"time": "2022/01/01"
}
}
]
}
}
参考:【ElasticSearch】ElasticSearch中字符串.keyword和.text类型区别和模糊查询
2.1.6、通配符查询
wildcard:ES中可以实现通配符搜索,通配符匹配也是扫描完整索引,通配符可以在 索引中使用,也可以在 keyword中使用。
ElsticSearch支持的通配符有2个,分别是:
*:0个或多个任意字符?:任意单个字符
注意: 为了防止极慢的通配符匹配,查询字符串不要以通配符开头,只在查询字符串中间或末尾使用通配符。
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"address.keyword": { # 如果是address 的话只能匹配 单字 才有数据
"value": "上海*"
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园张三家旁边",
"time": "2022/01/01"
}
}
]
}
}
2.2、范围查询
2.2.1、数字范围
range 查询可同时提供包含(inclusive)和不包含(exclusive)这两种范围表达式,可供组合的选项如下:
gt: > 大于(greater than)
lt: < 小于(less than)
gte: >= 大于或等于(greater than or equal to)
lte: <= 小于或等于(less than or equal to)
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query":{
"range": {
"age": { # 查询年龄在 10~20 之间的数据
"gte": 10,
"lte": 22
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园"
}
}
]
}
}
2.2.2、日期范围
添加下时间 time:
POST /test/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"time":"2021/01/01"
}
}
POST /test/_update/2
{
"doc": {
"time":"2022/01/01"
}
}
POST /test/_update/3
{
"doc": {
"time": "2023/01/01"
}
}
range 查询同样可以应用在日期字段上:
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"query":{
"range": {
"time": {
"gt": "2022/03/01",
"lt": "2023/03/01"
}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心",
"time": "2023/01/01"
}
}
]
}
}
2.3、多id查询
根据 ID 返回文档。此查询使用存储在 _id 字段中的文档 ID。
请求参数:
ids.values:(必填, 字符串数组) 文档的_id的数组
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": ["1","2"]
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 23,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园",
"time": "2022/01/01"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01"
}
}
]
}
}
3、多条件筛选
现实的查询需求从来都没有那么简单;它们需要在多个字段上查询多种多样的文本,并且根据一系列的标准来过滤。为了构建类似的高级查询,你需要一种能够将多查询组合成单一查询的查询方法。
3.1、布尔查询
bool 查询:可以实现你的需求。这种查询将多查询组合在一起,成为用户自己想要的布尔查询。它接收以下参数:
must:文档 必须 匹配这些条件才能被包含进来。must_not:文档 必须不 匹配这些条件才能被包含进来。should:如果满足这些语句中的任意语句,将增加_score,否则,无任何影响。它们主要用于修正每个文档的相关性得分。filter:必须 匹配,但它以不评分、过滤模式来进行。这些语句对评分没有贡献,只是根据过滤标准来排除或包含文档。
Filter Context 和 Query Context 的区别:
- 进行query context查询时,ES除了要判断某个文档是否与查询值匹配,还要计算相关度评分(relevance score),并放入到返回结果的_score字段中!
- 而当进行filter context查询时,仅仅判断某个文档是否与查询值匹配,不但无需进行相关度评分的计算,而且对于高频率的filter查询,ES还会自动将查询结果缓存起来,以提高filter查询的性能。
must和should属于Query Context,会对_score结果产生影响;
filter和must_not属于Filter Context,不会对_score结果产生影响;
测试:
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "name": "张三" }} # name 包含张三
],
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "address": "上海" }} # 地址不能包含 上海
],
"should": [
{ "term": { "hobby": "football" }} # 匹配到的数据中包含 football,_score 增加,未匹配到 _score 不变
],
"filter": [
{ "range": { "age": { "gte": "20" }}} # 过滤,筛选 age 大于等于 20 的数据
]
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 2.0440507,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 2.0440507,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01",
"hobby": "football, basketball"
}
}
]
}
}
参考:
ES - query-filter-context
Elasticsearch: 权威指南 - 组合多查询
4、指定字段
_source :指定返回的源数据字段。
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"_source": ["name"]
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "王五"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "李四"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "张三"
}
}
]
}
}
5、高亮查询
如果返回的结果集中很多符合条件的结果,那怎么能一眼就能看到我们想要的那个结果呢?比如像百度所示的那样,将搜索词高亮显示:
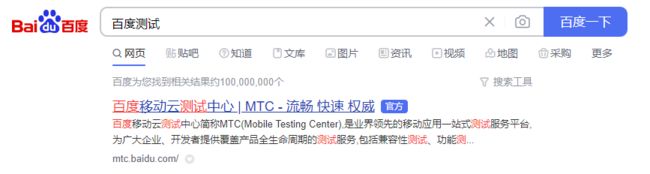
如果要达到上图的效果怎么做呢,ES 提供了 高亮查询 API 可以高亮显示搜索信息:
5.1、默认高亮显示
highlight:ES 会从查询到的数据中,找到匹配的短语或关键字词,并以 标签包裹起来。
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "江南"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"address": {}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.7658587,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1.7658587,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心",
"time": "2023/01/01"
},
"highlight": {
"address": [
"江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.395165,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01"
},
"highlight": {
"address": [
"江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
]
}
}
]
}
}
5.2、自定义高亮html标签
ES 可以在 highlight 中使用 pre_tags 和 post_tags 来自定义匹配内容前后高亮的html标签 。
//请求:
GET /test/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": "江南"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "",
"post_tags": "",
"fields": {
