极简c++(8)抽象类与多态
类型转换规则
父类定义的指针可以指向子类对象;

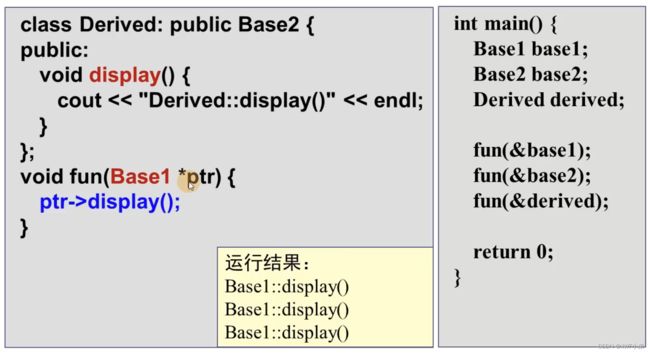
指针会误以为,他们指向的对象是Base1类型,导致错误;
虚函数定义
多态
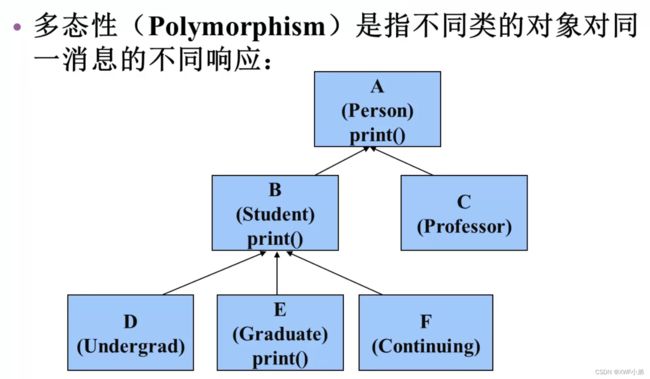
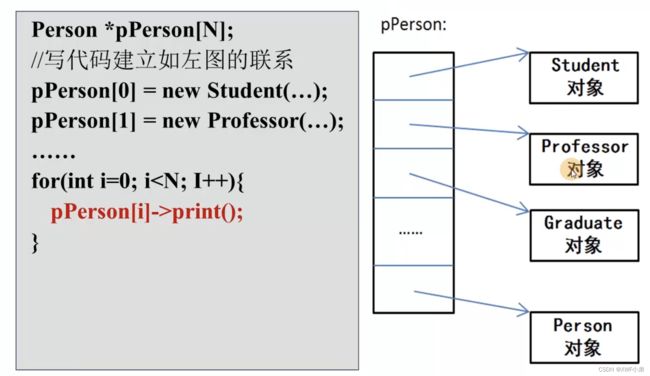

如何实现多态:
1.创建类的继承关系图
2.所以类对象都可以调用的这个函数
3.创建父类指针数组
4.子类的地址赋给父类指针
5.指针调用虚函数
动态绑定
和多态其实是一个概念

动态绑定我们是无法在运行之前,事先知道运行的结果是不知道的;

不仅是指针,引用也可以!

指针和引用可以,但最后一种情况无法实现多态
虚析构函数

创建的时候是先创建base再创建derived的;这个时候,不加virtual 的话会导致,只delete了base,但没有delete掉derived;
建议所有析构函数都加virtual
只有用new去创建的时候,才有可能出现这种错误。
纯虚函数与抽象类

对于暂时无法实现的函数,我们可以定义为纯虚函数,留给派生类去实现;
定义了纯虚函数的类叫抽象类;
抽象类只能作为基类来使用;
构造函数不能是虚函数,析构函数可以是虚函数;
为什么需要抽象类
抽象类的特点
作业
#include "shape.h"
#include "circle.h"
#include "rectangle.h"
#include "roundrectangle.h"
#include shape.cpp
#include "shape.h"
#include shape.h
#ifndef SHAPE_H
#define SHAPE_H
#include circle.cpp
#include "circle.h"
#include "shape.h"
#include circle.h
#ifndef CIRCLE_H
#define CIRCLE_H
#include rectangle.cpp
#include "rectangle.h"
#include "shape.h"
#include rectangle.h
#ifndef RECTANGLE_H
#define RECTANGLE_H
#include roundrectangle.cpp
#include "roundrectangle.h"
#include "rectangle.h"
#include"shape.h"
#include roundrectangle.h
#ifndef ROUNDRECTANGLE_H
#define ROUNDRECTANGLE_H
#include 
(1)必须要定义,因为getArea()是纯虚函数,派生类必须补全他的函数实现,否则Circle也会变成抽象类,无法创建对象
(2)不会,因为它可以调用他的父类Rectangle类的getArea(),编译不出错,但内容是错误的
(3)可以。但

#include "shape.h"
#include "circle.h"
#include "rectangle.h"
#include "roundrectangle.h"
#include 





