Java集合(一)—— Collection
1、集合的引入
数组、集合是对多个数据进行存储操作的,简称容器。
在引入集合使用我们更多的使用的是数组。
1.1 数组的特点
- 数组一旦指定了长度,那么长度就被确定了,不可以更改了;
- 数组一旦声明了类型以后,数组中只能存放这个类型的数组,数组中只能存放同一种类型的数据。
1.2 数组的缺点
- 数组一旦指定了长度,那么长度就被确定了,不可以更改;
- 删除,增加元素,效率低;
- 数组中实际元素的数量是没有办法获取的,没有提供对应的方法或者属性来获取;
- 数组存储:有序,可重复;对于无序的,不可重复的数组不能满足要求
集合的引入正是为了解决了以上的缺点。
分类
集合主要包括两种
Collection和Map两种,Collection存储着对象的集合,而Map存储着键值对(两个对象)的映射表。
参考博客
http://www.cyc2018.xyz/Java/Java%20%E5%AE%B9%E5%99%A8.html#%E4%B8%80%E3%80%81%E6%A6%82%E8%A7%88
https://snailclimb.gitee.io/javaguide/#/docs/java/collection/Java%E9%9B%86%E5%90%88%E6%A1%86%E6%9E%B6%E5%B8%B8%E8%A7%81%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E9%A2%98
2、Collection
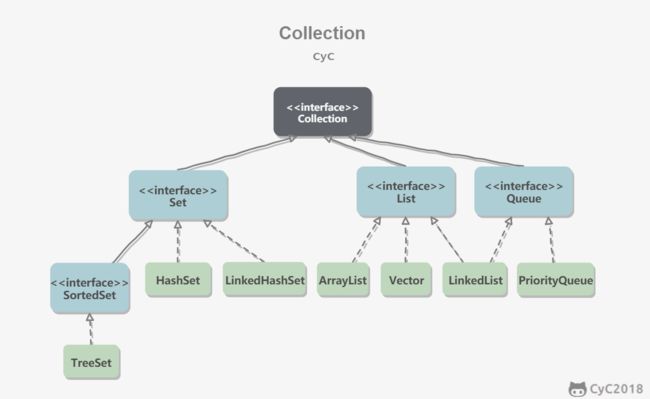
2.1 List
存储的元素是有序的、可重复的
- ArrayList:
Object[]数组; - Vector:
Object[]数组,线程安全; - LinkedList:双向链表(JDK1.6 之前为循环链表,JDK1.7 取消了循环)
2.1.1 说说它们的区别?从何说?
从何说:从底层组成,数据结构的特性说
2.1.2 ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的区别
- 底层数据结构:
ArrayList底层使用的是Object数组;LinkedList底层使用的是双向链表数据结构(JDK 1.6 之前为双向循环链表,JDK 1.7 后取消了循环); - 效率:
ArrayList查找快(支持快速随机访问)、插入删除慢;LinkedList查找慢、插入删除快; - 内存空间占用:
ArrayList的空间浪费主要体现,在 list 列表的结尾会预留一定的容量空间,而LinkedList的空间花费主要在它的每一个元素都需要消耗比ArrayList更多的空间,存放直接前驱和直接后继以及数据本身。 - 是否保证线程安全:
ArrayList和LinkedList都是不同步的,也就是不保证线程安全;
2.1.3 ArrayList 的扩容机制
从添加元素开始,判断是否扩容,默认扩容至原容器的 1.5倍左右(oldCapacity为奇数时,进行 oldCapacity >> 1)
以无参构造的
ArrayList为例分析
-
ArrayList的成员变量和三个构造函数public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; /** * 默认初始容器大小:10 */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * 用于表示空数组的共享数组实例 */ private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * 用于默认大小的空实例的共享空数组实例。 * 我们将其与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA区别开来,以便了解在添加第一个元素时应该膨胀多少。 */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; /** * 保存ArrayList数据的数组 */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access /** * ArrayList 所包含的元素个数 * 和 elementData.length 区分开 后者表示的是当前 elementData 的总容量 */ private int size; /** * 默认无参构造函数,创建一个具有标识的空数组实例 * 对,使用无参构造函数创建实例后,这时容器仍是一个空数组 * 在第一次添加元素时,容量扩容为10 */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } /** * 带初始容量参数的构造函数。(用户自己指定容量) */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } /** * 构造包含指定collection元素的列表,这些元素利用该集合的迭代器按顺序返回 * 如果指定的集合为null,throws NullPointerException。 */ public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // replace with empty array. this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } } -
ArrayList 的 add() 方法
/** * 将指定的元素附加到列表的末尾。 */ public boolean add(E e) { // 添加元素之前执行方法 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! // ArrayList 添加元素的本质就是给数组赋值 elementData[size++] = e; return true; } -
ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) 方法
minCapacity = size + 1,意思就是新增元素时,该容器至少的容量大小是多于当前元素个数的 1 个
// 第一次调用时,此时 elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA, // 返回 DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } // 此时的 minCapacity 是 size+1,也就是 当前元素的个数 + 1 = 1 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } -
ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) 方法
// 第一次调用时,此时 minCapacity = 10,当前 elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,长度为0 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // overflow-conscious code if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); }- 当我们要 add 进第 1 个元素到 ArrayList 时,elementData.length 为 0 (因为还是一个空的 list),因为执行了
ensureCapacityInternal()方法 ,所以 minCapacity 此时为 10。此时,minCapacity - elementData.length > 0成立,所以会进入grow(minCapacity)方法。 - 当 add 第 2 个元素时,minCapacity 为 2,此时 e lementData.length(容量)在添加第一个元素后扩容成 10 了。此时,
minCapacity - elementData.length > 0不成立,所以不会进入 (执行)grow(minCapacity)方法。 - 添加第 3、4···到第 10 个元素时,依然不会执行 grow 方法,数组容量都为 10。
- 当我们要 add 进第 1 个元素到 ArrayList 时,elementData.length 为 0 (因为还是一个空的 list),因为执行了
-
grow(int minCapacity)方法
/** * 数组能分配的最大大小 */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * ArrayList 扩容方法 */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // 原容器的大小 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 扩容,新容器的大小 = 原容器的1.5倍。 // 使用位运算的速度远快于整除运算 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 主要用在当前容器容量为0时 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; // 当容器容量大于MAX_ARRAY_SIZE时 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } /** * 当 minCapacity 大于 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 时,则返回 Integer.MAX_VALUE */ private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }- 当 add 第 1 个元素时,oldCapacity 为 0,经比较后第一个 if 判断成立,newCapacity = minCapacity(为 10)。但是第二个 if 判断不会成立,即 newCapacity 不比 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 大,则不会进入
hugeCapacity方法。数组容量为 10,add 方法中 return true,size 增为 1。 - 当 add 第 11 个元素进入 grow 方法时,newCapacity 为 15,比 minCapacity(为 11)大,第一个 if 判断不成立。新容量没有大于数组最大 size,不会进入 hugeCapacity 方法。数组容量扩为 15,add 方法中 return true,size 增为 11。
- 以此类推······
- 当 add 第 1 个元素时,oldCapacity 为 0,经比较后第一个 if 判断成立,newCapacity = minCapacity(为 10)。但是第二个 if 判断不会成立,即 newCapacity 不比 MAX_ARRAY_SIZE 大,则不会进入
2.1.4 System.arraycopy 和 Arrays.copyOf 的区别
-
System.arraycopy()将一个数组复制到目标数组中,目标数组长度必须足够,否则报错ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException// src:源数组;srcPos:源数组起始下标;dest:目标数组;destPos:目标数组起始下标;length:要复制的源数组的长度 System.arraycopy(Object src,int srcPos,Object dest,int destPos,int length) public static void test2(){ System.out.println("==== System.arraycopy ===="); int[] arr1 = {2,4,2,34,12,4}; int[] arr2 = new int[10]; arr2[0] = 7; arr2[1] = 8; arr2[2] = 9; System.arraycopy(arr1,0,arr2,1,arr1.length); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2)); } // 复制后的元素,原数组与目标数组重叠的下标,源数组的元素替换目标数组的元素 ==== System.arraycopy ==== [7, 2, 4, 2, 34, 12, 4, 0, 0, 0] -
Arrays.copyOf返回一个包含源数组所有元素的新数组,长度自定义public static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) public static void test3(){ System.out.println("==== Arrays.copyOf ===="); int[] arr3 = {11,22,33,44,55}; int[] arr4 = Arrays.copyOf(arr3,10); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr4)); } ==== Arrays.copyOf ==== [11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] -
System.arraycopy()需要原数组和目标数组,将原数组拷贝到自定义的数组中,而且可以选择原数组的拷贝起点、长度、放在目标数组的位置; -
Array.copyOf()是系统自动在内部新建了一个数组,并返回该数组。(源码内部调用的仍是System.arraycopy())
2.2 Set
存储的元素是无序的、不可重复的
- HashSet:(无序、唯一)基于
HashMap实现的,底层采用HashMap来保存元素,线程不安全,可以存储null值; - LinkedHashSet:
LinkedHashSet是HashSet的子类,并且其内部是通过LinkedHashMap来实现的,能够按添加顺序遍历; - TreeSet:(有序、唯一)红黑树(自平衡的排序二叉树)
2.3 Comparable 和 Comparator 区别
-
它们都是接口,都必须实现并重写相应方法才能使用,目的是为了
自定义排序; -
Comparable接口是排序的元素(一般为自定义类)实现的,并重写compareTo(T t)方法,在方法中自定义排序方式;compareTo(T t)返回的是int类型,一般记忆为:this的值 大于 参数的值,return 1;this的值 小于 参数的值,return -1;升序Integer、String等类都实现了Comparable接口;
public class Person implements Comparable<Person>{ private Integer num; // 注意这里类型是 Integer ,后面会用到 private String name; private int age; // get、set方法省略 setter()/getter()... public Person() { } public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Person(Integer num, String name, int age) { this.num = num; this.name = name; this.age = age; } // 年龄升序 @Override public int compareTo(Person p) { if(this.age > p.getAge()){ return 1; } else if(this.age < p.getAge()){ return -1; } return 0; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { ... } @Override public int hashCode() { ... } @Override public String toString() { ... } }/** * 要排序的类 Person 实现了 Comparable 接口, * 并重写了 Comparator 方法,按年龄升序 */ public static void comparableTest(){ System.out.println("+++++++ comparableTest ++++++++"); System.out.println("============ list =========="); List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>(); personList.add(new Person(3,"小贱",22)); personList.add(new Person(8,"小红",5)); personList.add(new Person(7,"小华",15)); personList.add(new Person(9,"小明",20)); Collections.sort(personList); Iterator iterator = personList.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } System.out.println("============ set =========="); TreeSet<Person> personTreeSet = new TreeSet<>(); personTreeSet.add(new Person("小贱",22)); personTreeSet.add(new Person("小红",5)); personTreeSet.add(new Person("小华",15)); personTreeSet.add(new Person("小明",20)); Iterator iterator1 = personTreeSet.iterator(); while(iterator1.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator1.next()); } }============= 输出 ============ +++++++ comparableTest ++++++++ ============ list ========== Person{num=8, name='小红', age=5} Person{num=7, name='小华', age=15} Person{num=9, name='小明', age=20} Person{num=3, name='小贱', age=22} ============ set ========== Person{num=null, name='小红', age=5} Person{num=null, name='小华', age=15} Person{num=null, name='小明', age=20} Person{num=null, name='小贱', age=22} -
Comparator接口需自定义实现类,或在排序时使用匿名类实现,并重写compare(T t1,T t2)方法-
compare(T t1,T t2)返回的是int类型,一般记忆为:p1的值 大于p2的值,return 1;p1的值 小于p2的值,return -1;升序/** * 排序是实现 Comparator 接口,自定义排序 */ public static void comparatorTest(){ System.out.println(); System.out.println("+++++++ comparatorTest ++++++++"); List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>(); personList.add(new Person(3,"小贱",22)); personList.add(new Person(8,"小红",5)); personList.add(new Person(7,"小华",15)); personList.add(new Person(9,"小明",20)); // 定制排序 Collections.sort(personList, new Comparator<Person>() { @Override public int compare(Person p1, Person p2) { if(p1.getNum() > p2.getNum()){ return -1; } else if(p1.getNum() < p2.getNum()){ return 1; } return 0; // 因为 num 定义为了 Integer 类型,这里也可以使用 Integer 定义的 compareTo 方法 // return p1.getNum().compareTo(p2.getNum()); // 默认升序 } }); Iterator iterator = personList.iterator(); while(iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } }========= 输出 ============= +++++++ comparatorTest ++++++++ Person{num=9, name='小明', age=20} Person{num=8, name='小红', age=5} Person{num=7, name='小华', age=15} Person{num=3, name='小贱', age=22}
-