"address": {}
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 1,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1.7658587,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1.7658587,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心",
"time": "2023/01/01"
},
"highlight": {
"address": [
"江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心"
]
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.395165,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三222",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01"
},
"highlight": {
"address": [
"江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区"
]
}
}
]
}
}
6、排序
sort:指定字段排序方式。
数据模型的复杂程度决定了排序的复杂程度,排序的复杂程度随着模型的复杂程度成指数级增加。这里就简单的介绍普通用法。
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"sort": {
"id": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": null,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01"
},
"sort": [
1
]
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园",
"time": "2022/01/01"
},
"sort": [
2
]
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心",
"time": "2023/01/01"
},
"sort": [
3
]
}
]
}
}
7、分页
from:起始数据位置。
size:返回数据数量。
ES 分页查询限制总数能不超过10000,原因是基本用不到10000条以后数据,如果前面10000条数据还没有找到你想要的数据,那么后面的匹配度更低,找到的概率更小,查询速度也会越来越慢,合理没必要查10000以后的。
//请求:
GET test/_search
{
"from": 0, # 0 开始
"size": 2 # 获取两条数据
}
//返回:
{
"took": 0,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3, # 总数3
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 3,
"name": "王五",
"age": 3,
"address": "江苏省南通市崇川区兴通路98-99号南通国际会展中心",
"time": "2023/01/01"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园",
"time": "2022/01/01"
}
}
]
}
}
六、批量操作(Mget、Bulk) API
批量操作的好处在于可以一次请求完成多次操作,不需要发送多次,可以解决很多网络的开销,可以显著的提高索引的速度。
1、批量查询
_mget:可以同时执行不同的 get 操作,多个API操作之间的结果互不影响。
1.1、同一个索引
//请求:
GET /test/_mget
{
"docs":[
{
"_id": 1
},
{
"_id": 2
}
]
}
都是根据id,查询的话,也可以使用下面 ids 这种写法,结果一样:
GET /test/_mget
{
"ids": [1,2]
}
//返回:
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 5,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01"
}
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 4,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"age": 22,
"address": "上海市浦东新区锦绣路1001号世纪公园",
"time": "2022/01/01"
}
}
]
}
1.2、不同索引
创建索引 test2,添加一条数据:
POST test2/_doc/1
{
"id":1,
"name":"赵六",
"age":30,
"address": "杭州市上城区万松岭路81号"
}
//请求:
GET /_mget
{
"docs":[
{
"_index":"test", # ES 8.x 以后不需要 _type
"_id": 1
},
{
"_index":"test2",
"_id": 1
}
]
}
//返回:
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"_seq_no": 5,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"address": "江苏省苏州市苏州工业园区",
"time": "2021/01/01"
}
},
{
"_index": "test2",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"id": 1,
"name": "赵六",
"age": 30,
"address": "杭州市上城区万松岭路81号"
}
}
]
}
2、批量修改
_bulk:可以同时执行不同的CUD操作,多个API操作之间的结果互不影响。
bulk request会加载到内存中,如果太大的话,性能反而下降,因此需要反复尝试一个最大的 bulk size。一般从1000~5000条数据开始,尝试逐渐增加。另外,如果看大小的话,最好在5M。
注意:bulk操作不能进行代码换行。
POST /_bulk
{action1:{metadata1}}
{requestbody1}
{action2:{metadata2}}
{requestbody2}
测试:
//请求:
POST /_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"test3","_id":1}}
{"doc":{"id":1,"name":"孙七","age":50,"address":"地球"}}
{"create":{"_index":"member","_id":999}}
{"doc":{"id":1,"name":"周八","age":80,"address":"地球2"}}
{"delete":{"_index":"test2","_id":"1"}}
{"update":{"_index":"test","_id":1}}
{"doc":{"name":"张三222"}}
//返回:
{
"took": 471,
"errors": false,
"items": [
{
"index": {
"_index": "test3",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"create": {
"_index": "member",
"_id": "999",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 0,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 201
}
},
{
"delete": {
"_index": "test2",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 2,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
},
{
"update": {
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 3,
"result": "updated",
"_shards": {
"total": 2,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 6,
"_primary_term": 1,
"status": 200
}
}
]
}
七、离线文档下载
elastic 官网 访问缓慢已常态,还经常无法访问,为了方便看文档,我使用 DownGit 从 GitHub 下载了离线文档,但是下载的离线文档没有左侧API导航栏这个比较坑。
还有一点是关于翻译的问题,ES 的中文版版本太低,我们常用的还是英文版,谷歌的翻译功能又不可用,想要翻译成中文可以使用 Edge 浏览器。
下载离线文档参考:
DownGit
GitHub ES 8.6 文档地址(也可选择其他版本)
GitHub ES 8.6 文档样式渲染地址
Elasticsearch进阶教程:生成离线官方文档