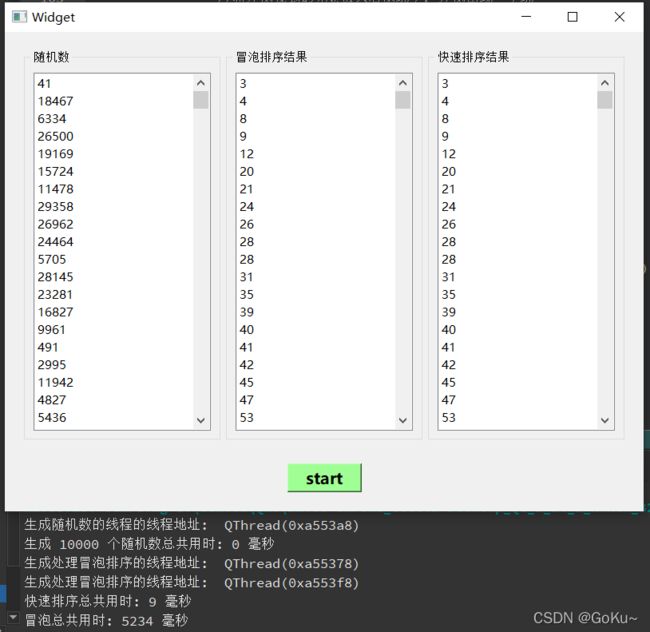
QT多线程应用实例二(方法 2)
Qt 提供的第二种线程的创建方式弥补了第一种方式的缺点,用起来更加灵活,但是这种方式写起来会相对复杂一些,主要是为了不用在run方法里面处理过多逻辑处理,方法1会导致冗余易出错,创建一个公共的任务成员函数,新建子线程去处理里面任务即可,一个子线程里可以处理多个任务,也可以创建不同的任务函数,其具体七个操作步骤如下:
1,创建一个新的类,让这个类从 QObject 派生
class MyWork:public QObject
{
.......
}
2,在这个类中添加一个公共的成员函数,函数体就是我们要子线程中执行的业务逻辑
class MyWork:public QObject
{
public:
.......
// 函数名自己指定, 叫什么都可以, 参数可以根据实际需求添加
void working();
}
3,在主线程中创建一个 QThread 对象,这就是子线程的对象
QThread* sub = new QThread;
在主线程中创建工作的类对象(千万不要指定给创建的对象指定父对象)
MyWork* work = new MyWork(this); // error
MyWork* work = new MyWork; // ok
4,将 MyWork 对象移动到创建的子线程对象中,需要调用 QObject 类提供的 moveToThread() 方法
// void QObject::moveToThread(QThread *targetThread);
// 如果给work指定了父对象, 这个函数调用就失败了
// 提示: QObject::moveToThread: Cannot move objects with a parent
work->moveToThread(sub); // 移动到子线程中工作
6,启动子线程,调用 start(), 这时候线程启动了,但是移动到线程中的对象并没有工作
7,调用 MyWork 类对象的工作函数,让这个函数开始执行,这时候是在移动到的那个子线程中运行的。
Widget(h/cpp):
#ifndef WIDGET_H
#define WIDGET_H
#include
QT_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
namespace Ui { class Widget; }
QT_END_NAMESPACE
class Widget : public QWidget
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
Widget(QWidget *parent = nullptr);
~Widget();
signals:
void starting(int num);
private:
Ui::Widget *ui;
};
#endif // WIDGET_H
#include "widget.h"
#include "ui_widget.h"
#include "mythread.h"
#include
Widget::Widget(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
, ui(new Ui::Widget)
{
ui->setupUi(this);
//创建任务处理对象
GetRandNum *getRand = new GetRandNum;
BubbelSort *bubble = new BubbelSort;
QuickSort *quick = new QuickSort;
QThread *t1 = new QThread;
QThread *t2 = new QThread;
QThread *t3 = new QThread;
getRand->moveToThread(t1);
bubble->moveToThread(t2);
quick->moveToThread(t3);
connect(this,&Widget::starting,getRand,&GetRandNum::working);
//启动子线程
connect(ui->start,&QPushButton::clicked,this,[=](){
emit starting(10000);
t1->start();
});
connect(getRand,&GetRandNum::sendArray,bubble,&BubbelSort::working);
connect(getRand,&GetRandNum::sendArray,quick,&QuickSort::working);
connect(getRand, &GetRandNum::sendArray, this, [=](QVector nums){
t2->start();
t3->start();
for(int i=0; irandList->addItem(QString::number((nums.at(i))));
}
});
connect(bubble, &BubbelSort::finish, this, [=](QVector nums){
for(int i=0; ibubbelList->addItem(QString::number((nums.at(i))));
}
});
connect(quick, &QuickSort::finish, this, [=](QVector nums){
for(int i=0; iquickList->addItem(QString::number((nums.at(i))));
}
});
//最后记得销毁线程
connect(this, &Widget::destroyed, this, [=]()
{
t1->quit();
t1->wait();
t1->deleteLater(); // delete t1;
