Design Patterns in Android:策略模式
- 前言
- 策略模式定义
- 策略模式UML类图
- 策略模式的示例代码
- Android源码中的策略模式
- Android开发中的策略模式实践
- 总结
前言
刚过去的春节,大家有没有从“节后综合征”中痊愈满血呢?
新年里给大家带来的第一篇是《设计模式Android篇:策略模式》。
点击此处查看《Design Patterns in Android》系列其他文章。
本文原创作者MichaelX(xiong_it),博客链接:http://blog.csdn.net/xiong_it,转载请注明出处。
策略模式定义
策略模式(Strategy pattern):定义一组算法,将其各个封装,并且使他们有交换性。
策略模式好处在于使得算法在用户使用的时候能独立的改变,单一的修改,并且有良好扩展性。
算法:指的是各个策略的实现逻辑,而非算法领域的数据算法。
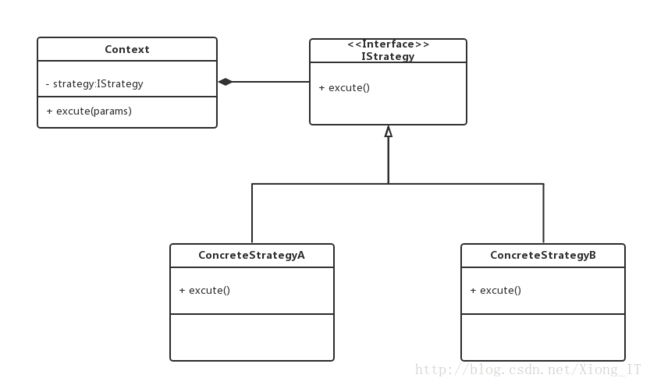
策略模式UML类图
策略模式各角色讲解
- IStrategy:策略基类(接口或者抽象类),定义子策略需要实现的方法,比如excute(),该方法取决于客户端代码(高层代码)需要该策略实现什么功能,子类则实现该方法,封装自己的算法,供外部调用。
- Context:此Context,非彼(Android中的)Context,它持有IStrategy真实的实例对象,提供给客户端调用IStrategy时的上下文调度者。
- ConcreteStrategyA:实现父类IStrategy的方法,封装自身算法逻辑。
- ConcreteStrategyB:同上
策略模式的示例代码
IStrategy
public interface IStrategy {
void excute();
}ConcreteStrategyA
public class ConcreteStrategyA implements IStrategy{
public void excute() {
System.out.println("1.我是ConcreteStrategyA的算法实现");
}
}ConcreteStrategyB
public class ConcreteStrategyB implements IStrategy{
public void excute() {
System.out.println("2.我是ConcreteStrategyB的算法实现");
}
}Context上下文角色
public class Context {
private IStrategy strategy;
public Context(Strategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void excute() {
this.strategy.excute();
}
}好了,下面是就是客户端代码,描述了如何使用策略模式
Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context context;
context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyA());
context.excute();
// context = new Context(new ConcreteStrategyB());
// context.excute();
}
}如上,客户端需要什么策略就new什么策略,完全取决于客户端需求,而且如果策略A出现问题,修改策略A就是了,和其他地方完全无关,如果现有策略不符合需求,再实现一个ConcreteStrategyA即可。
Android源码中的策略模式
大家在使用Animation动画时,可以给Animation对象设置不同的插值器(Interpolator)来实现动画快慢速度动态效果。
比如:
LinearInterpolator,线性插值器,实现匀速动画
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator:加速减速插值器,实现开始加速,结尾时减速的动画
BaseInterpolator类:Interpolator的实现类,就是速度插值器策略的基类
/**
* An abstract class which is extended by default interpolators.
*/
abstract public class BaseInterpolator implements Interpolator {
private int mChangingConfiguration;
/**
* @hide
*/
public int getChangingConfiguration() {
return mChangingConfiguration;
}
/**
* @hide
*/
void setChangingConfiguration(int changingConfiguration) {
mChangingConfiguration = changingConfiguration;
}
}Animation:Context上下文角色
public abstract class Animation implements Cloneable {
// ...
