WinMIps64指令集实验
目录
- MIPS
-
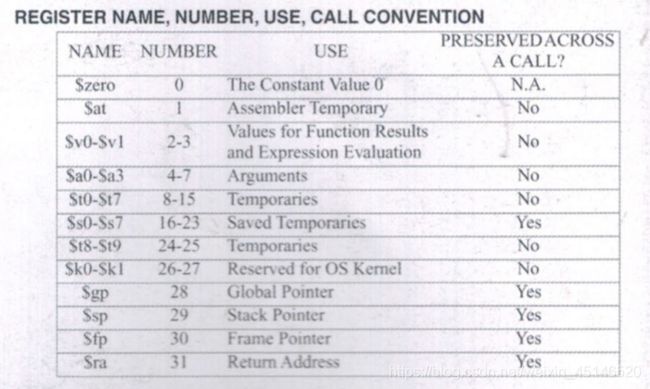
- 寄存器种类
- 算术及寻址指令
-
- Arithmetic Instructions
- Load / Store
- Indirect and Based Addressing
- 程序结构
-
- 数据声明
- 系统调用
-
- Control Structures
-
- **Branch**
- **Jump**
- **Subroutine Calls**
- MIPS指令集实验
-
- MinMIPS64模拟器
- 使用流程
- IO内存映射
- hello world demo
- bubble sort
MIPS
寄存器种类
算术及寻址指令
Arithmetic Instructions
!!!算术操作指令不能用于地址!!!
简单的加减法如下:

![]()
对于乘法和除法,有特殊的寄存器:Lo 和 Hi ,分别对应乘除后64位的低位和高位储存。
![]()
![]()
Load / Store
只有这两个指令能对地址进行操作。
example:
lw register_destination, RAM_source ;load a word
lb register_destination, RAM_source ;load a byte
sw register_source, RAM_destination
sb register_source, RAM_destination
load immediate:
li register_dedstination, 5
Indirect and Based Addressing
load address:
la $t0,val ;$t0 = address of val ----($t0)=val
lw $t0,4($t1) ; $t0 = address of ($t1+4)
程序样例:
.data
array1: .space 12
# declare 12 bytes of storage to hold array of 3 integers
# 定义一个 12字节 长度的数组 array1, 容纳 3个整型
.text
__start: la $t0, array1
# load base address of array into register $t0
# 让 $t0 = 数组首地址
li $t1, 5 # $t1 = 5 ("load immediate")
sw $t1, ($t0)
# first array element set to 5; indirect addressing
# 对于 数组第一个元素赋值 array[0] = $1 = 5
li $t1, 13 # $t1 = 13
sw $t1, 4($t0) # second array element set to 13# 对于 数组第二个元素赋值 array[1] = $1 = 13 # (该数组中每个元素地址相距长度就是自身数据类型长度,即4字节, 所以对于array+4就是array[1])
li $t1, -7 # $t1 = -7
sw $t1, 8($t0) # third array element set to -7
# 同上, array+8 = (address[array[0])+4)+ 4 = address(array[1]) + 4 = address(array[2])
done
程序结构
基本模板如下:
# Comment giving name of program and description of function
# 说明下程序的目的和作用(其实和高级语言都差不多了)
# Template.s
#Bare-bones outline of MIPS assembly language program
.data # variable declarations follow this line
# 数据变量声明
# ...
.text # instructions follow this line
# 代码段部分
main: # indicates start of code (first instruction to execute)
# 主程序
# ...
# End of program, leave a blank line afterwards to make SPIM happy
# 必须多给你一行,你才欢?
数据声明
format for declarations
name storage_type value(s)
-->example: val .word 3
lables:
.word
.byte
.space 开辟数组空间
.asciiz 用于字符串
系统调用
Control Structures
Branch
comparison for conditional branches is built into instruction
b target # unconditional branch to program label target
beq $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 = $t1
bne $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 != $t1
slt $t0,$t1,target # branch to target if $t0 < $t1
还有其它的可以自己翻阅上传的文件。
Jump
j target
# unconditional jump to program label target 看到就跳, 不用考虑任何条件
jr $t3
# jump to address contained in $t3 ("jump register") 类似相对寻址,跳到该寄存器给出的地址处
Subroutine Calls
jal sub_label ;跳转到指定位置,且保存之前的pc于$ra寄存器
jr $ra ;用$ra寄存器恢复之前的pc值
这个只适用于一次跳转,毕竟$ra只有一个,要递归的话还是要用栈帧。
MIPS指令集实验
MinMIPS64模拟器
关于平台这个大佬讲得很清楚了:MinMips64模拟机
使用流程
用记事本等写出代码后,保存为.s文件,使用命令行执行asm程序,以代码txt为参数。
会提示无errors等信息则可以在winmips64中运行了。
打开winmips64并导入txt文件:
并且excute->run to 程序就直接执行完了(除非有输入等停顿)。
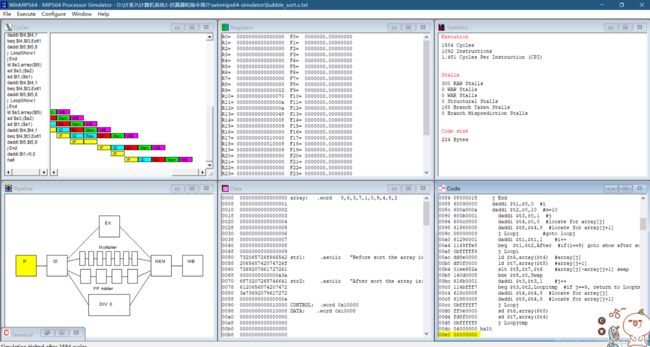
然后这个程序是有输出的,想看输出的cmd窗口,要在上面windows那里选择terminal,最后都显示出来了:

IO内存映射
hello world demo
.data
str: .asciiz "Hello World"
CONTROL: .word32 0x10000
DATA: .word32 0x10008
.text
main:
lwu r31,CONTROL(r0) ;$r31 = address of CONTROL register
lwu r30,DATA(r0) ;$r30 = address of DATA register
daddi r29,r0,4 ;set control(4):output string
daddi r28,r0,str ;get address of str and store in r28
sd r28,(r30) ;write address of message to DATA
sd r29,(r31) ;output
halt
bubble sort
代码结构
main
first_show
sort
last_show
sort
loopi
loopj
looj
if array[j] > array[j+1] swap
swap
sd -> array[j]
sd -> array[j+1]
完整代码以后发布。