2 Day DBA Part1
1.Common Oracle database administrator (DBA) task:
2. Tools for Administering the Database
3.Installing Oracle Database and Creating a Database
3.1 Installing Oracle Database Software and Creating a Database
- Oracle Universal Installer(OUI): OUI is a graphical user interface utility that enables you to install new Oracle Database software.
- OUI automatically starts Oracle Database Configuration Assistant(DBCA) to guide you through the process of creating and configuring a database.
3.1.1 Checking Oracle Database Installation Prerequisites
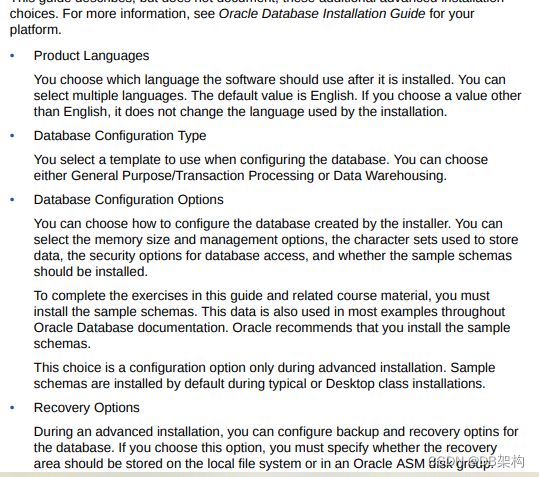
3.1.2 Deciding on Oracle Database Installation Choices
3.1.3 Installation Class for Oracle Database
3.1.4 Installation Edition for Oracle Database
3.1.5 Software Installation Directories for Oracle Database(oraInventory)
3.1.6 Database File Location for Oracle Database
3.1.7 Database Identifier for Oracle Database
3.1.8 About Advanced Installation for Oracle Database
3.2 Installing Oracle Database Software
3.2.1 To perform a basic installation
3.3 Creating and Managing a Database with DBCA
3.3.1 Starting DBCA
This section describes how to start Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA)
3.3.2 Creating a Database Using DBCA
Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) enables you to create an Oracle database by following a step-by-step guided workflow.
4. Getting Started with Database Administration
4.1 Managing Your Database: An Overview
To manage your Oracle database:
1. Start the database instance.
See "Shutting Down and Starting Up the Oracle Instance".
2. Optionally, configure the network environment to enable clients to connect to your database.
See " Configuring the Network Environment ".
3. Review your database storage structures: tablespaces and data files, online redo log files, and control files. Create or modify storage structures as needed.
See " Managing Database Storage Structures".
4. Review memory allocation and adjust as needed.
See "Managing Memory".
5. Review, unlock, and reset passwords for predefined database users as needed. Create new users, and assign privileges and roles to them.
See " Administering User Accounts and Security".
6. Create the necessary schema objects, including tables, views, and indexes. Populate the tables with data.
See " Managing Schema Objects".
7. Create or review the backup strategy for the database and back up the database.
See " Performing Backup and Recovery".
8. Enable archiving of online redo log files, if not already done.
See "Configuring Recovery Settings".
9. Monitor database performance, diagnose performance problems, and tune the database as necessary.
See " Monitoring and Tuning the Database".
10. Keep Oracle Database software up-to-date with the latest releases.
See " Managing Oracle Database Software ".
4.2 Configuring the Operating System Environment Variables
Linux and Unix systems:
Windows:
To configure operating system environment variables for your database instance on Windows systems:
5.Configuring the Network Environment
5.1 Understanding Network Configuration
A client is any application that connects to Oracle Database to send or retrieve data.
A service name is a logical representation of a database, which is the way a database is presented to clients. A single database can be presented as multiple services.
5.2 Viewing Listener Configuration
5.3 Starting and Stopping the Listener
5.4 Connecting to an Oracle Database from a Client Computer
6.Managing the Oracle Instance
6.1 Overview of the Oracle Instance and Instance Management
An Oracle database system consists of an Oracle database and an Oracle instance (in an Oracle Real Application Clusters environment, there can be more than one instance).
A database consists of a set of disk files that store user data and metadata. Metadata, or "data about the data," consists of structural, configuration, and control information about the database. An Oracle instance (also known as a database instance) contains the set of Oracle Database background processes that operate on the stored data and the shared allocated memory that those processes use to do their work. Each instance has an instance ID, also known as a system ID (SID). Because there can be multiple Oracle databases on a host computer, each with its own set of data files, you must identify the instance to which you want to connect. For a local connection, you identify the instance by setting operating system environment variables ORACLE_SID and ORACLE_HOME. For a remote connection, you identify the instance by specifying a network address and a database service name. An Oracle instance must be started to read and write information to the database. The Oracle instance creates the database upon receipt of instructions from the Oracle Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) utility or the CREATE DATABASE SQL statement. When the Oracle instance is not available, your data is safe in the database, but it cannot be accessed by any user or application. The properties of an Oracle instance are specified using instance initialization parameters. When the instance is started, an initialization parameter file is read, and the instance is configured accordingly.
This section presents some concepts of an Oracle instance and its management. It contains the following topics: