《剑指offer C/C++ or Java 》
JZ3 数组中重复的数字

排序之后查找是否有前后两个相同的数字,如果有任意输出一个即可,无则输出-1
class Solution {
public:
int duplicate(vector<int>& numbers) {
int l=numbers.size();
sort(numbers.begin(),numbers.begin()+l);
for(int i=0;i<l-1;i++)
{
if(numbers[i]==numbers[i+1])
return numbers[i];
}
return -1;
}
};
JZ4 二维数组中的查找

二维数组中查找是否存在有目标数字,计算出二维数组的大小,遍历即可
Leecode需要多加一个判断,否则题目过不去
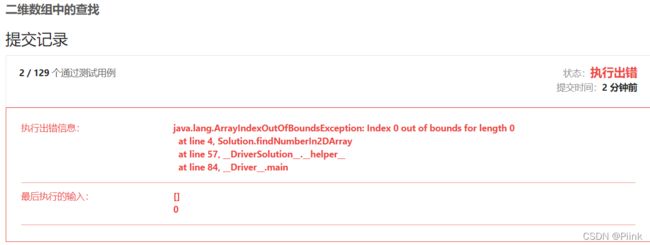
if(matrix.length==0||matrix[0].length==0)
return false;
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> > array) {
int len=array.size();
int len1=array[0].size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
for(int j=0;j<len1;j++)
{
if(array[i][j]==target)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
JZ5 替换空格
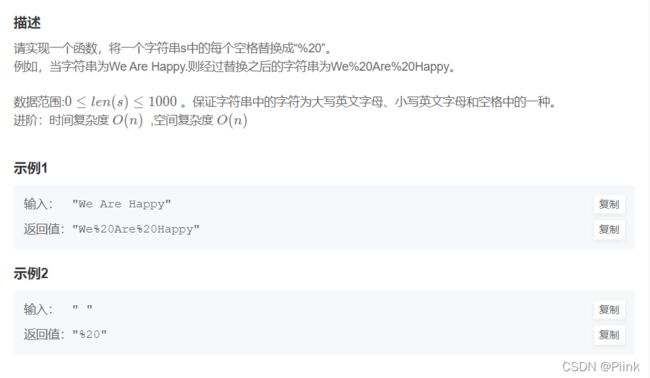
法一:将字符串的空格更换为%20,用一个新的字符串保存,遇到空格则保存%20,遇到其它的直接存入字符串即可
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpace(string s) {
int l=s.length();
string s1;
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
if(s[i]==' ')
{
s1+='%';
s1+='2';
s1+='0';
}
else
s1+=s[i];
}
return s1;
}
};
法二:Java种replace用法
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
s=s.replace(" ","%20");
return s;
}
}
JZ6 从尾到头打印链表
/**
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList list=new ArrayList<>();//动态数组
//add方法用于添加一个元素到当前列表的末尾
while(listNode!=null){
//add(x,y) 在集合中指定x位置,添加新元素y
list.add(0,listNode.val);
listNode=listNode.next;//遍历链表中的元素
}
return list;
}
}
JZ7 重建二叉树


给出前序遍历和中序遍历结果,求层序遍历
首先我们知道前序遍历第一个元素就是根节点,在中序遍历结果中根节点可以将中序遍历分成两段,即左子树和右子树
再进行递归,用Java中Arrays.copyOfRange函数将前序遍历的前一部分(即左子树)和中序遍历的左子树的一段递归求,同理右子树也是如此

import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] vin) {
if(pre.length==0||vin.length==0)
return null;
//前序遍历中第一个就是根root
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(pre[0]);//前序遍历根左右
//中序遍历找到根 左右分开
//copyOfRange(original,int from,int to)
//该方法返回一个长度为to-from的数组
//其中from~min(original.length,to)之间的元素
//不包括min(original.length,to)
for(int i=0;i<vin.length;i++){
if(vin[i]==pre[0]){
root.left=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, i + 1), Arrays.copyOfRange(vin, 0, i));
root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, i+1, pre.length), Arrays.copyOfRange(vin, i+1, vin.length));
}
}
return root;
}
}
JZ8 二叉树的下一个结点
分为三种情况
1.只有一个根节点,返回空
2.有右孩子,那么中序遍历的下一个节点是右孩子的最左孩子,如果没有左孩子,那就是自己
3.左子树上的节点的下一个节点是他的父节点或者他的右孩子节点,没有右孩子就是自己
写代码可以分成两种情况
1.找右孩子的最左孩子,没有即本身
2.找父节点的右孩子,没有即本身
/*
struct TreeLinkNode {
int val;
struct TreeLinkNode *left;
struct TreeLinkNode *right;
struct TreeLinkNode *next;
TreeLinkNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode) {
if(!pNode)
return pNode;
//右孩子节点的最左孩子节点,若没有左孩子,就是自己
if(pNode->right)
{
pNode=pNode->right;
//找最左
while(pNode->left){
pNode=pNode->left;
}
return pNode;
}
//父节点的右孩子节点
//next指针是指向父节点的
while(pNode->next){
TreeLinkNode* root=pNode->next;
//父节点的右孩子,但不是最右孩子
if(root->left==pNode)
return root;
pNode=pNode->next;
}
//两种情况都不是则返回空
return nullptr;
}
};
JZ9 用两个栈实现队列
class Solution
{
public:
void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);//尾部
}
int pop() {
//如果存储头部的栈为空,那么就把尾部的加入头部,同时删除尾部栈的元素
if(stack2.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.top());
stack1.pop();
}
}
int node=stack2.top();
stack2.pop();
return node;
}
private:
stack<int> stack1;//模拟尾部
stack<int> stack2;//模拟头部
};
JZ10 斐波那契数列
class Solution {
public:
int Fibonacci(int n) {
int f[50];
f[1]=1;
f[2]=1;
for(int i=3;i<=40;i++)
f[i]=f[i-1]+f[i-2];
return f[n];
}
};
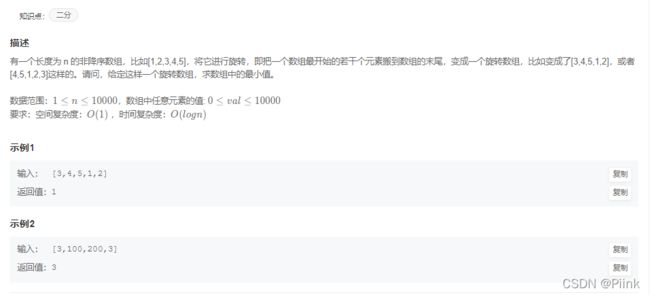
JZ11 旋转数组的最小数字
class Solution {
public:
int minNumberInRotateArray(vector<int> rotateArray) {
int len=rotateArray.size();
int minn=99999;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
minn=min(minn,rotateArray[i]);
}
return minn;
}
};
JZ12 矩阵中的路径

DFS模板,for循环控制4个方向,保证不出矩阵且走的格子所在的英文字母与字符串的相等,当走的步数等于字符串的长度,则搜索结束
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param matrix char字符型vector<vector<>>
* @param word string字符串
* @return bool布尔型
*/ int book[30][30];
bool f;
void dfs(int n,int m,vector<vector<char> >& matrix,string word,int x,int y,int z){
int dir[4][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
int dx,dy;
if(z==word.size())
{
f=true;
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
dx=x+dir[i][0];
dy=y+dir[i][1];
if(dx>=0&&dx<n&&dy>=0&&dy<m&&book[dx][dy]==0&&matrix[dx][dy]==word[z])
{
book[dx][dy]=1;
dfs(n,m,matrix,word,dx,dy,z+1);
book[dx][dy]=0;
}
}
}
bool hasPath(vector<vector<char> >& matrix, string word) {
// write code here
int n=matrix.size();
int m=matrix[0].size();
memset(book,0,sizeof(book));
int tx,ty;
f=false;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{
if(matrix[i][j]==word[0])
{
tx=i;
ty=j;
book[tx][ty]=1;
dfs(n,m,matrix,word,tx,ty,1);
book[tx][ty]=0;
if(f)
break;
}
}
if(f)
break;
}
return f;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int n,m;
bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word,int i,int j,int k){
if(i<0||i>=n||j<0||j>=m||board[i][j]!=word[k])
return false;
if(k==word.size()-1)
return true;
board[i][j]='\0';/标记走过了
bool f=(dfs(board,word,i,j+1,k+1)||dfs(board,word,i,j-1,k+1)||dfs(board,word,i+1,j,k+1)||dfs(board,word,i-1,j,k+1));
board[i][j]=word[k];//取消标记
return f;
}
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
n=board.size();
m=board[0].size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(dfs(board,word,i,j,0))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
JZ13 机器人的运动范围
class Solution {
public:
int book[110][110];
//计算数位之和
int f(int n){
int ans=0;
while(n)
{
int s=n%10;
ans+=s;
n=n/10;
}
return ans;
}
int dfs(int x,int y,int threshold, int rows, int cols)
{
book[x][y]=1;
int step=0;
int dir[4][2]={0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0};
int tx,ty;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
tx=x+dir[i][0];
ty=y+dir[i][1];
if(tx>=0&&tx<rows&&ty>=0&&ty<cols&&f(tx)+f(ty)<=threshold&&!book[tx][ty]){
step+=dfs(tx,ty,threshold,rows,cols)+1;
}
}
return step;
}
int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {
//下面两行写不写都行,没影响
// if(threshold<0||rows<=0||cols<=0)
// return 0;
return dfs(0,0,threshold,rows,cols)+1;
}
};
JZ14 剪绳子
绳长为2,分为两段,1和1 乘积为1
绳长为3,分为两段,1和2 乘积为2
绳长为4,可以分为1 1 2和1 3和2 2,最大乘积为4
从小到大进行枚举,当我们进行求解某一个数字的时候,我们已经求出了之前的所有的数的最优的情况,那么我们可以枚举将这个数字x分解出1,2,…x-1的所有的情况,维护最大值即可
class Solution {
public:
int cutRope(int number) {
int f[100];
for(int i=2;i<=number;i++)
{
f[2]=2;
f[3]=3;
for(int j=1;j<i;j++)
{
f[i]=max(f[i],f[j]*(i-j));
}
}
return f[number];
}
};
绳子长分为长度2和3即可,如果%3的结果为2直接乘,如果%3的结果为1那么借一个3,和余的1分为两个2,如果%3的结果为0,直接计算所有3相乘即可
class Solution {
public:
int cutRope(int number) {
if(number<=3)
return number-1;
else
{
int x=number/3;
int y=number%3;
long long ans;
if(y==2){
ans=pow(3,x);
ans*=2;
}
else if(y==1){
ans=pow(3,x-1);
ans*=4;
}
else
ans=pow(3,x);
return ans;
}
}
};
JZ15 二进制中1的个数
//Java代码
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
String str=Integer.toBinaryString(n);//数字转换为二进制字符串
String[] str1=str.split("");//拆分函数
int ans=0;
//遍历数组,和1比较,计数即可
for(int i=0;i<str1.length;i++){
if(str1[i].equals("1"))
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
}
JZ16 数值的整数次方
class Solution {
public:
double Power(double base, int exponent) {
double sum=1;
int f=0;
//指数为负数
if(exponent<0)
{
f=1;
exponent=-exponent;
}
//快速幂
while(exponent)
{
//Leecode网站的这里需要用位运算优化
if(exponent%2==1){//if(exponent&1)
sum*=base;
}
base=base*base;
exponent=exponent/2;//exponent=exponent<<1;
}
if(f==1)
return 1.0/sum;
else
return sum;
}
};
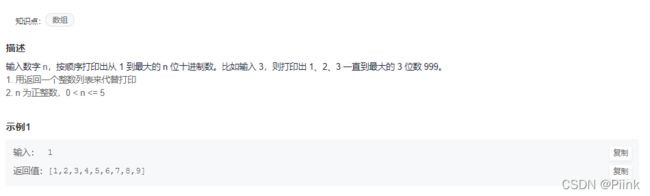
JZ17 打印从1到最大的n位数
For循环,用一个数组存储即可
//Java代码
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] printNumbers (int n) {
int sum=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
sum*=10;
int[] p = new int[sum-1];
for(int i=0;i<sum-1;i++)
{
p[i]=i+1;
}
return p;
}
}
//C++代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printNumbers(int n) {
vector<int>v;
int s=pow(10,n);
for(int i=1;i<s;i++)
v.push_back(i);
return v;
}
};
JZ18 删除链表的节点
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode (ListNode head, int val) {
// write code here
ListNode p=null,p1=head;
while(p1!=null)
{
if(p1.val==val)//存在与val相同的值
{
if(p1==head)//如果是头指针
return head.next;//删除头指针后,头指针则变为头指针指向的下一个
p.next=p1.next;
p1.next=null;
break;
}
p=p1;
p1=p1.next;
}
return head;//返回头指针
}
}
JZ20 表示数值的字符串


Java中try catch的用法
可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34427165/article/details/83929470
try catch:自己处理异常
try {
可能出现异常的代码
} catch(异常类名A e)
{
如果出现了异常类A类型的异常,那么执行该代码
}
…(catch可以有多个)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public boolean isNumeric (String str) {
try{
//Double.parseDouble()把括号里面内容变成double类型的
//如果要变成int,则用Integer.parseInt()
double x=Double.parseDouble(str);
return true;
}catch(Exception e){
return false;
}
}
}
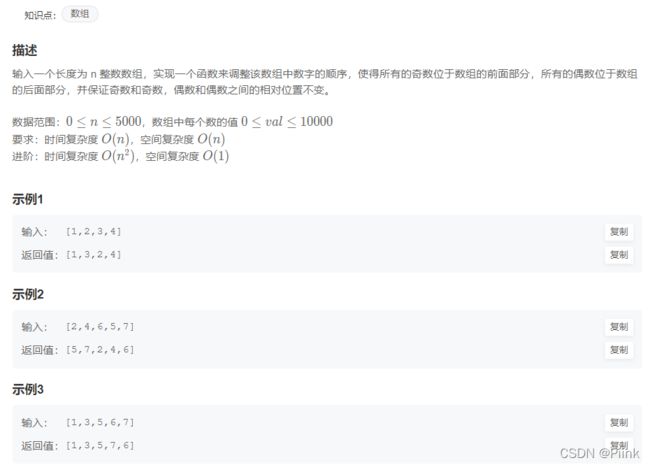
JZ21 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面(一)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param array int整型一维数组
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public int[] reOrderArray (int[] array) {
// write code here
int l=array.length;
int[] arr=new int[l];
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<l;i++){
if(array[i]%2==1)
arr[j++]=array[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<l;i++){
if(array[i]%2==0)
arr[j++]=array[i];
}
return arr;
}
}
JZ22 链表中倒数最后k个结点
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
ListNode* FindKthToTail(ListNode* pHead, int k) {
// write code here
stack<ListNode*>st;
ListNode *p=NULL;
//节点全部入栈
while(pHead){
st.push(pHead);
pHead=pHead->next;
}
if(k>st.size()||st.size()==0)
return p;
//栈顶元素出k个
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
p=st.top();
st.pop();
}
return p;
}
};
JZ23 链表中环的入口结点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode* pHead) {
set<ListNode*>s;
while(pHead){
if(s.find(pHead)==s.end()){
s.insert(pHead);
pHead=pHead->next;
}
else {
return pHead;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
JZ24 反转链表
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
ListNode *pre=nullptr;//pre指向反转后的头节点
ListNode *cur=pHead;//cur指向反转前的第一个节点,也就是头节点pHead
ListNode *next=nullptr;//next指向反转前第二个节点保存链表,因为cur改变指向后,后面的链表则失效了,所以需要保存
while(cur){
next=cur->next;
cur->next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
return pre;
}
};
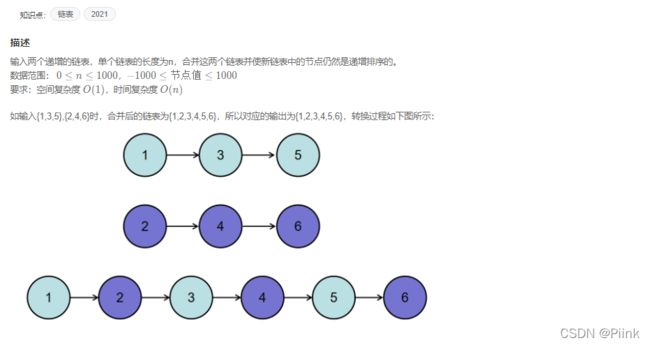
JZ25 合并两个排序的链表
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* Merge(ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
//合并两个链表,若其中一个为空,则直接返回另一个即可
if(!pHead1)
return pHead2;
if(!pHead2)
return pHead1;
//比大小,小的先合并
if(pHead1->val<=pHead2->val){
pHead1->next=Merge(pHead1->next,pHead2);
return pHead1;
}
else{
pHead2->next=Merge(pHead2->next,pHead1);
return pHead2;
}
}
};
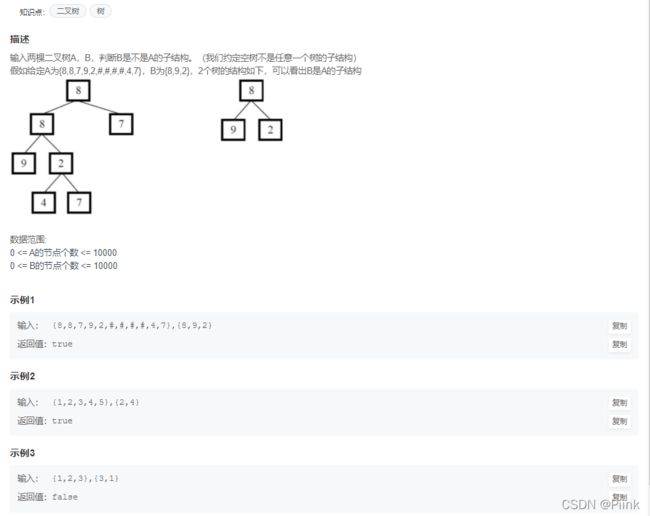
JZ26 树的子结构
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
bool issame(TreeNode* p1, TreeNode* p2){
//判断B是不是A的子结构
//空树不是任意一个树的子结构
bool left=true,right=true;
if(!p1||p1->val!=p2->val)
return false;
if(p2->left)
left=issame(p1->left,p2->left);
if(p2->right)
right=issame(p1->right,p2->right);
return left&&right;
}
bool HasSubtree(TreeNode* pRoot1, TreeNode* pRoot2) {
if(!pRoot1||!pRoot2)
return false;
if(issame(pRoot1,pRoot2))
return true;
if(HasSubtree(pRoot1->left,pRoot2)||HasSubtree(pRoot1->right,pRoot2))
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
JZ27 二叉树的镜像
/**
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pRoot TreeNode类
* @return TreeNode类
*/
TreeNode* Mirror(TreeNode* pRoot) {
// write code here
if(pRoot==NULL)
return NULL;
//求镜像树,中间变量实现交换左右树
TreeNode *tmp=pRoot->right;
pRoot->right=Mirror(pRoot->left);
pRoot->left=Mirror(tmp);
return pRoot;
}
};
JZ28 对称的二叉树
三种情况
1.左右都为空,说明也是对称
2.左空右不空,右空左不空,左右有一个为空,说明不对称
3.都不为空,左=右,右=左,说明对称
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool issame(TreeNode* p1,TreeNode* p2){
if(!p1&&!p2)
return true;
if(!p1||!p2)
return false;
//根节点值相等,左=右 右=左 即对称
if ((p1->val==p2->val)&&issame(p1->left,p2->right)&&issame(p1->right,p2->left))
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot) {
return issame(pRoot,pRoot);
}
};
JZ29 顺时针打印矩阵
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int [][] matrix) {
int l1=matrix.length;
int l2=matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] book=new boolean[110][110];
int[] dx={0,1,0,-1};//右下左上
int [] dy={1,0,-1,0};
int tx=0,ty=0,dir=0;
ArrayList<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();//存储
while(tx>=0&&tx<l1&&ty>=0&&ty<l2&&!book[tx][ty]){
list.add(matrix[tx][ty]);
book[tx][ty]=true;
while(tx+dx[dir]>=0&&tx+dx[dir]<l1&&ty+dy[dir]>=0&&ty+dy[dir]<l2&&!book[tx+dx[dir]][ty+dy[dir]])
{
tx+=dx[dir];
ty+=dy[dir];
list.add(matrix[tx][ty]);
book[tx][ty]=true;
}
dir=(dir+1)%4;
tx+=dx[dir];
ty+=dy[dir];
}
return list;
}
}
JZ30 包含min函数的栈

获取最小值需要用两个栈来实现,一个栈存储数据,用于push和pop,另一个栈用于存储最最小值
class Solution {
public:
stack<int>s1;//用于push和pop
stack<int>s2;//用于存储min
void push(int value) {
s1.push(value);//放入栈中
if(s2.empty()||s2.top()>value)//栈为空或者新的元素比较小
s2.push(value);
else //新的元素比较大时,则放入栈顶元素,不放较大的新元素,所以s2.top()始终保持最小值
s2.push(s2.top());
}
void pop() {//删除操作要把两个栈中的数据都删除
s1.pop();
s2.pop();
}
int top() {//获取栈顶元素
return s1.top();
}
int min() {//获取最小元素
return s2.top();
}
};
JZ31 栈的压入、弹出序列
class Solution {
public:
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) {
stack<int>st1;//栈模拟
int l1=pushV.size();
int l2=popV.size();
int l3=0;
for(int i=0;i<l1;i++){
st1.push(pushV[i]);
while(!st1.empty()&&st1.top()==popV[l3]){
st1.pop();
l3++;
}
}
if(st1.empty())
return true;
else
return false;
}
};
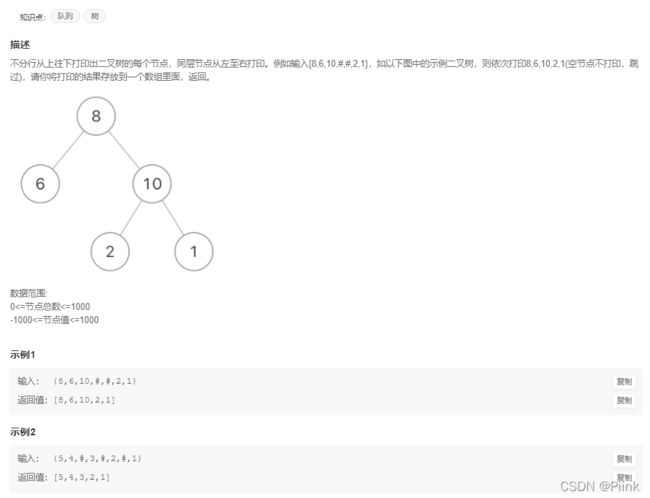
JZ32 从上往下打印二叉树
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> PrintFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>v;
if(!root)
return v;
queue<TreeNode*>q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode *node=q.front();
q.pop();
v.push_back(node->val);//这里是node->val,不是node,存的是值,不是指针
if(node->left)
q.push(node->left);
if(node->right)
q.push(node->right);
}
return v;
}
};
JZ33 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
class Solution {
public:
bool VerifySquenceOfBST(vector<int> sequence) {
int l=sequence.size();
if(l==0)
return false;
return check(sequence,0,l-1);
}
bool check(vector<int> sequence,int l,int r){
if(l>=r)
return true;//如果当前子树只有一个节点
int root=sequence[r];//左右根 最后一个节点是根节点
int j=r-1;
//右子树
while(j>=0&&sequence[j]>root)
j--;
//左子树如果有大于根节点的数就不属于是二叉搜索树
for(int i=l;i<=j;i++){
if(sequence[i]>root)
return false;
}
return check(sequence,l,j) && check(sequence,j+1,r-1);
}
};
JZ34 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(二)
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>v;
vector<vector<int>>v1;
void abc(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber){
v.push_back(root->val);
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr&&root->val==expectNumber)
v1.push_back(v);
if(root->left)
abc(root->left,expectNumber-root->val);
if(root->right)
abc(root->right,expectNumber-root->val);
v.pop_back();// 回溯 当前v中的root节点不需要了
}
vector<vector<int>> FindPath(TreeNode* root,int expectNumber) {
if(root==nullptr)
return {};
abc(root,expectNumber);
return v1;
}
};
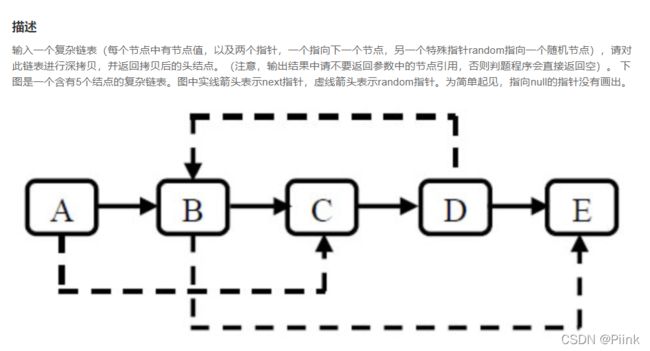
JZ35 复杂链表的复制
/*
struct RandomListNode {
int label;
struct RandomListNode *next, *random;
RandomListNode(int x) :
label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
map<RandomListNode*,RandomListNode*>mp;
RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==nullptr)
return nullptr;
if(!mp.count(pHead)){
RandomListNode* newhead=new RandomListNode(pHead->label);
mp[pHead]=newhead;
newhead->next=Clone(pHead->next);
newhead->random=Clone(pHead->random);
return newhead;
}
return mp[pHead];
}
};
JZ36 二叉搜索树与双向链表
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<TreeNode*>v;
void inorder(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)
return ;
inorder(root->left);
v.push_back(root);
inorder(root->right);
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
if(!pRootOfTree)
return pRootOfTree;
inorder(pRootOfTree);
for(int i=0;i<v.size()-1;i++){
v[i]->right=v[i+1];
v[i+1]->left=v[i];
}
return v[0];
}
};
JZ38 字符串的排列
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> Permutation(string str) {
sort(str.begin(),str.end());
vector<string>v;
v.push_back(str);//向容器尾部添加一个元素str
while(next_permutation(str.begin(),str.end())){
v.push_back(str);
}
return v;
}
};
JZ39 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
public class Solution {
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
int[] book=new int[10010];
int l=array.length;
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
book[array[i]]++;
if(book[array[i]]>l/2)
{
return array[i];
// break;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
JZ40 最小的K个数
由于个人用Java写Arrays.sort(input)总是报错改不对,用c++函数里返回一个数组写不对,所以Give up
这个代码真的很不戳啊很不戳 [赞]
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(vector<int> input, int k) {
vector<int>ret;
if(k==0||k>input.size())
return ret;
sort(input.begin(),input.end());
return vector<int>(input.begin(),input.begin()+k);
}
};
JZ41 数据流中的中位数
class Solution {
public:
vectorv;
void Insert(int num) {
v.push_back(num);
}
double GetMedian() {
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
if(v.size()&1)//奇数个元素
return v[(v.size()-1)/2];
else //偶数个元素
return (v[(v.size()-1)/2]+v[(v.size()-1)/2+1])/2.0;
}
};
JZ42 连续子数组的最大和
class Solution {
public:
int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(vector<int> array) {
int l=array.size();
int dp[200010];
dp[0]=array[0];
int maxx=dp[0];
for(int i=1;i<l;i++)
{
if(dp[i-1]+array[i]<array[i])//保证加的数不是负数
{
dp[i]=array[i];
}
else
{
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+array[i];
}
maxx=max(maxx,dp[i]);
}
return maxx;
}
};
JZ43 整数中1出现的次数(从1到n整数中1出现的次数)
class Solution {
public:
int getf(int x){
int ans=0;
while(x){
// int s=x%10;
if(x%10==1)
ans++;
x=x/10;
}
return ans;
}
int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
sum+=getf(i);
}
return sum;
}
};
JZ44 数字序列中某一位的数字
一位数[1,10) 有 数字 9个
两位数[10,100) 有 数字 90 * 2个
三位数[100,1000) 有 数字 900 * 3个
四位数[1000,10000) 有 数字 9000 * 4个…
想知道第n位所在的数字是多少,我们需要知道
- 给出的第n位 在哪个数里?
- 在这个数的第几位?
如何计算?
- 用n不断地去减1位数的数字个数,2位数的数字个数,3位数的数字个数,减一次位数+1(记录几位数,记为digit),直到n小于需要减的数字个数,此时就可以知道他是几位数的第几个数字(即减过数字个数后的n值,)
- 用n除以digit得出第几个数,加上num/10(即digit-1位数的最大数)即可得出第n位数字在哪个数中
- 已知这个数,求第n位是这个数的第几位,直接用n%digit即可,如果取余结果为0,那么就是这个数的最后一位
4.注意在求第几位上是数字几的时候,是从后往前计算,一般用的是取余求该位上的数字,那么第num位就是digit-num+1,最后一位在计算过程中计算第一位,倒数第二位就是计算第二位等等…
class Solution {
public:
int findNthDigit(int n) {
if(n<10)
return n;
//digit表示位数,num表示几位数一共有几个数字
int st=1,digit=1;
long long num=9;
n=n-9;
while(n-num*digit>0)
{
n-=num*digit;
digit++;
num=num*10;
}
long long shu=n/digit+num/10;//表示第n位所在的数
long long wei=n%digit;//在数的第几位
if(wei==0)
wei=1;
else
wei=digit-wei+1;
int shu1;
while(wei--)
{
shu1=shu%10;
shu=shu/10;
}
return shu1;
}
};
JZ45 把数组排成最小的数
class Solution {
public:
bool static cmp(string a,string b){
return a+b<b+a;
}
string PrintMinNumber(vector<int> numbers) {
vector<string>v;
int l=numbers.size();
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
v.push_back(to_string(numbers[i]));
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp);
string ans;
for(string s1:v)
ans+=s1;
return ans;
}
};
JZ46 把数字翻译成字符串
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 解码
* @param nums string字符串 数字串
* @return int整型
*/
public int sorts(char[] nums,int start){
if(start==nums.length)//走到头了
return 1;
//0没有对应的译码字母,所以直接返回0
if(nums[start]=='0')
return 0;
int ans1=sorts(nums,start+1);
int ans2=0;
//如果当前字符等于1或者当前字符加上下一个字符合起来小于等于26则可以一次性解码两个字符
if((start<nums.length-1)&&(nums[start]=='1'||(nums[start]=='2'&&nums[start+1]<='6'))){
ans2=sorts(nums,start+2);
}
return ans1+ans2;
}
public int solve (String nums) {
// write code here
return sorts(nums.toCharArray(),0);
}
}
JZ47 礼物的最大价值
class Solution {
public:
int maxValue(vector<vector<int> >& grid) {
int n=grid.size();
int m=grid[0].size();
int x,y;
int dp[210][210];
dp[1][1]=grid[0][0];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
x=i+1;
y=j+1;
dp[x][y]=max(dp[x-1][y],dp[x][y-1])+grid[i][j];
}
}
return dp[n][m];
}
};
JZ48 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
遍历 如果mp.count(s[i])不为0说明之前出现过,记录出现的位置下标,如果没出现过记为-1,接下来mp存储该字母出现的位置下表,更新最大值
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param s string字符串
* @return int整型
*/
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
// write code here
if(s.size()<2)
return s.size();
int maxx=0,left=0;
map<char,int>mp;//记录s[i]出现的次数以及s[i]出现的位置
int dp[40010];
mp[s[0]]=0;
dp[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<s.size();i++){
left=mp.count(s[i])?mp[s[i]]:-1;
mp[s[i]]=i;
dp[i]=i-left>dp[i-1]?dp[i-1]+1:i-left;//所在位置上不含重复字符的子字符串的最长长度
maxx=max(maxx,dp[i]);//更新最大值
}
return maxx;
}
};
JZ49 丑数
public class Solution {
public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int index) {
if(index<=6)
return index;
int[] arr=new int[index];
arr[0]=1;
int a2=0,a3=0,a5=0;
for(int i=1;i<index;i++){
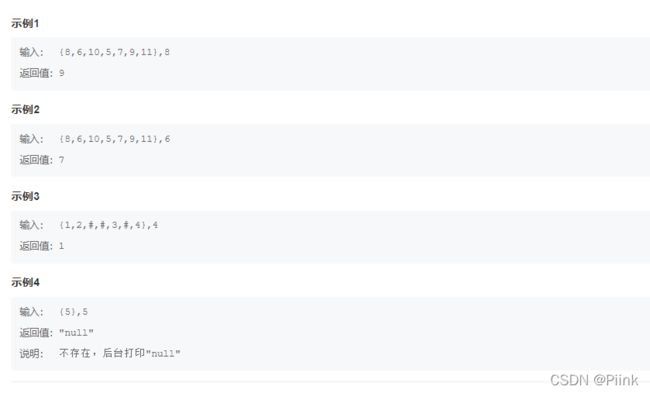
arr[i]=Math.min(arr[a2]*2,Math.min(arr[a3]*3,arr[a5]*5));
if(arr[i]==arr[a2]*2)
a2++;
if(arr[i]==arr[a3]*3)
a3++;
if(arr[i]==arr[a5]*5)
a5++;
}
return arr[index-1];
}
}
JZ50 第一个只出现一次的字符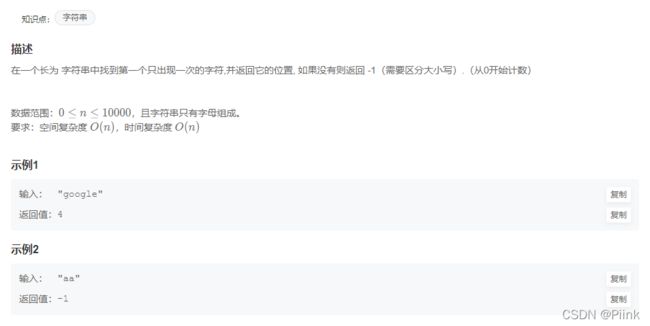
统计所有字符出现的次数,然后查询只出现过一次的字符,遍历维护下标最小值,没有则返回-1
class Solution {
public:
int FirstNotRepeatingChar(string str) {
map<int,int>mp;
map<int,int>mp1;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++)
{
if(str[i]>='A'&&str[i]<='Z'){
mp[str[i]-'A']++;
mp1[str[i]-'A']=i;
}
else
{
mp[str[i]-'a'+27]++;
mp1[str[i]-'a'+27]=i;
}
}
int minn=999;
for(int i=0;i<52;i++)
{
if(mp[i]==1)
{
minn=min(minn,mp1[i]);
}
}
if(minn==999)
return -1;
else
return minn;
}
};
JZ52 两个链表的第一个公共结点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) {
ListNode *p1=pHead1;
ListNode *p2=pHead2;
while(p1!=p2)
{
p1=p1?p1->next:pHead2;
p2=p2?p2->next:pHead1;
}
return p1;
}
};
JZ53 数字在升序数组中出现的次数
class Solution {
public:
int GetNumberOfK(vector<int> data ,int k) {
int len =data.size();
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(data[i]==k)
sum++;
}
return sum;
}
};
JZ54 二叉搜索树的第k个节点
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param proot TreeNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int KthNode (TreeNode proot, int k) {
// write code here
if(proot==null)
return -1;
Stack<TreeNode> s=new Stack<TreeNode>();
s.push(proot);
//System.out.println(proot.val);
TreeNode node=proot;
int x=0;
while(!s.empty()){
while(node.left!=null){
s.push(node.left);
node=node.left;
}
x++;
if(x==k)
//System.out.println(s.pop().val);
return s.pop().val;
TreeNode node1=s.pop();
if(node1.right!=null){
s.push(node1.right);
node=node1.right;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
JZ55 二叉树的深度
//c++代码
class Solution {
public:
int TreeDepth(TreeNode* pRoot) {
if(!pRoot)
return 0;
int l=TreeDepth(pRoot->left);
int r=TreeDepth(pRoot->right);
return max(l,r)+1;
}
};
JZ56 数组中只出现一次的两个数字
//Java代码
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] FindNumsAppearOnce (int[] array){
// write code here
int[] a=new int[2];
int l=array.length,j=0;
Arrays.sort(array);
if(array[0]!=array[1])
a[j++]=array[0];
if(array[l-1]!=array[l-2])
a[j++]=array[l-1];
for(int i=1;i<l-1;i++)
{
if(array[i]!=array[i+1]&&array[i]!=array[i-1])
a[j++]=array[i];
}
if(a[0]>a[1])
{
int t=a[0];
a[0]=a[1];
a[1]=t;
}
return a;
}
}
JZ57 和为S的两个数字
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> FindNumbersWithSum(vector<int> array,int sum) {
int left=0,right=array.size()-1;
while(left<right){
if(sum==array[left]+array[right]){
return vector<int>{array[left],array[right]};
}
else if(array[left]+array[right]<sum){
left++;
}
else {
right--;
}
}
return {};
}
};
JZ58 左旋转字符串
使用 substring 获取指定区间的字符串,最后拼接返回
public class Solution {
public String LeftRotateString(String str,int n) {
if (str == null || str.length()==0) {
return str;
}
n=n%str.length();
return str.substring(n) + str.substring(0, n);
}
}
JZ59 滑动窗口的最大值
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxInWindows(const vector<int>& num, unsigned int size) {
vector<int>v;
int pos=0;
int l=num.size();
int end=l-size+1;
if(size==0)
return v;
while(end--){
v.push_back(*max_element(num.begin()+pos,num.begin()+pos+size));
pos++;
}
return v;
}
};
JZ61 扑克牌顺子
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution
{
public boolean IsContinuous(int [] numbers){
Arrays.sort(numbers);
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
if(numbers[i]==0)
ans++;
else if(numbers[i]==numbers[i+1])
return false;
}
if(numbers[4]-numbers[ans]<5)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
JZ62 孩子们的游戏(圆圈中最后剩下的数)
class Solution {
public:
int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) {
int f=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
f=(f+m)%i;
}
return f;
}
};
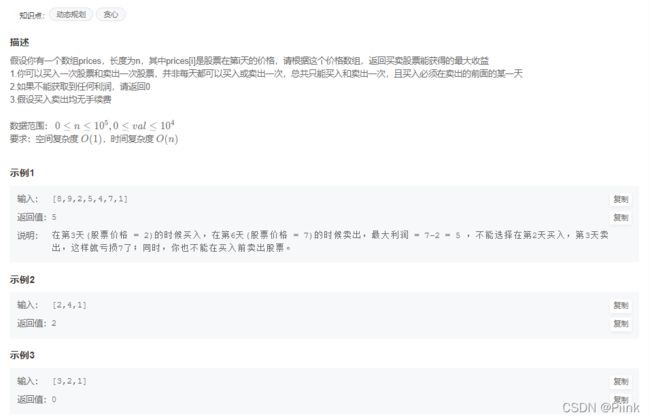
JZ63 买卖股票的最好时机(一)
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
// write code here
int minn=prices[0],profit=0;
for(int i=1;i<prices.size();i++){
if(prices[i]<minn)
minn=prices[i];//找出最小值
profit=max(profit,prices[i]-minn);//求出最大差值
}
return profit;
}
};
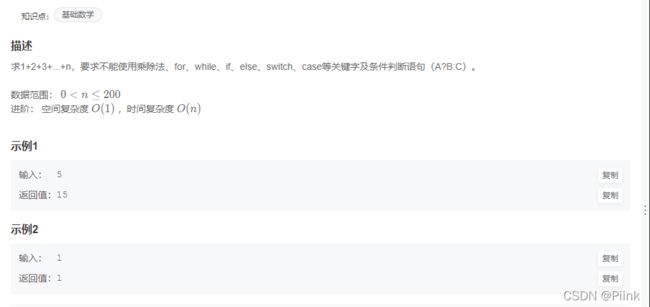
JZ64 求1+2+3+…+n
class Solution {
public int sumNums(int n) {
if(n==0)
return 0;
else
return n+sumNums(n-1);
}
}
JZ65 不用加减乘除做加法
与运算(&):同1为1,有0即为0
0&0=0;0&1=0;1&0=0;1&1=1
或运算(|):有1为1
0|0=0; 0|1=1;1|0=1;1|1=1;
异或运算(^):相同为0, 不同为1
0^ 0=0; 0 ^ 1=1;1^ 0=1;1^1=0;
a+b s为不进位上的值,s1为需要进位的值
不进位和 与 异或运算 规律相同,进位 和 与运算 规律相同(并需左移一位)

class Solution {
public:
int Add(int num1, int num2) {
int sum = num1 ^ num2, sum1 = (num1 & num2) << 1;
return sum + sum1;
}
};
JZ66 构建乘积数组
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> multiply(const vector<int>& A) {
vector<int>v;
int l=A.size();
int sum[15],sum1[15];
sum[0]=A[0];
for(int i=1;i<l;i++)
{
sum[i]=sum[i-1]*A[i];
}
sum1[l-1]=A[l-1];
for(int i=l-2;i>=0;i--){
sum1[i]=sum1[i+1]*A[i];
}
int sum2[15];
sum2[0]=sum1[1];
v.push_back(sum2[0]);
for(int i=1;i<l-1;i++){
sum2[i]=sum[i-1]*sum1[i+1];
v.push_back(sum2[i]);
}
sum2[l-1]=sum[l-2];
v.push_back(sum2[l-1]);
return v;
}
};
JZ67 把字符串转换成整数(atoi)
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param s string字符串
* @return int整型
*/
public int StrToInt (String s) {
// write code here
int l=s.length();
if(l==0)
return 0;
int f=1;
long num=0;
// long ans=-2147483649;
int i=0;
while(i<l&&s.charAt(i)==' ')
i++;//找第一个非空字符
if(i<l){
if(s.charAt(i)=='-')
{
f=-1;
i++;
}
else if(s.charAt(i)=='+')
i++;
}
while(i<l){
if(s.charAt(i)>='0'&&s.charAt(i)<='9'){
num=num*10+(s.charAt(i)-'0');
if(f==-1&&num*(-1)<Integer.MIN_VALUE)
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
else if(f==1&&num>Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
i++;
}
else
break;
}
int res=(int)num;
res=res*f;
return res;
}
}
JZ68 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param p int整型
* @param q int整型
* @return int整型
*/
public int CommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
if(p==root.val||q==root.val)
return root.val;
if(p<root.val&&q<root.val){
return CommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
}
else if(p>root.val&&q>root.val){
return CommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
}
else
return root.val;
}
public int lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, int p, int q) {
// write code here
return CommonAncestor(root,p,q);
}
}
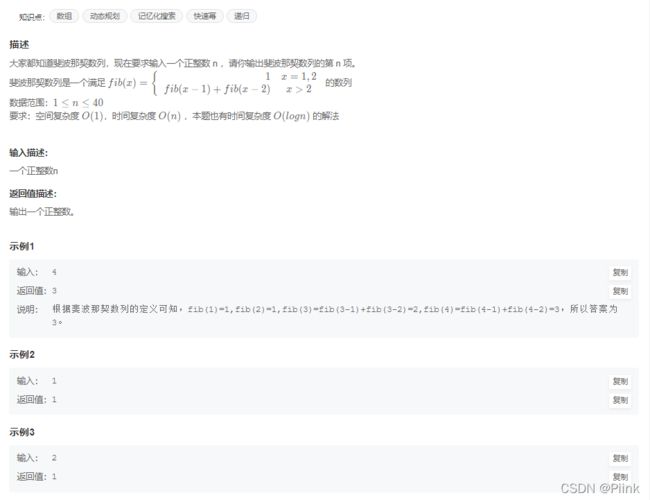
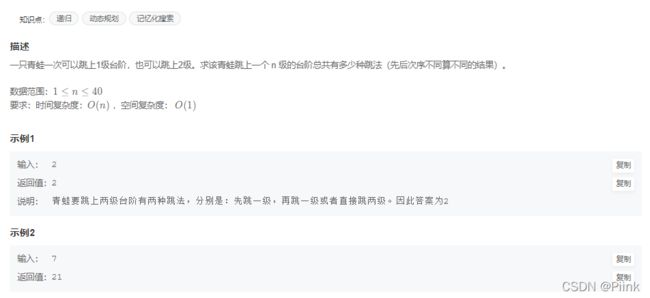
JZ69 跳台阶
1级楼梯 1种
2级楼梯 2种
3级楼梯 3种
4级楼梯 5种
4级楼梯 8种
得出规律即可
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloor(int number) {
if(number==1)
return 1;
else if(number==2)
return 2;
else
return jumpFloor(number-1)+jumpFloor(number-2);
}
};
JZ70 矩形覆盖
class Solution {
public:
int rectCover(int number) {
int dp[40];
dp[1]=1,dp[2]=2;
if(number==0)
return 0;
for(int i=3;i<=38;i++)
{
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
}
return dp[number];
}
};
JZ71 跳台阶扩展问题
class Solution {
public:
int jumpFloorII(int number) {
if(number==1)
return 1;
int ans=1;
for(int i=2;i<=number;i++)
ans*=2;
return ans;
}
};
JZ73 翻转单词序列

Java字符串拆分与拼接

Leecode这么写是不对的,过不了全部的样例
for循环里面加一句Leecode就可以过完全部样例了
可能有空单词的存在就是两个单词之间有多于一个的空格
if(s1[i].equals(""))
continue;//遇到空单词跳过
public class Solution {
public String ReverseSentence(String str){
//String str="nowcoder. a am I";
String[] str1 =str.split(" ");//以空格拆分
StringBuilder str2= new StringBuilder();//StringBuilder是一个字符拼接的工具类
for(int i=str1.length-1;i>=0;i--){
str2.append(str1[i]+' ');
}
return str2.toString().trim();//toString()转换为字符串,trim()去掉两边的空格
}
}
JZ74 和为S的连续正数序列
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {
vector<vector<int>>v1;
int st=1,ed=2,sn=0;
while(st<ed){
sn=(ed-st+1)*(ed+st)/2;
if(sn>sum)
st++;
else if(sn==sum){
vector<int>v;
for(int i=st;i<=ed;i++)
v.push_back(i);
v1.push_back(v);
ed++;
}
else
ed++;
}
return v1;
}
};
JZ75 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
class Solution
{
public:
//Insert one char from stringstream
queue<char>q;
map<char,int>mp;
void Insert(char ch) {
if(mp.find(ch)==mp.end()){
q.push(ch);
}
mp[ch]++;
}
//return the first appearence once char in current stringstream
char FirstAppearingOnce() {
while(!q.empty()){
char u=q.front();
if(mp[u]==1){
return u;
}
else
q.pop();
}
return'#';
}
};
JZ76 删除链表中重复的结点
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead==NULL)
return NULL;
set<int>s;
ListNode *p=pHead;
ListNode *cur=pHead->next;
while(cur){
if(p->val==cur->val)
s.insert(p->val);
p=p->next;
cur=cur->next;
}
ListNode *v=new ListNode(-1);
v->next=pHead;
p=v;
cur=pHead;
while(cur){
if(s.count(cur->val)){
cur=cur->next;
p->next=cur;
}
else
{
p=p->next;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
return v->next;
}
};
JZ79 判断是不是平衡二叉树
public class Solution {
int flag=0;
public int depth(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)
return 0;
int l=depth(root.left);
int r=depth(root.right);
if(Math.abs(l-r)>1)
{
flag=1;
}
return Math.max(l,r)+1;
}
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
depth(root);
if(flag==0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
JZ81 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面(二)
//Java代码
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] reOrderArrayTwo (int[] array) {
int l=array.length;
int[] a =new int[50010];
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
if(array[i]%2==1)
a[j++]=array[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
{
if(array[i]%2==0)
a[j++]=array[i];
}
a[j++]='\0';
return a;
}
}
JZ82 二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @param sum int整型
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int sum) {
// write code here
if(root==null)
return false;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null&&root.val==sum)
return true;
return hasPathSum (root.left,sum-root.val)||hasPathSum (root.right,sum-root.val);
}
}
JZ83 剪绳子(进阶版)
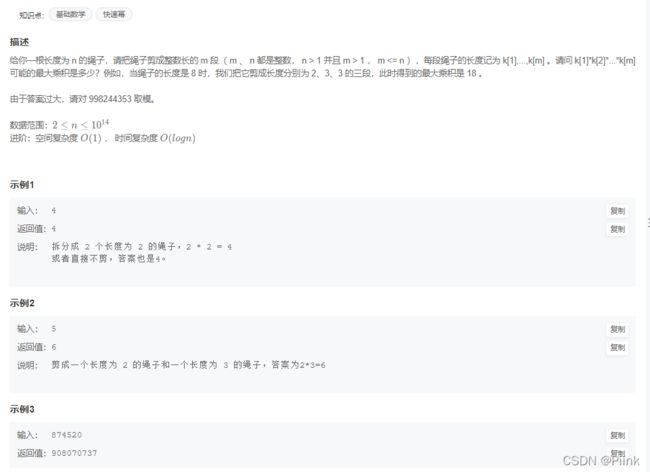
所有数都分解成2和3
先计算能分成3的个数,如果取余3得出的结果是1,就借用一个3,变为两个2,乘积会更大,如果取余3得出的结果是2,直接再乘2即可
当然,做题期间遇到一个问题:当余数为2,我先计算出3的n次方,然后对结果除以3,再乘两个2就过不去10的14次方这个数据,计算3的n-1次方,再乘4就可以AC这个题(原因可能是取模后再除以3不一定是整数)
class Solution {
public:
long long quickpow(long long n){
long long sum=1,k=3;
long long mod=998244353;
while(n)
{
if(n&1)
{
sum=sum*k%mod;
}
k=k*k%mod;
n=n/2;
}
return sum;
}
long long cutRope(long long number) {
// write code here
if(number==2)
return 1;
if(number==3)
return 2;
long long n=number/3;
long long s=number%3;
long long mod=998244353;
long long ans;
if(s==1)
{
ans=quickpow(n-1);
// sum=sum/3;
ans=ans*2*2%mod;
}
else if(s==2)
{
ans=quickpow(n);
ans=ans*2%mod;
}
else {
ans=quickpow(n);
}
return ans;
}
};