Mybatis拦截器源码详细分析
一.基础步骤
拦截器的代理对像生成就在打开会话和通过代理对象执行接口方法返回结果集这一步。
首先我们要了解创建拦截器的方式
1.通过注解创建拦截器,type属性是拦截器类型 方法属性是拦截方法 参数属性是拦截的参数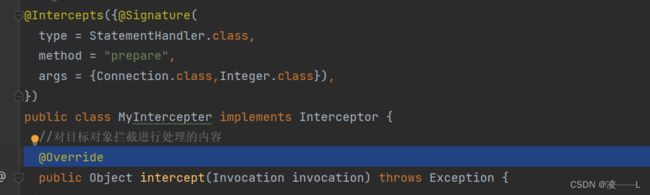
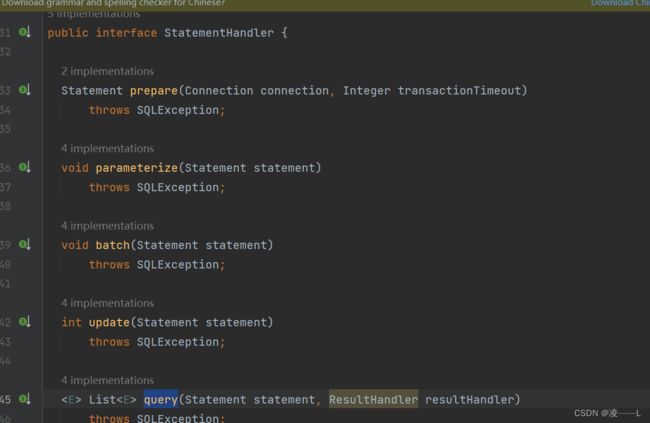
2.参数类型怎么获取只要点进对应的类型就可以看到,比如StatementHandler,有prepare准备statement进行拦截,参数是connection和integer
3.xml方式创建拦截器
这一步要在mybastis配置文件写plugins标签,获取DefaultSqlSessionFactory会解析配置文件存放到map中,创建拦截器对象匹配时要用到。
二,进入源码
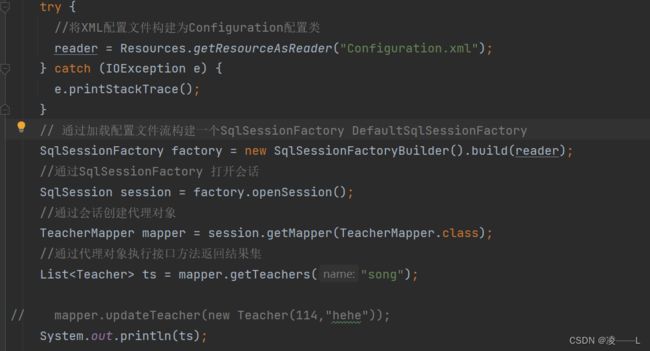
从SqlSession session = factory.openSession()出发
进入到openSessionFromDataSource创建Excutor,Executor分成两大类,一类是CacheExecutor,另一类是普通Executor。 普通Executor分为三种基本的Executor执行器
BatchExecutor:执行update(没有select,JDBC批处理不支持select),将所有sql都添加到批处理中(addBatch()),等待统一执行(executeBatch()),它缓存了多个Statement对象,每个Statement对象都是addBatch()完毕后,等待逐一执行executeBatch()批处理。与JDBC批处理相同。
ReuseExecutor:执行update或select,以sql作为key查找Statement对象,存在就使用,不存在就创建,用完后,不关闭Statement对象,而是放置于Map内,供下一次使用。
SimpleExecutor:每执行一次update或select,就开启一个Statement对象,用完立刻关闭Statement对象 private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//获取环境对象有数据源信息
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//获取Transaction mybastis里是new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit),整合spring是spring事物对象
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//获取执行器,获得的执行器已经代理拦截器的功能
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//根据获取的执行器创建SqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}newExecutor
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//Executor分成两大类,一类是CacheExecutor,另一类是普通Executor。
//普通Executor分为三种基本的Executor执行器
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
//执行update(没有select,JDBC批处理不支持select),将所有sql都添加到批处理中(addBatch()),等待统一执行(executeBatch()),它缓存了多个Statement对象,每个Statement对象都是addBatch()完毕后,等待逐一执行executeBatch()批处理。与JDBC批处理相同。
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
//ReuseExecutor:执行update或select,以sql作为key查找Statement对象,存在就使用,不存在就创建,用完后,不关闭Statement对象,而是放置于Map内,供下一次使用。
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
//每执行一次update或select,就开启一个Statement对象,用完立刻关闭Statement对象
//默认类型
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
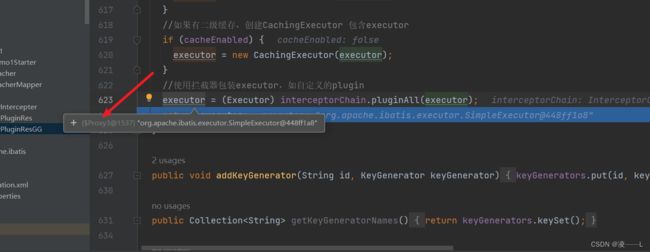
//如果有二级缓存,创建CachingExecutor 包含executor
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//使用拦截器包装executor,如自定义的plugin
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
} 如果开启二级缓存,把简单类Executor包装,形成CachingExecutor。下面就是创建代理对象勒,
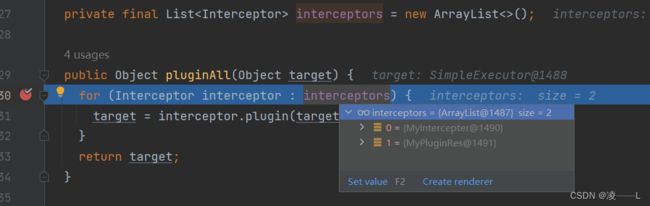
使用拦截器包装executor,如自定义的plugin,plugALL会常见代理对象,可以看到有interceptors两个这是之前解析配置文件封装list,调用pluugin方法再调用warp方法创建代理对象
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map, Set> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
//获取当前类类型
Class type = target.getClass();
//匹配当前拦截器是否当前类型
Class[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
//匹配上创建代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
//匹配不上返回源对象
return target;
} 可以看到返回的是代理对象
以上是代理对象创建。
三.执行代理对象目标方法:
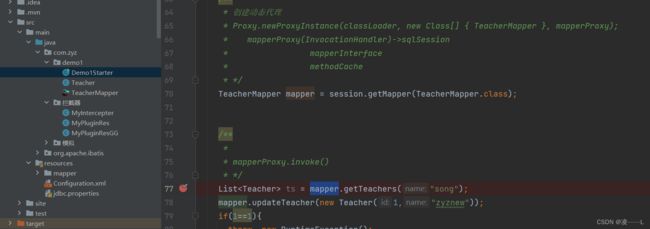
入口是先拿到要执行mapper的代理对象这里是TeacherMapper(不涉及拦截器省略源码部分),执行getTeacher方法
TeacherMapper代理对象执行invoke方法,主要获取MapperMethod里面有一个command字段,该字段是增删改查,存放到methodCache,k是method,value是MapperMethod
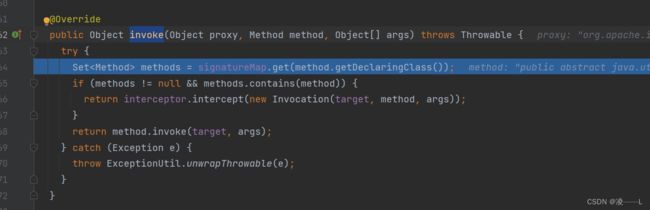
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return invokeDefaultMethodJava8(proxy, method, args);
} else {
return invokeDefaultMethodJava9(proxy, method, args);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//获取MapperMethod,并调用MapperMethod
//主要工作就是创建MapperMethod对象或者是从缓存中获取MapperMethod对象
//获取到这个对象后执行execute方法。
//public MapperMethod(Class mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
// this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
// this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
//}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
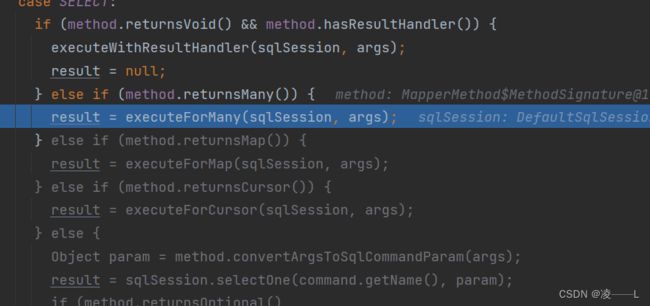
}进入excute方法,我这是个查询返回值是list进入executeForMany
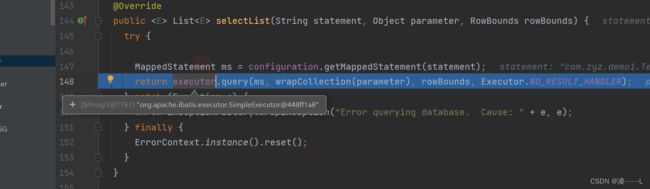
最终调用到selectlist,我是对Executor的query方法进行拦截,这里执行的是代理对象query
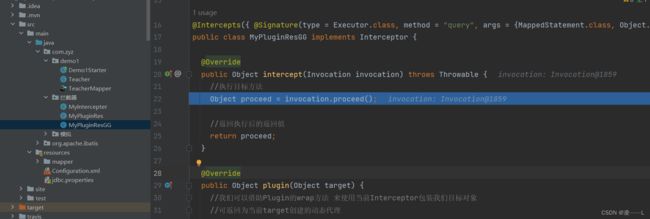
执行代理对象invoke方法,这里面会执行自定义拦截器interceptor.intercept方法,我这是演示直接返回不做处理。
增强方法执行完之后调用invocation.proceed()原来目标方法query方法,以上就是Executor拦截器增强全部过程。
四、拓展
拦截器有以下几种,另外三个Handler拦截器在哪里创建代理对象的勒.
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}),
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = {Connection.class, Integer.class}),
@Signature(type = ParameterHandler.class, method = "setParameters", args = {PreparedStatement.class}),
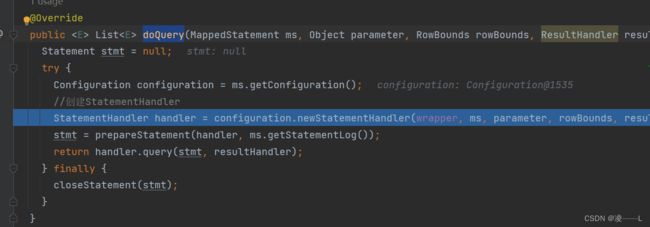
@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class, method = "handleResultSets", args = {Statement.class})续上,执行完增强方法继续执行目标方法query方法,过程就省略勒直接到doquery方法这里会创建StatementHandler
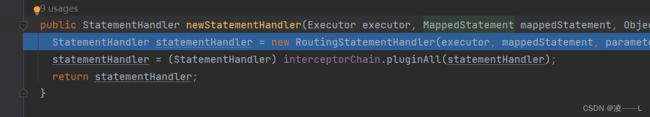
原来同Executor一样在创建完StatementHandler都会调用interceptorChain.pluginAll包装,所以同上,如果自定义了拦截器拦截StatementHandler,interceptorChain.pluginAll创建代理对象。
StatementHandler 找到了,还有parameterHandler,resultSetHandler没有找到。
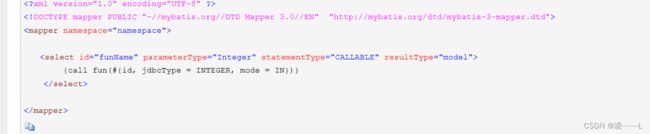
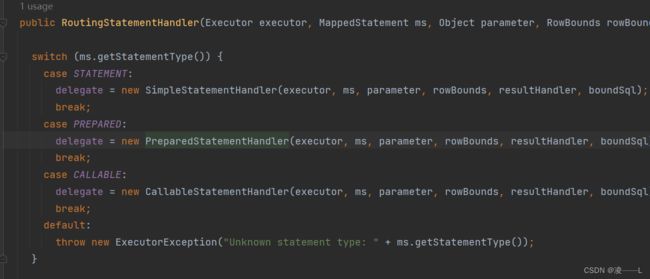
续上,在创建StatementHandler是调用RoutingStatementHandler构造方法,这个构造方法做了什么事勒,这会根据mapper文件statementType选择不同类型Statement,这三个方法都会调用父类BaseStatementHandler构造方法
再来看看BaseStatementHandler 构造方法,不难看出同StatementHandler一样ParameterHandler和resultSetHandler里面会调用interceptorChain.pluginAll获取代理对象,结论是在创建StatementHandler同时把resultSetHandler和ParameterHandler同时创建,如果自定义代理拦截器就会创建代理对象。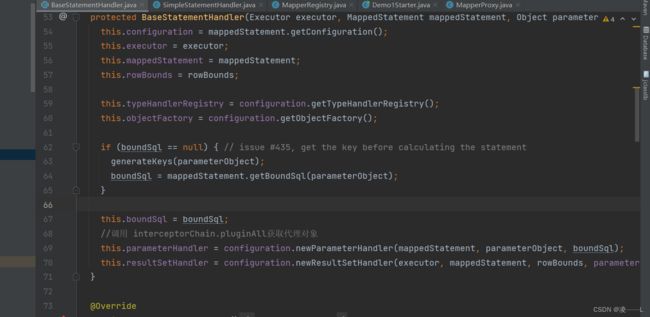
以上就是,mybatis拦截器什么创建,什么时候调用的具体过程,不难看出,这四个拦截器,都是在初始化之后有自定义拦截器调用interceptorChain.pluginAll包装,执行到具体方法时就会调用代理对象的invoke方法,调用自定义拦截器然后才执行目标方法