// 省略无关代码
// ...
private Interpolator mInterpolator;
/**
* Sets the acceleration curve for this animation. Defaults to a linear
* interpolation.
*
* @param i The interpolator which defines the acceleration curve
* @attr ref android.R.styleable#Animation_interpolator
*/
public void setInterpolator(Interpolator i) {
mInterpolator = i;
}
}LinearInterpolator等子类就实现了各自速度快慢的算法逻辑
@HasNativeInterpolator
public class LinearInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator {
public LinearInterpolator() {
}
public LinearInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return input;
}
}现在,我们给一个ImageView添加View动画
ImageView view;
Animation animation = getResources().getAnimation(R.anim.pop_anim);
// 给view的动画设置一个插值器策略
animation.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
view.startAnimation(animation);Android开发中的策略模式实践
需求,现在你开发的Android app需要实现盈利,PM经过一番规划,想要你接入微信支付,支付宝支付,银联支付等移动端通用支付方式。
这个功能好实现,接入相关支付SDK即可,问题就在如何优雅的实现这个功能呢?
延伸阅读:
《 Android App支付系列(一):微信支付接入详细指南(附官方支付demo)》
《 Android App支付系列(二):支付宝SDK接入详细指南(附官方支付demo)》
以下是笔者是实现,供各位读者参考。
- PayActivity:客户端角色,支付方式选择界面
- AbsPayStrategy:作为支付策略基类,定义了一个pay方法
- PayContext:上下文角色,用来封装支付AbsPayStrategy对象
- WeChatPayStrategy:封装了微信支付算法逻辑
- ALiPayStrategy:封装了支付宝支付算法逻辑
- BankCardPayStrategy:封装了银行卡支付算法逻辑
支付功能的示意代码
AbsPayStrategy的实际实现应该为抽象类,它需要持有Activity对象。
public interface AbsPayStrategy {
// private Activity mActivity;
// 本策略主要就是实现支付功能
void pay();
} Context上下文角色
public class PayContext {
private AbsPayStrategy mPayStrategy;
public PayContext(AbsPayStrategy payStrategy) {
mPayStrategy = payStrategy;
}
public void pay() {
mPayStrategy.pay();
}
}微信支付策略实现
/**
* 微信支付策略
*/
public class WeChatPayStrategy implements AbsPayStrategy {
public void pay() {
// 此处封装微信支付逻辑
// 具体请参考笔者的博文《 Android App支付系列(一):微信支付接入详细指南(附官方支付demo)》
}
}支付宝支付策略实现
/**
* 支付宝支付策略
*/
public class ALiPayStrategy implements AbsPayStrategy {
public void pay() {
// 此处封装支付宝支付逻辑
// 具体请参考笔者的博文《 Android App支付系列(二):支付宝支付SDk接入详细指南(附官方支付demo)》
}
}具体的客户端代码,此处为PayActivity
public class PayActivity extends Activity implements View.OnclickListener{
private PayContext mPayContext;
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
switch(v.getId()) {// 客户端来决定使用哪种支付策略
case R.id.wechat_pay:
mPayContext = new PayContext(new WechatPayStrategy());
break;
case R.id.wechat_pay:
mPayContext = new PayContext(new ALiPayStrategy());
break;
case R.id.wechat_pay:
mPayContext = new PayContext(BankCardPayStrategy());
break;
default:
mPayContext = new PayContext(new WechatPayStrategy());
break;
}
// 利用实际的支付策略对象进行支付
mPayContext.pay();
}
}这样就实现了一个app内的支付功能,如果微信支付出现问题了,改动微信支付策略代码,支付宝支付出现问题,改动想要实现即可,职责单一。
如果PM有一天说:我们需要接入百付宝,京东支付。怎么办?
简单啊,实现相应的支付策略即可,完美适应需求变更,实现功能扩展。
总结
如果在开发某功能时,可能出现多种平等的选择,可以考虑使用策略模式实现。
好了,今天的《设计模式Android篇:策略模式》就到这里,请继续关注《Design Patterns in Android》(设计模式Android篇)系列博文,欢迎各位读者朋友评论区拍砖交流,共同进步。
查看本文最新版本,请进入:MichaelX’s Blog。