t2->quit();
t2->wait();
t2->deleteLater();
t3->quit();
t3->wait();
t3->deleteLater();
getRand->deleteLater();
bubble->deleteLater();
quick->deleteLater();
});
}
Widget::~Widget()
{
delete ui;
}
myThread(h/cpp):
#ifndef MYTHREAD_H
#define MYTHREAD_H
#include
//1生成随机数的线程
class GetRandNum : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit GetRandNum(QObject *parent = nullptr);
void working(int num);
signals:
void sendArray(QVector nums);
};
//2生成处理冒泡排序的线程
class BubbelSort : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit BubbelSort(QObject *parent = nullptr);
void bubbleSort(QVector &nums);
void working(QVector nums);
signals:
void finish(QVector nums);
};
//2生成处理快速排序的线程
class QuickSort : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit QuickSort(QObject *parent = nullptr);
void working(QVector nums);
void quickSort(QVector &nums,int l,int r);
signals:
void finish(QVector nums);
};
#endif // MYTHREAD_H
#include "mythread.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
GetRandNum::GetRandNum(QObject *parent)
: QObject{parent}
{
}
//给全局变量赋值
void GetRandNum::working(int num)
{
qDebug() << "生成随机数的线程的线程地址: " << QThread::currentThread();
QElapsedTimer time;
QVector nums;
time.start();
for(int i = 0;i &nums)
{
int n = nums.size();
bool isChange = false;
for(int i = 1;inums[j+1])
{
int t = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[j+1];
nums[j+1] = t;
isChange = true;
}
}
if(!isChange){//冒泡排序优化了也比不上快排
break;
}
}
}
void BubbelSort::working(QVector nums)
{
qDebug() << "生成处理冒泡排序的线程地址: " << QThread::currentThread();
QElapsedTimer time;
time.start();
bubbleSort(nums);
int useTime = time.elapsed();
qDebug() << "冒泡总共用时:" << useTime << "毫秒";
emit finish(nums);
}
QuickSort::QuickSort(QObject *parent)
: QObject(parent)
{
}
void QuickSort::quickSort(QVector &nums,int l,int r)
{
if (l < r)
{
int i = l, j = r;
// 拿出第一个元素, 保存到x中,第一个位置成为一个坑
int x = nums[l];
while (i < j)
{
// 从右向左找小于x的数
while (i < j && nums[j] >= x)
{
//左移, 直到遇到小于等于x的数
j--;
}
if (i < j)
{
//将右侧找到的小于x的元素放入左侧坑中, 右侧出现一个坑
//左侧元素索引后移
nums[i++] = nums[j];
}
// 从左向右找大于等于x的数
while (i < j && nums[i] < x)
{
//右移, 直到遇到大于x的数
i++;
}
if (i < j)
{
//将左侧找到的元素放入右侧坑中, 左侧出现一个坑
//右侧元素索引向前移动
nums[j--] = nums[i];
}
}
//此时 i=j,将保存在x中的数填入坑中
nums[i] = x;
quickSort(nums, l, i - 1); // 递归调用
quickSort(nums, i + 1, r);
}
}
void QuickSort::working(QVector nums)
{
qDebug() << "生成处理快速排序的线程地址: " << QThread::currentThread();
QElapsedTimer time;
time.start();
quickSort(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
int useTime = time.elapsed();
qDebug() << "快速排序总共用时:" << useTime << "毫秒";
emit finish(nums);
}
执行: