算法刷题专辑60分版本
文章目录
-
- 目标
- leetcode
-
- 1.两数之和
- 2.两数相加(同时遍历2个链表)
- 3.最长不重复子字符串
- 4.寻找两个正序数组的中位数
- 5.最长回文字串(双指针从中间向两边遍历的写法)
- 6. N字形变换(flag=1/-1实现转圈遍历)
- 7.整数转字符串(取模和除法操作)
- 8. 字符串转整数--
- 9. 回文数--
- 10. 正则表达式(todo)
- 11. 盛最多水的容器(最差的动起来可能更差可能更好,但不动一定很差)
- 12. 整数转罗马数字(贪心hash表)
- 13. 罗马转整数(普通hash表&特殊hash表,先试走2步看特殊,再走一步看普通)
- 14. 最长公共前缀---
- 15. 三数之和-最接近三数之和-四数之和(组合拳:排序+定一移二(双指针))
- 17. 电话号码组合(递归回溯的框架来解)
-
-
- Excel表列名称_字母转EXCEL列(10进制转26进制)
-
- 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 20. 有效的括号(辅助栈)
- 21. 合并两个有序链表
- 22. 括号生成(递归)
- 23. 合并K个升序链表(todo)
- 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 25. K 个一组翻转链表(todo)
- 26. 删除有序数组中的重复项(双指针的有趣解释)
- 27. 移除元素(空间优化)
- 28.找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标(KMP 算法todo)
- 29 两数相除---
- 30. 串联所有单词的子串todo
- 31. 下一个排列
- 32. 最长有效括号todo
- 33. 搜索旋转排序数组
- 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
- 35.搜索插入位置---
- 36.有效的数独
- 37. 解数独todo
- 38. 外观数列
- 39. 组合总和
- 40. 组合总和 II
- 41. 缺失的第一个正数todo
- 42. 接雨水
- 43. 字符串相乘---
- 44. 通配符匹配 todo
- 45. 跳跃游戏I,II
- 46. 全排列I,II
- 48. 旋转图像
- 49. 字母异位分词
- 50. pow(x,n)
- 51. N皇后‖
- 53. 最大子数组和
- 54. 螺旋矩阵1..2
- 56. 合并区间
- 57. 插入区间
- 58. 最后一个单词的长度x
- 60. 排列序列todo
- 61. 旋转链表
- 62. 不同路径I,II
- 64. 最小路径和
- 65. 有效数字todo
- 66. 加一
- 67. 二进制求和
- 68. 文本左右对齐todo
- 69. x 的平方根
- 71. 简化路径
- 72. 编辑距离todo
- 73. 矩阵置零
- 75. 颜色分类
- 76. 最小覆盖子串todo
- 78. 子集(做过)
- 79. 单词搜索
- 84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 todo
- 85. 最大矩形 todo
- 93. 复原 IP 地址
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 101. 对称二叉树
- 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 (队列)
- 103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历(双端队列)
- 104. 二叉树的最大深度
- 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树todo
- 106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树todo
- 107.二叉树的层序遍历 II(正向输出然后再逆转)
- 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树(递归构造平衡二叉树搜索树)
- 109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
- 115. 不同的子序列(todo)
- 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 118. 杨辉三角
- 119. 杨辉三角 II
- 128. 最长连续序列(在hash表中不断枚举匹配x+1,x+2...x+y,判断x-1在hash表中是否存在就能避免重复的枚举)
- 134. 加油站
- 136. 只出现一次的数字(异或运算的经典案例)
- 137. 只出现一次的数字 II(delete)
- 138. 复制带随机指针的链表
- 139. 单词拆分
- 141. 环形链表(龟兔赛跑算法-空间优化)
- 142. 环形链表 II
- 143. 重排链表
- 144. 二叉树的前序遍历/后序遍历
- 146. LRU 缓存
- 147. 对链表进行插入排序todo
- 148. 排序链表
- 150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- 151. 反转字符串中的单词(要求O(1))
- 169. 多数元素(投票算法)
- 229. 多数元素 II
- 224. 基本计算器
- 227. 基本计算器 II
- 232. 用栈实现队列
- 237. 删除链表中的节点
- 257. 二叉树的所有路径
- 258. 各位相加(数学问题)
- 260. 只出现一次的数字 III(位运算-跳过)
- 263. 丑数
- 264. 丑数 II
- 268. 丢失的数字(原地哈希将空间复杂度降低为O(1)很6)
- 274. H 指数(H 指数换一种理解就是:统计降序排列的数组中下标比下标值大的个数)
- 275. H 指数 II
- 279. 完全平方数
- 283. 移动零(双指针)
- 287. 寻找重复数
- 290. 单词规律(将map的put性质发挥到了极致:如果key不存在,插入成功,返回null;如果key存在,返回之前对应的value)
- 287. 寻找重复数
- 289. 生命游戏todo
- 292. Nim 游戏
- 299. 猜数字游戏
- 300. 最长递增子序列
- 附加
目标
算法60分的标准:夯实基础
- 把leedcode200道题默写3遍
- 把算法框架(每框架最经典的3个题)默写3遍
算法80分的标准:扩展提升
- Lfu,lru,跳表,排序,红黑树,背包问题,外企算法50题默写3遍
- Leedcode200-300的题目默写3遍
- 把算法框架(每框架10个题)默写3遍
leetcode
https://leetcode.cn/problemset/all/?page=1
1.两数之和
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> hashtable = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (hashtable.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{hashtable.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
hashtable.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
func twoSum(nums []int, target int) []int {
hashmap := make(map[int]int)
for i,v := range nums{
if index,ok := hashmap[target-v]; ok{
return []int{i,index}
}
hashmap[v]=i
}
return nil
}
2.两数相加(同时遍历2个链表)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// 学习点
ListNode pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = pre;
int carry = 0;
// 学习点:同时遍历2个链表
while(l1 != null || l2 != null) {
// 学习点
int x = l1 == null ? 0 : l1.val;
int y = l2 == null ? 0 : l2.val;
int sum = x + y + carry;
// 学习点
carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
cur.next = new ListNode(sum);
cur = cur.next;
if(l1 != null)
l1 = l1.next;
if(l2 != null)
l2 = l2.next;
}
if(carry == 1) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return pre.next;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func addTwoNumbers(l1 *ListNode, l2 *ListNode) *ListNode {
flag := 0
l3 := &ListNode{Val:0}
head := l3
for l1 != nil || l2 != nil {
a1,a2 := 0,0
if l1 != nil{
a1 = l1.Val
l1 = l1.Next
}
if l2 != nil{
a2 = l2.Val
l2 = l2.Next
}
temp := a1+a2+flag
l3.Next = &ListNode{Val:temp%10}
l3 = l3.Next
flag = temp/10
}
if flag > 0{
l3.Next = &ListNode{Val:flag}
}
return head.Next
}
3.最长不重复子字符串
快指针先往前试探(看看会不会重复:重复就移动左指针,并计数)
rk,ans = -1,0
for i:=0;i<n;i++{
delete(map,arr[i])
//未出现过重复的
for r < n && map[arr[i+1]] == 0 {
//等价于 map[arr[i]] = 1
map[arr[i+1]]++
rk++
}
}
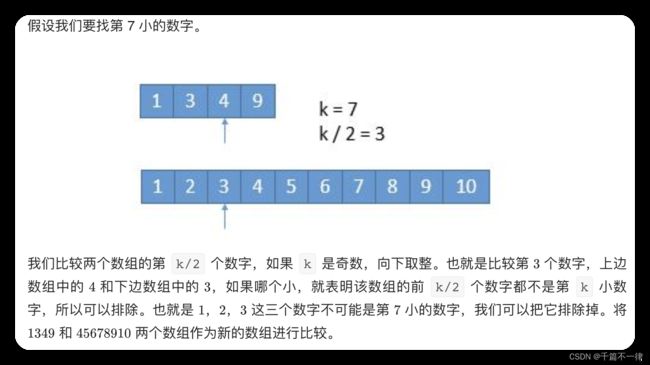
4.寻找两个正序数组的中位数
(困难题:能说出思路就行)
//题目是求中位数,其实就是求第 k 小数,比如下面2个有序数组合并后长度为14,其中位数就是第7小的数(14/2=7)
https://leetcode.cn/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by-w-2/
// 如果下图的1数组1349只有9,那么1数组去第三小的数不是4而是用1代替,取第三小的数,但如果数组只有第1小或者第二小就用第1小或者第二小代替
int i = start1 + Math.min(len1, k / 2) - 1;
5.最长回文字串(双指针从中间向两边遍历的写法)
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() < 1) return "";
int start = 0, end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int len1 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i);
int len2 = expandAroundCenter(s, i, i + 1);
int len = Math.max(len1, len2);
if (len > end - start) {
start = i - (len - 1) / 2;
end = i + len / 2;
}
}
return s.substring(start, end + 1);
}
// 学习点
private int expandAroundCenter(String s, int left, int right) {
int L = left, R = right;
while (L >= 0 && R < s.length() && s.charAt(L) == s.charAt(R)) {
L--;
R++;
}
return R - L - 1;
}
作者:windliang
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/solutions/9001/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-bao-gu/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
expandAroundCenter(i,i)
expandAroundCenter(i,i+1)
func expandAroundCenter(L,R){
for L >= 0 && R <= len(s) && s[L]=s[R] {
L++
R++
}
}
6. N字形变换(flag=1/-1实现转圈遍历)
class Solution {
public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
if(numRows < 2) return s;
List<StringBuilder> rows = new ArrayList<StringBuilder>();
for(int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) rows.add(new StringBuilder());
int i = 0, flag = -1;
for(char c : s.toCharArray()) {
rows.get(i).append(c);
// 学习点 :
if(i == 0 || i == numRows -1) flag = - flag;
i += flag;
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(StringBuilder row : rows) res.append(row);
return res.toString();
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/zigzag-conversion/solutions/21610/zzi-xing-bian-huan-by-jyd/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
var flag = 1
if j==0 || j = numRows-1 {
flag = -flag
j = j+flag
}
7.整数转字符串(取模和除法操作)
//取模和除法操作
//一旦涉及整数的运算,我们需要注意溢出。本题可能产生溢出的步骤在于推入、乘以 1010 操作和累加操作都可能造成溢出。对于溢出的处理方式通常可以转换为 INT_MAX 的逆操作。比如判断某数乘以 1010 是否会溢出,那么就把该数和 INT_MAX 除以 1010 进行比较。
while(num != 0)
num%10
num/10
8. 字符串转整数–
9. 回文数–
10. 正则表达式(todo)
1. 考虑*可能为0,所以可以在遍历的时候往后多看一步
2. 从左往右分析可能较复杂,那么可以从右往左分析
// todo
11. 盛最多水的容器(最差的动起来可能更差可能更好,但不动一定很差)
果然,第一次做题很难想到双指针。就像我昨天说的,有些题目思路到底怎么来的?凭什么就是这样,怎么想到的。原来是见过了才知道。解题思路解题思路,解过了才有思路。以后别再跟我扯什么解题模板,多解题才有模板。双指针模板我也知道,但这道题就是想不到用双指针。以后就知道了,所以啊,还是要多解题,多解题才有解题思路。
感觉这个移动有点博弈论的味了,每次都移动自己最差的一边,虽然可能变得更差,但是总比不动(或者减小)强,动最差的部分可能找到更好的结果,但是动另一边总会更差或者不变,兄弟们,这不是题,这是人生,逃离舒适圈!!(这解释我觉得无敌了,哈哈哈)
让快指针多往后看几步
12. 整数转罗马数字(贪心hash表)
贪心hash表,从最大的开始匹配
class Solution:
def intToRoman(self, num: int) -> str:
# 使用哈希表,按照从大到小顺序排列
hashmap = {1000:'M', 900:'CM', 500:'D', 400:'CD', 100:'C', 90:'XC', 50:'L', 40:'XL', 10:'X', 9:'IX', 5:'V', 4:'IV', 1:'I'}
res = ''
for key in hashmap:
if num // key != 0:
count = num // key # 比如输入4000,count 为 4
res += hashmap[key] * count
num %= key
return res
作者:腐烂的橘子
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/integer-to-roman/solutions/87905/tan-xin-ha-xi-biao-tu-jie-by-ml-zimingmeng/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
13. 罗马转整数(普通hash表&特殊hash表,先试走2步看特殊,再走一步看普通)
class Solution {
public static int romanToInt(String s) {
Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put('I',1);
map.put('V',5);
map.put('X',10);
map.put('L',50);
map.put('C',100);
map.put('D',500);
map.put('M',1000);
// I 可以放在 V (5) 和 X (10) 的左边,来表示 4 和 9。
// X 可以放在 L (50) 和 C (100) 的左边,来表示 40 和 90。
// C 可以放在 D (500) 和 M (1000) 的左边,来表示 400 和 900。
Map<String,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("IV",4);
map1.put("IX",9);
map1.put("XL",40);
map1.put("XC",90);
map1.put("CD",400);
map1.put("CM",900);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (i+2<=s.length()&&map1.get(s.substring(i,i+2))!=null){
sum+=map1.get(s.substring(i,i+2));
i++;
}else {
sum+=map.get(s.charAt(i));
}
}
return sum;
}
}
作者:黄吉华
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/roman-to-integer/solutions/2175843/java-ha-xi-biao-luo-ji-jian-dan-yi-dong-so3qw/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
14. 最长公共前缀—
15. 三数之和-最接近三数之和-四数之和(组合拳:排序+定一移二(双指针))
排序+定一移二(双指针)
三数之和
class Solution {
public static List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
int len = nums.length;
if(nums == null || len < 3) return ans;
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序
for (int i = 0; i < len ; i++) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break; // 如果当前数字大于0,则三数之和一定大于0,所以结束循环
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) continue; // 去重
int L = i+1;
int R = len-1;
while(L < R){
int sum = nums[i] + nums[L] + nums[R];
if(sum == 0){
ans.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[L],nums[R]));
while (L<R && nums[L] == nums[L+1]) L++; // 去重
while (L<R && nums[R] == nums[R-1]) R--; // 去重
L++;
R--;
}
else if (sum < 0) L++;
else if (sum > 0) R--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
作者:画手大鹏
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/solutions/12307/hua-jie-suan-fa-15-san-shu-zhi-he-by-guanpengchn/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
最接近三数之和
17. 电话号码组合(递归回溯的框架来解)
隐形的二叉树来分析
Excel表列名称_字母转EXCEL列(10进制转26进制)
class Solution {
public String convertToTitle(int columnNumber) {
return columnNumber == 0 ? "" : convertToTitle(--columnNumber / 26) + (char)('A' + (columnNumber % 26));
}
}
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
问题转化:快指针先往前走array.length-N步
快指针往前多走几步,去探路,情况ok,慢指针再跟上
20. 有效的括号(辅助栈)
辅助栈—遇到左括号入栈,遇到右括号出栈
class Solution {
private static final Map<Character,Character> map = new HashMap<Character,Character>(){{
put('{','}'); put('[',']'); put('(',')'); put('?','?');
}};
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s.length() > 0 && !map.containsKey(s.charAt(0))) return false;
LinkedList<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>() {{ add('?'); }};
for(Character c : s.toCharArray()){
if(map.containsKey(c)) stack.addLast(c);
else if(map.get(stack.removeLast()) != c) return false;
}
return stack.size() == 1;
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/solutions/9185/valid-parentheses-fu-zhu-zhan-fa-by-jin407891080/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
21. 合并两个有序链表
22. 括号生成(递归)
剩余左括号总数要小于等于右括号。 递归把所有符合要求的加上去就行了:
class Solution {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
if(n <= 0){
return res;
}
getParenthesis("",n,n);
return res;
}
private void getParenthesis(String str,int left, int right) {
if(left == 0 && right == 0 ){
res.add(str);
return;
}
if(left == right){
//剩余左右括号数相等,下一个只能用左括号
getParenthesis(str+"(",left-1,right);
}else if(left < right){
//剩余左括号小于右括号,下一个可以用左括号也可以用右括号
if(left > 0){
getParenthesis(str+"(",left-1,right);
}
getParenthesis(str+")",left,right-1);
}
}
}
23. 合并K个升序链表(todo)
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
while(temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) {
25. K 个一组翻转链表(todo)
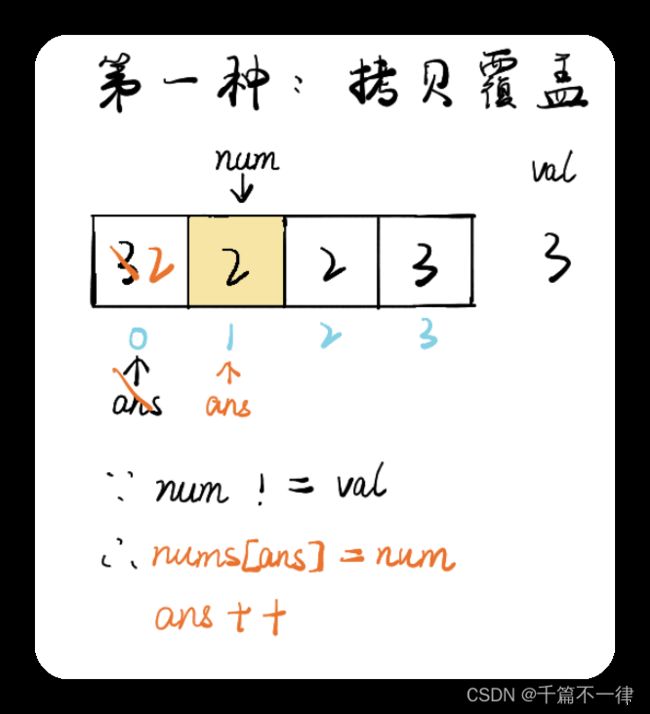
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项(双指针的有趣解释)
常用于查找或者删除相同元素、判定链表中是否含有环、寻找链表的中点等相关问题的求解
我们常用的二分查找也是利用了这钟算法思想,常见的还有两数之和、反转数组等问题的求解
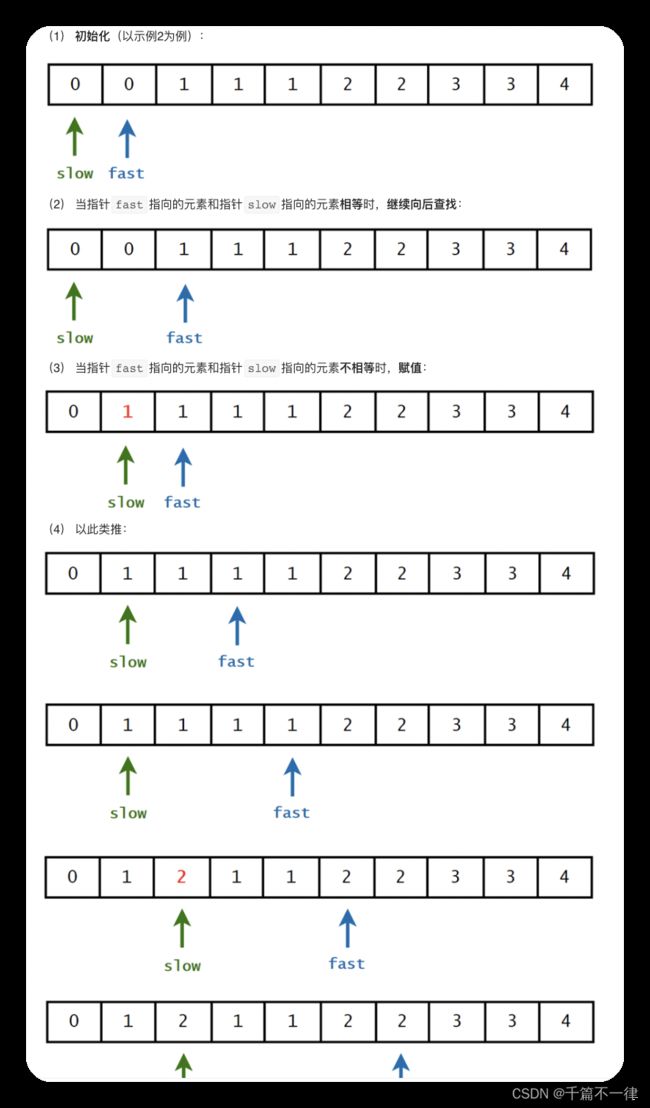

int removeDuplicates(std::vector<int>& nums) {
int length = nums.size();
if (length == 0) return 0;
int slow = 0, fast = 1;
while (fast < length) {
if (nums[fast] != nums[slow]) {
nums[++slow] = nums[fast];
}
fast++;
}
return slow + 1;
}
题目:外面有宝,赶紧捡回来按序放好,不能重样哟 有点像小夫妻俩,老公q在外面淘宝,找到后运回来,找到一个新的宝,老婆p在家里就给挖个新坑放好,最后外面没宝了,就结束咯
中间对话
老公:老婆,这个家里有没?(if) 老婆:有了。(nums[p] == nums[q])你再找找(q++)
老公:老婆,这个家里有没?(if) 老婆:有了。(nums[p] == nums[q])你再找找(q++)
老公:老婆,这个家里有没?(if) 老婆:这个没有,拿回来吧 (nums[p] != nums[q]) 放好了,我到下一个位置等你(p++) 你再继续找吧(q++)
貌似双指针都可以这么理解
27. 移除元素(空间优化)
双指针—图解
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/solution/hua-jie-suan-fa-27-yi-chu-yuan-su-by-guanpengchn/
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int ans = 0;
for(int num: nums) {
if(num != val) {
nums[ans] = num;
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
作者:画手大鹏
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/solutions/10388/hua-jie-suan-fa-27-yi-chu-yuan-su-by-guanpengchn/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
28.找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标(KMP 算法todo)
暴力匹配
我们可以让字符串 needle与字符串 haystack的所有长度为 m 的子串均匹配一次。
为了减少不必要的匹配,我们每次匹配失败即立刻停止当前子串的匹配,对下一个子串继续匹配。如果当前子串匹配成功,我们返回当前子串的开始位置即可。如果所有子串都匹配失败,则返回 −1。
// 简化代码的写法也很巧妙
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
int n = haystack.length(), m = needle.length();
for (int i = 0; i + m <= n; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (haystack.charAt(i + j) != needle.charAt(j)) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-index-of-the-first-occurrence-in-a-string/solutions/732236/shi-xian-strstr-by-leetcode-solution-ds6y/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
29 两数相除—
转乘法:官方题解
朴素的想法,没有位运算,没有移位操作
30. 串联所有单词的子串todo
31. 下一个排列
思路:逆序—(交换)—正序操作
https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-permutation/solution/xia-yi-ge-pai-lie-yi-kan-jiu-dong-by-ych-983q/

从最后一个数开始排,依次往前找有比它小的没有,有就交换位置,结束循环,找了一圈都没有,从倒数第二个数重复上述操作。直到第一个数都还没有进行一次操作,就反转整个数就是答案
123--->132
132--->213
231--->321--->123
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
int cur=nums.size()-2;
while(cur>=0&&nums[cur]>=nums[cur+1])//前面大于后面的
{
cur--;
}
if(cur<0)//已经是最大数组了
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
else//表示找到了降序的一个位置
{
int pos=nums.size()-1;
while(nums[pos]<=nums[cur])
{
pos--;
}
swap(nums[cur],nums[pos]);
reverse(nums.begin()+cur+1,nums.end());
}
}
};
32. 最长有效括号todo
33. 搜索旋转排序数组
34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
35.搜索插入位置—
36.有效的数独
用hash表
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
int[][] rows = new int[9][9];
int[][] columns = new int[9][9];
int[][][] subboxes = new int[3][3][9];
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
char c = board[i][j];
if (c != '.') {
int index = c - '0' - 1;
rows[i][index]++;
columns[j][index]++;
subboxes[i / 3][j / 3][index]++;
if (rows[i][index] > 1 || columns[j][index] > 1 || subboxes[i / 3][j / 3][index] > 1) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-sudoku/solution/you-xiao-de-shu-du-by-leetcode-solution-50m6/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
37. 解数独todo
38. 外观数列
【【LeetCode 每日一题】38. 外观数列 | 手写图解版思路 + 代码讲解-哔哩哔哩】 https://b23.tv/ArN8pXT
i
111221
j
i
111221
j
可得31
i
111221
j
i
111221
j
可得22【3122】
string dg(){
if n ==1 return "1"
string s = dg(n - 1 )
string ans
for(双指针)
}
39. 组合总和
40. 组合总和 II
排序2大好处:可剪枝,可去重arr[i]==arr[i-1]----直接跳过本次操作
【40-组合总和Ⅱ-哔哩哔哩】 https://b23.tv/aVWOyiO
41. 缺失的第一个正数todo
42. 接雨水
https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water/solution/by-lfool-5see/
这个题目也差不多,我们需要维护一个高度 h,表示能使水不流走的最大高度!!
在使用双指针收缩区间的时候,不断的更新该高度 h
public int trap(int[] height) {
int h = 0, ans = 0;
int l = 0, r = height.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
h = Math.max(h, height[l]);
ans += h - height[l];
l++;
} else {
h = Math.max(h, height[r]);
ans += h - height[r];
r--;
}
}
return ans;
}
43. 字符串相乘—
44. 通配符匹配 todo
45. 跳跃游戏I,II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/jump-game-ii/solution/tiao-yue-you-xi-ii-by-leetcode-solution/
46. 全排列I,II
排序,用下面这个判断条件就能进行过滤
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !vis[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
48. 旋转图像
class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
//先沿斜对角线翻转
int n = matrix.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
swap(matrix[i][j],matrix[j][i]);
//再沿垂直竖线翻转
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0, k = n - 1; j < k ; j++, k--) //类似于双指针,由两端向中心靠齐
swap(matrix[i][j],matrix[i][k]);
}
};
作者:lin-shen-shi-jian-lu-k
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-image/solution/48-xuan-zhuan-tu-xiang-chao-jian-ji-yi-d-nuau/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
49. 字母异位分词
https://leetcode.cn/problems/group-anagrams/solution/zi-mu-yi-wei-ci-fen-zu-by-leetcode-solut-gyoc/
50. pow(x,n)
二分快速幂方法
https://leetcode.cn/problems/powx-n/solution/powx-n-by-leetcode-solution/
51. N皇后‖
53. 最大子数组和
54. 螺旋矩阵1…2
https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/solution/spiral-matrix-ii-mo-ni-fa-she-ding-bian-jie-qing-x/
56. 合并区间
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end());
int start = intervals[0][0], end = intervals[0][1];
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); i++) {
if (intervals[i][0] > end) {
ans.push_back({start, end});
start = intervals[i][0];
end = intervals[i][1];
} else {
end = max(end, intervals[i][1]);
}
}
ans.push_back({start, end});
return ans;
}
};
57. 插入区间
可参考视频讲解链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1VZ4y1C7po?spm_id_from=333.1007.top_right_bar_window_history.content.click&vd_source=d482cc951729db66c853a9d4fef3b529

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> insert(vector<vector<int>>& a, vector<int>& b) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int n = a.size(), i = 0;
// 添加左侧不重叠区间
while (i < n && a[i][1] < b[0]) {
ans.push_back(a[i++]);
}
// 合并中间重叠区间
if (i < n) {
b[0] = min(a[i][0], b[0]);
while (i < n && a[i][0] <= b[1]) {
b[1] = max(a[i++][1], b[1]);
}
}
ans.push_back(b);
// 添加右侧不重叠区间
while (i < n) {
ans.push_back(a[i++]);
}
return ans;
}
};
58. 最后一个单词的长度x
60. 排列序列todo
61. 旋转链表
闭合为环,然后砍断(官方题解就行)
62. 不同路径I,II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/unique-paths/solution/san-chong-shi-xian-xiang-xi-tu-jie-62-bu-4jz1/
64. 最小路径和
65. 有效数字todo
66. 加一
思路都一样,编码方式却又不同—该题比较有启发性
分两种情况处理每一位上的数加一后的结果:加到10,没加到10
没加到10直接返回
加到10,继续进行下一位的加一操作,表示进1
https://leetcode.cn/problems/plus-one/solution/by-leer-e-xsy9/
67. 二进制求和
官方题解中的位运算可以拓展学习
https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-binary/solution/er-jin-zhi-qiu-he-by-leetcode-solution/
class Solution {
public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
int i = a.length() - 1;
int j = b.length() - 1;
int carry = 0;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
//循环相加两个字符串相同长度的低位数部分
while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
int sum = carry;
sum += a.charAt(i--) - '0';
sum += b.charAt(j--) - '0';
carry = sum / 2;
builder.append(sum % 2);
}
// 如果 a 还没遍历完成(a串比b串长),则继续遍历添加 a 的剩余部分
while (i >= 0) {
int sum = carry + a.charAt(i--) - '0';
carry = sum / 2;
builder.append(sum % 2);
}
// 如果 b 还没遍历完成(b串比a串长),则继续遍历添加 b 的剩余部分
while (j >= 0) {
int sum = carry + b.charAt(j--) - '0';
carry = sum / 2;
builder.append(sum % 2);
}
//如果 carry 不等于0 还有个进位数没加进去,需要补充
if (carry == 1) {
builder.append(carry);
}
//反转字符串获得正常结果
return builder.reverse().toString();
}
68. 文本左右对齐todo
69. x 的平方根
二分查找
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sqrtx/solution/x-de-ping-fang-gen-by-leetcode-solution/
71. 简化路径
72. 编辑距离todo
73. 矩阵置零
75. 颜色分类
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sort-colors/solution/yan-se-fen-lei-by-leetcode-solution/
看完所有的数
循环不变量


76. 最小覆盖子串todo
78. 子集(做过)
79. 单词搜索
https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-search/solution/dan-ci-sou-suo-by-leetcode-solution/
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 todo
85. 最大矩形 todo
93. 复原 IP 地址
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
101. 对称二叉树
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
return check(root,root)
}
func check(l *TreeNode ,r *TreeNode) bool{
if l == nil && r == nil {
return true
}
if (l == nil && r!=nil ) || ( l != nil && r == nil ) {
return false
}
return l.Val == r.Val && check(l.Left,r.Right) && check(l.Right,r.Left)
}
102. 二叉树的层序遍历 (队列)
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历(双端队列)
如果从左至右,我们每次将被遍历到的元素插入至双端队列的末尾。
如果从右至左,我们每次将被遍历到的元素插入至双端队列的头部。
104. 二叉树的最大深度
遇到null返回0,否则返回max(递归函数())+1
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树todo
class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> indexMap;
public TreeNode myBuildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder, int preorder_left, int preorder_right, int inorder_left, int inorder_right) {
if (preorder_left > preorder_right) {
return null;
}
// 前序遍历中的第一个节点就是根节点
int preorder_root = preorder_left;
// 在中序遍历中定位根节点
int inorder_root = indexMap.get(preorder[preorder_root]);
// 先把根节点建立出来
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorder_root]);
// 得到左子树中的节点数目
int size_left_subtree = inorder_root - inorder_left;
// 递归地构造左子树,并连接到根节点
// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1 开始的 size_left_subtree」个元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 左边界 开始到 根节点定位-1」的元素
root.left = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + 1, preorder_left + size_left_subtree, inorder_left, inorder_root - 1);
// 递归地构造右子树,并连接到根节点
// 先序遍历中「从 左边界+1+左子树节点数目 开始到 右边界」的元素就对应了中序遍历中「从 根节点定位+1 到 右边界」的元素
root.right = myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, preorder_left + size_left_subtree + 1, preorder_right, inorder_root + 1, inorder_right);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int n = preorder.length;
// 构造哈希映射,帮助我们快速定位根节点
indexMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
indexMap.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return myBuildTree(preorder, inorder, 0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/solutions/255811/cong-qian-xu-yu-zhong-xu-bian-li-xu-lie-gou-zao-9/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树todo
107.二叉树的层序遍历 II(正向输出然后再逆转)
题目描述:给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值 自底向上的层序遍历 。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
思路:在遍历完一层节点之后,将存储该层节点值的列表添加到结果列表的头部。
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树(递归构造平衡二叉树搜索树)
中序遍历,总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
// 总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/solutions/312607/jiang-you-xu-shu-zu-zhuan-huan-wei-er-cha-sou-s-33/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
115. 不同的子序列(todo)
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
118. 杨辉三角
第i行的第j个数=第i-1行的j-1个数 + 第i-1行的第j个数。注意下,左右边界都是1,就这么简单。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i) {
List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
if (j == 0 || j == i) {
row.add(1);
} else {
row.add(ret.get(i - 1).get(j - 1) + ret.get(i - 1).get(j));
}
}
ret.add(row);
}
return ret;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/pascals-triangle/solutions/510638/yang-hui-san-jiao-by-leetcode-solution-lew9/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
119. 杨辉三角 II
滚动数组优化
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getRow(int rowIndex) {
List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<Integer>();
row.add(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
row.add(0);
for (int j = i; j > 0; --j) {
row.set(j, row.get(j) + row.get(j - 1));
}
}
return row;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/pascals-triangle-ii/solutions/601082/yang-hui-san-jiao-ii-by-leetcode-solutio-shuk/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
128. 最长连续序列(在hash表中不断枚举匹配x+1,x+2…x+y,判断x-1在hash表中是否存在就能避免重复的枚举)
我们考虑枚举数组中的每个数 x,考虑以其为起点,不断尝试匹配 x+1,x+2,是否存在,假设最长匹配到了 x+y,那么以 x 为起点的最长连续序列即为 x,x+1,x+2,⋯ ,x+y,其长度为 y+1,我们不断枚举并更新答案即可。
对于匹配的过程,暴力的方法是 O(n)遍历数组去看是否存在这个数,但其实更高效的方法是用一个哈希表存储数组中的数,这样查看一个数是否存在即能优化至 O(1)的时间复杂度。
仅仅是这样我们的算法时间复杂度最坏情况下还是会达到 O(n^2)(即外层需要枚举 O(n)个数,内层需要暴力匹配 O(n)次,无法满足题目的要求。但仔细分析这个过程,我们会发现其中执行了很多不必要的枚举,如果已知有一个 x,x+1,x+2,⋯ ,x+y的连续序列,而我们却重新从x+1,x+2或者是 x+y处开始尝试匹配,那么得到的结果肯定不会优于枚举 x为起点的答案,因此我们在外层循环的时候碰到这种情况跳过即可。
那么怎么判断是否跳过呢?由于我们要枚举的数 x 一定是在数组中不存在前驱数 x−1的,不然按照上面的分析我们会从 x−1开始尝试匹配,因此我们每次在哈希表中检查是否存在 x−1即能判断是否需要跳过了。
增加了判断跳过的逻辑之后,时间复杂度是多少呢?外层循环需要 O(n) 的时间复杂度,只有当一个数是连续序列的第一个数的情况下才会进入内层循环,然后在内层循环中匹配连续序列中的数,因此数组中的每个数只会进入内层循环一次。根据上述分析可知,总时间复杂度为O(n),符合题目要求。
134. 加油站
基于简单事实:如果x到不了y+1(但能到y),那么从x到y的任一点出发都不可能到达y+1。因为从其中任一点出发的话,相当于从0开始加油,而如果从x出发到该点则不一定是从0开始加油,可能还有剩余的油。既然不从0加油开车都到不了y+1,那么从0开始就更不可能到达y+1了…
最容易想到的解法是:从头到尾遍历每个加油站,并检查以该加油站为起点,最终能否行驶一周。我们可以通过减小被检查的加油站数目,来降低总的时间复杂度。
假设我们此前发现,从加油站 x出发,每经过一个加油站就加一次油(包括起始加油站),最后一个可以到达的加油站是 y(不妨设 x 从上面的推导中,能够得出结论:从 x,y之间的任何一个加油站出发,都无法到达加油站 y 的下一个加油站。 在发现了这一个性质后,算法就很清楚了:我们首先检查第 0 个加油站,并试图判断能否环绕一周;如果不能,就从第一个无法到达的加油站开始继续检查。 对于这道题,可使用位运算中的异或运算 ⊕。异或运算有以下三个性质。 因此,数组中的全部元素的异或运算结果即为数组中只出现一次的数字。 数字电路设计优化 第一次遍历原链表,每遍历到一个节点,都新建一个相同val的节点,然后使用HashMap建立旧链表节点和新链表节点的映射。第二次遍历时通过HashMap,建立新链表节点之间的next和random关系。 最容易想到的做法是hash表:我们可以使用哈希表来存储所有已经访问过的节点。每次我们到达一个节点,如果该节点已经存在于哈希表中,则说明该链表是环形链表,否则就将该节点加入哈希表中。重复这一过程,直到我们遍历完整个链表即可。 龟兔赛跑算法 我们可以根据上述思路来解决本题。具体地,我们定义两个指针,一快一慢。慢指针每次只移动一步,而快指针每次移动两步。初始时,慢指针在位置 head,而快指针在位置 head.next。这样一来,如果在移动的过程中,快指针反过来追上慢指针,就说明该链表为环形链表。否则快指针将到达链表尾部,该链表不为环形链表。 比较简单的hash表做法 空间复杂度为O(1)的快慢指针做法 ps:为什么不能复用 环形链表 I的做法,因为你可以演示一下3->2->0->-4(->2):快慢指针首次相遇是在值0的位置。但实际题意要求是值为2的位置 快指针和慢指针从head出发,快指针每次走2步,慢指针每次走1步,当快指针和慢指针相遇后,再用第三个指针从节点出点,同时慢指针从相遇点出发,二者都每次走一步,相遇点即入环点(至于为什么可行:这是个数学问题:按照这个例子手动模拟一遍就会发现这个规律:严谨的就需要数学推导证明3->2->0->-4(->2)) 感觉官解的双指针解释有点复杂。快慢指针的思路,两指针一开始都指向头指针,然后 fast 每次走两步,slow 每次走一步。记 fast 走过的步数为 f,slow 走过的步数为 s,链表环外长度为 a,环内长度为 b。这样两指针第一次相遇时,有 f = 2s,且 f = s + nb。 因此 s = nb。也就是说第一次相遇时,slow 走了若干个环的长度。我们还知道,环的入口应该走 a + nb 步,因此我们可以让第一次相遇后的 slow 指针走 a 步,这样 slow 就指向的环的入口。 那么 a 是多少呢? 我们不知道,但我们知道从头指针走到入口是 a 步,从 slow 第一次相遇的位置走到入口也是 a 步。 因此让 fast 指针在头指针的位置,slow 保持在第一次相遇位置,那么两个指针每次移动一步,当再次相遇,就说明走到了环形链表的入口位置。 方法一:线性表 因此比较容易想到的一个方法是,我们利用线性表存储该链表,然后利用线性表可以下标访问的特点,直接按顺序访问指定元素,重建该链表即可。 方法二:寻找链表中点 + 链表逆序 + 合并链表(三个方法直接背下来) 排序 一个例子解释清楚算法在干什么 citations = [3,0,6,1,5]:首先排序6,5,3,1,0, 指数h初值设为0 其实h-index的定义很简单,一个作者有h篇论文被引用次数不少于h,则这个作者的h-index即为h。题设给出的后一半定义”其余的 N - h 篇论文每篇被引用次数不多于 h 次“,只是一个补充说明——可以用反证法证明:如果我们查验了一个作者h篇文章,发现其h-index已经为h,如果剩余的文章还有引用次数大于h的,那他的h-index就不应是h,而应该至少是h+1。 反过来说,一个h-index为h的作者,想要提高自己的h-index,有两种方式——再发一篇文章,引用次数达到h + 1;或者,现有的文章,有一篇引用次数低于h的,突然被好多人引用,引用次数达到h次以上(但这种”翻红“估计非常少)。也就是说,引用次数本来就很多(>= h)的那些文章,再怎么传播也不会再增加这个作者的h-index。这是不是也是鼓励这个作者在本领域不断创造新的、高质量的研究成果呢~ 因此,初见此题时,可能被这种补充说明带偏,其实在做题时只需要关注前半句即可:”一个作者有h篇论文被引用次数不少于h“。如果数组已排序,我们实际上是在就是在校验index(代表文章数x)和citations[index](代表有x篇文章拥有不低于/不高于某个引用次数)的大小关系。 首先我们可以将初始的 H 指数 h 设为 0,然后将引用次数排序,并且对排序后的数组从大到小遍历。 根据 H 指数的定义,如果当前 H 指数为 h 并且在遍历过程中找到当前值 citations[i]>h ,则说明我们找到了一篇被引用了至少 h+1 次的论文,所以将现有的 h 值加 1。继续遍历直到 h 无法继续增大。最后返回 h作为最终答案。 采用二分法 翻译一下题面 你有m种硬币,面额分别为1,4,9,16…你需要购买一个价格为n的商品,问最少花费几枚硬币 硬币问题的板子了 使用双指针,左指针指向当前已经处理好的序列的尾部,右指针指向待处理序列的头部。 右指针不断向右移动,每次右指针指向非零数,则将左右指针对应的数交换,同时左指针右移。 将这个题目给的特殊的数组当作一个链表来看,数组的下标就是指向元素的指针,把数组的元素也看作指针。如 0 是指针,指向 nums[0],而 nums[0] 也是指针,指向 nums[nums[0]]. 假设有这样一个样例:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,5]。如果我们按照上面的循环下去就会得到这样一个路径:1 2 3 4 5 [6 7 8 9] [6 7 8 9] [6 7 8 9] . . .这样就有了一个环,也就是 6 7 8 9。point 会一直在环中循环的前进。 快慢指针-如何把数组当链表来处理 第一个错误版本:二分查找 根据题目特殊性:寻找可优化点 65310 1 数学推理 我们进一步推理 既然剩下四块石头,先手必输,那么我只要保证每次只剩下4的倍数块石头,并且朋友拿,最后剩下只4块石头时我就必赢,换句话说,只要我在有4的倍数块石头时拿石头我必输 我们再想,只有在开始有4的倍数块石头时我才能最后4块石头先手拿,因为当n%4为1、2、3时我只要把多出来的这几个拿走,朋友就先手拿了 到了这一步,已经思路很清晰了,n%4==0时返回false,否则返回true 根据题意,我们可以对 secret 和 guess进行诸位比较,统计公牛数量 a和奶牛数量 b。 对于字符相同的位置,我们可以直接对 a 进行自增;对于字符不同的位置,使用「哈希表」进行分别统计 secret 和 guess 的词频,某个数字 x 在两者词频中的较小值,即为该数字对应的奶牛数量,统计所有数字 [0,9] 的奶牛数量总和即为 b hash表是用int[10]来表示的map[‘9’]=1,map[‘9’]=2这样c2= guess.charAt(i) - ‘0’【c - ‘0’ 就相当于计算c的实际数值,例如 c 是 ‘1’, 则 c - ‘0’ = 1, 把字符值转为数字值了】 排序 动态规划136. 只出现一次的数字(异或运算的经典案例)
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int single = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
single ^= num;
}
return single;
}
}
137. 只出现一次的数字 II(delete)
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int a = 0, b = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
b = ~a & (b ^ num);
a = ~b & (a ^ num);
}
return b;
}
}
138. 复制带随机指针的链表
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
HashMap<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();
while(cur!=null){
map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
map.get(cur).next=map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random=map.get(cur.random);
cur=cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
139. 单词拆分
141. 环形链表(龟兔赛跑算法-空间优化)
假想「乌龟」和「兔子」在链表上移动,「兔子」跑得快,「乌龟」跑得慢。当「乌龟」和「兔子」从链表上的同一个节点开始移动时,如果该链表中没有环,那么「兔子」将一直处于「乌龟」的前方;如果该链表中有环,那么「兔子」会先于「乌龟」进入环,并且一直在环内移动。等到「乌龟」进入环时,由于「兔子」的速度快,它一定会在某个时刻与乌龟相遇,即套了「乌龟」若干圈。public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return false;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (slow != fast) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/solutions/440042/huan-xing-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
142. 环形链表 II
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while (head != null) {
if (!seen.add(head)) {
return head;
}
head = head.next;
}
return null;
}
}
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (true) {
if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) break;
}
ListNode third = head;
while (slow != third) {
slow = slow.next;
third = third.next;
}
return third;
}
}
作者:Krahets
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/solutions/12616/linked-list-cycle-ii-kuai-man-zhi-zhen-shuang-zhi-/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
143. 重排链表
因为链表不支持下标访问,所以我们无法随机访问链表中任意位置的元素。class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode mid = middleNode(head);
ListNode l1 = head;
ListNode l2 = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
l2 = reverseList(l2);
mergeList(l1, l2);
}
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode nextTemp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = nextTemp;
}
return prev;
}
public void mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode l1_tmp;
ListNode l2_tmp;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
l1_tmp = l1.next;
l2_tmp = l2.next;
l1.next = l2;
l1 = l1_tmp;
l2.next = l1;
l2 = l2_tmp;
}
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reorder-list/solutions/452867/zhong-pai-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
144. 二叉树的前序遍历/后序遍历
146. LRU 缓存
147. 对链表进行插入排序todo
148. 排序链表
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
151. 反转字符串中的单词(要求O(1))
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
int start, end; // 每个单词的开始和结束索引(左闭右开)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.charAt(i) == ' ') continue; //跳过空格
end = i + 1; //找到结束索引
while (i >= 0 && s.charAt(i) != ' ') i--; //跳过空格
start = i + 1; //找到开始索引
for (int j = start; j < end; j++) //将每个单词按开始结束索引赋值到StringBuilder
sb.append(s.charAt(j));
sb.append(' '); //加上单词间的空格
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1); //删掉最后一个多余的空格
return sb.toString();
}
}
169. 多数元素(投票算法)
229. 多数元素 II
224. 基本计算器
227. 基本计算器 II
232. 用栈实现队列
237. 删除链表中的节点
257. 二叉树的所有路径
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
constructPaths(root, "", paths);
return paths;
}
public void constructPaths(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths) {
if (root != null) {
StringBuffer pathSB = new StringBuffer(path);
pathSB.append(Integer.toString(root.val));
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { // 当前节点是叶子节点
paths.add(pathSB.toString()); // 把路径加入到答案中
} else {
pathSB.append("->"); // 当前节点不是叶子节点,继续递归遍历
constructPaths(root.left, pathSB.toString(), paths);
constructPaths(root.right, pathSB.toString(), paths);
}
}
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/solutions/400326/er-cha-shu-de-suo-you-lu-jing-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
258. 各位相加(数学问题)
int addDigits(int num)
{
if(0 == num % 9)
{
return 9;
}
return num % 9;
}
260. 只出现一次的数字 III(位运算-跳过)
263. 丑数
class Solution {
public boolean isUgly(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return false;
}
int[] factors = {2, 3, 5};
for (int factor : factors) {
while (n % factor == 0) {
n /= factor;
}
}
return n == 1;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/ugly-number/solutions/712106/chou-shu-by-leetcode-solution-fazd/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
264. 丑数 II
class Solution {
public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
int p2 = 1, p3 = 1, p5 = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int num2 = dp[p2] * 2, num3 = dp[p3] * 3, num5 = dp[p5] * 5;
dp[i] = Math.min(Math.min(num2, num3), num5);
if (dp[i] == num2) {
p2++;
}
if (dp[i] == num3) {
p3++;
}
if (dp[i] == num5) {
p5++;
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/ugly-number-ii/solutions/712102/chou-shu-ii-by-leetcode-solution-uoqd/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
268. 丢失的数字(原地哈希将空间复杂度降低为O(1)很6)
hash
原地哈希class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i && nums[i] < n) swap(nums, nums[i], i--);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i) return i;
}
return n;
}
void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int c = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = c;
}
}
作者:宫水三叶
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/missing-number/solutions/1086545/gong-shui-san-xie-yi-ti-wu-jie-pai-xu-ji-te3s/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
274. H 指数(H 指数换一种理解就是:统计降序排列的数组中下标比下标值大的个数)
然后计数:
6>(i=1) —h+1=1
5>(i=2) —h+1=2
3>=(i=3) —h+1=3
1<(i=3) —运行结束返回结果3class Solution {
public int hIndex(int[] citations) {
Arrays.sort(citations);
int h = 0, i = citations.length - 1;
while (i >= 0 && citations[i] > h) {
h++;
i--;
}
return h;
}
}
275. H 指数 II
class Solution {
public int hIndex(int[] citations) {
int n = citations.length;
int left = 0, right = n - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (citations[mid] >= n - mid) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return n - left;
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/h-index-ii/solutions/870989/h-zhi-shu-ii-by-leetcode-solution-si7h/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
279. 完全平方数
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int minn = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 1; j * j <= i; j++) {
minn = Math.min(minn, f[i - j * j]);
}
f[i] = minn + 1;
}
return f[n];
}
}
class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int size = (int)Math.sqrt(n) + 5;
int[] coins = new int[size];
int[] dp = new int[n + 5];
for(int i = 1; i < coins.length; i++){
coins[i] = i * i;
}
//全用1填
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
dp[i] = i;
}
for(int i = 2; i < coins.length; i++){
int money = coins[i];
for(int j = money; j <= n; j++){
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j],dp[j - coins[i]] + 1);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
283. 移动零(双指针)
287. 寻找重复数
int point = 0;
while(true){
point = nums[point]; // 等同于 next = next->next;
}
2
3290. 单词规律(将map的put性质发挥到了极致:如果key不存在,插入成功,返回null;如果key存在,返回之前对应的value)
class Solution {
public boolean wordPattern(String pattern, String str) {
String[] words = str.split(" ");
//字符和单词是互相映射,数量必须相等
if (words.length != pattern.length()) {
return false;
}
Map<Object, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Integer i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
/*
如果key不存在,插入成功,返回null;如果key存在,返回之前对应的value。
以pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat dog"为例,
第1次:map.put('a',0)返回null,map.put("dog",0)返回null,两者相等;
第2次:map.put('b',1)返回null,map.put("cat",1)返回null,两者相等;
第3次:map.put('b',2)返回1,map.put("cat",2)返回1,两者相等;
第4次:map.put('a',3)返回0,map.put("dog",3)返回0,两者相等,
结果为 true。
以pattern = "abba", str = "dog cat cat fish"为例,
第1次:map.put('a',0)返回null,map.put("dog",0)返回null,两者相等;
第2次:map.put('b',1)返回null,map.put("cat",1)返回null,两者相等;
第3次:map.put('b',2)返回1,map.put("cat",2)返回1,两者相等;
第4次:map.put('a',3)返回0,map.put("fish",3)返回null,两者不相等,
结果为 false。
*/
if (map.put(pattern.charAt(i), i) != map.put(words[i], i)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
287. 寻找重复数
289. 生命游戏todo
292. Nim 游戏
这道题,显而易见的是1、2、3块石头你能一次全拿走。但是4块石头,你无论怎么拿,朋友肯定能拿走剩下的所有石头 因此只要最后剩下4块石头,先手必输class Solution {
public boolean canWinNim(int n) {
return n % 4 != 0;
}
}
299. 猜数字游戏
class Solution {
public String getHint(String secret, String guess) {
int n = secret.length();
int a = 0, b = 0;
int[] cnt1 = new int[10], cnt2 = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int c1 = secret.charAt(i) - '0', c2= guess.charAt(i) - '0';
if (c1 == c2) {
a++;
} else {
cnt1[c1]++;
cnt2[c2]++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) b += Math.min(cnt1[i], cnt2[i]);
return a + "A" + b + "B";
}
}
作者:宫水三叶
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/bulls-and-cows/solutions/1089829/gong-shui-san-xie-jian-dan-mo-ni-ti-by-a-tdhs/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
300. 最长递增子序列
附加
归并/快排/堆排
最长递增子序列
最长连续递增子序列
最大连续子序列的和(连续子数组的最大和)
最长公共子序列
最长公共连续子序列
最长不重复子串