设计模式 -- 解释器模式(Interpreter)
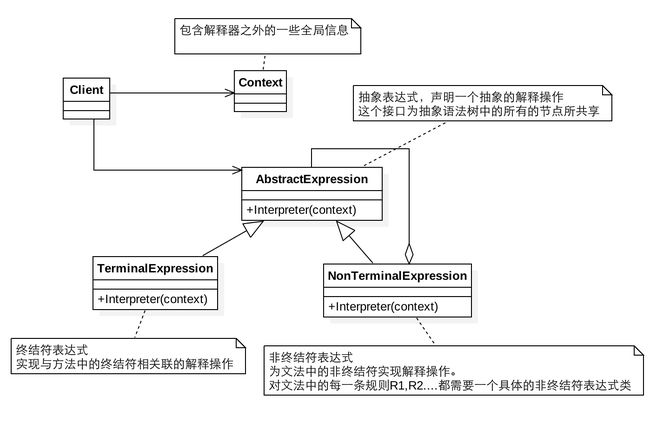
给分析对象定义一个语言,并定义该语言的文法表示,再设计一个解析器来解释语言中的句子。也就是说,用编译语言的方式来分析应用中的实例。这种模式实现了文法表达式处理的接口,该接口解释一个特定的上下文。
一般主要应用在OOP开发中的编译器的开发中,所以适用面比较窄。
在软件开发中,会遇到有些问题多次重复出现,而且有一定的相似性和规律性。如果将它们归纳成一种简单的语言,那么这些问题实例将是该语言的一些句子,这样就可以用“编译原理”中的解释器模式来实现了。
优点
-
扩展性好。由于在解释器模式中使用类来表示语言的文法规则,因此可以通过继承等机制来改变或扩展文法。
-
容易实现。在语法树中的每个表达式节点类都是相似的,所以实现其文法较为容易。
缺点
-
执行效率较低。解释器模式中通常使用大量的循环和递归调用,当要解释的句子较复杂时,其运行速度很慢,且代码的调试过程也比较麻烦。
-
会引起类膨胀。解释器模式中的每条规则至少需要定义一个类,当包含的文法规则很多时,类的个数将急剧增加,导致系统难以管理与维护。
-
可应用的场景比较少。在软件开发中,需要定义语言文法的应用实例非常少,所以这种模式很少被使用到。
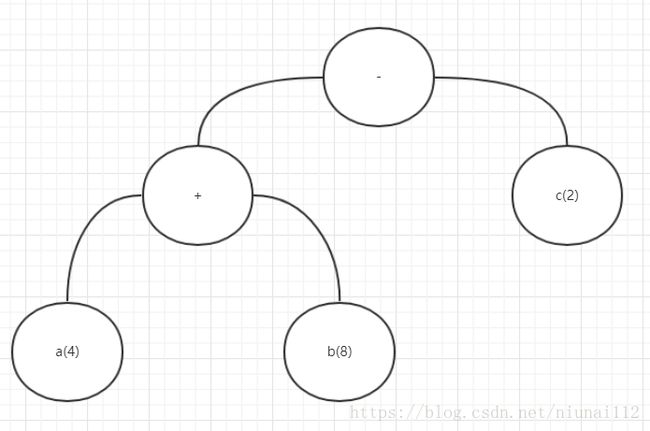
非终结符表达式(相当于树的树杈):在这个例子中就是相加,相减的表达式。
终结符表达式(相当于树的叶子):遇到这个表达式interpreter执行能直接返回结果,不会向下继续调用。
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:解释器接口
*@Date: Created in 16:20 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public interface Expression {
int interpreter(Context context);//一定会有解释方法
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:抽象非终结符表达式
*@Date: Created in 16:22 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public abstract class NonTerminalExpression implements Expression{
Expression e1,e2;
public NonTerminalExpression(Expression e1, Expression e2){
this.e1 = e1;
this.e2 = e2;
}
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:减法表达式实现类
*@Date: Created in 16:57 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class MinusOperation extends NonTerminalExpression {
public MinusOperation(Expression e1, Expression e2) {
super(e1, e2);
}
//将两个表达式相减
@Override
public int interpreter(Context context) {
return this.e1.interpreter(context) - this.e2.interpreter(context);
}
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:终结符表达式(在这个例子,用来存放数字,或者代表数字的字符)
*@Date: Created in 16:22 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class TerminalExpression implements Expression{
String variable;
public TerminalExpression(String variable){
this.variable = variable;
}
@Override
public int interpreter(Context context) {
return context.lookup(this);
}
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:
*@Date: Created in 16:56 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class PlusOperation extends NonTerminalExpression {
public PlusOperation(Expression e1, Expression e2) {
super(e1, e2);
}
//将两个表达式相加
@Override
public int interpreter(Context context) {
return this.e1.interpreter(context) + this.e2.interpreter(context);
}
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:上下文类(这里主要用来将变量解析成数字【当然一开始要先定义】)
*@Date: Created in 16:48 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class Context {
private Map map = new HashMap<>();
//定义变量
public void add(Expression s, Integer value){
map.put(s, value);
}
//将变量转换成数字
public int lookup(Expression s){
return map.get(s);
}
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:测试类
*@Date: Created in 13:27 2018/4/8
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context context = new Context();
TerminalExpression a = new TerminalExpression("a");
TerminalExpression b = new TerminalExpression("b");
TerminalExpression c = new TerminalExpression("c");
context.add(a, 4);
context.add(b, 8);
context.add(c, 2);
System.out.println(new MinusOperation(new PlusOperation(a,b), c).interpreter(context));
}
}
运行结果如下
-----------------------------------
10
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:
*@Date: Created in 16:48 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class Context {
private Map map = new HashMap<>();
public void add(Expression s, Integer value){
map.put(s, value);
}
public Integer lookup(Expression s){
return map.get(s);
}
//构建语法树的主要方法
public static Expression build(String str) {
//主要利用栈来实现
Stack objects = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){
char c = str.charAt(i);
//遇到运算符号+号时候
if (c == '+'){
//先出栈
Expression pop = objects.pop();
//将运算结果入栈
objects.push(new PlusOperation(pop, new TerminalExpression(String.valueOf(str.charAt(++i)))));
} else if (c == '-'){
//遇到减号类似加号
Expression pop = objects.pop();
objects.push(new MinusOperation(pop, new TerminalExpression(String.valueOf(str.charAt(++i)))));
} else {
//遇到非终结符直接入栈(基本就是第一个数字的情况)
objects.push(new TerminalExpression(String.valueOf(str.charAt(i))));
}
}
//把最后的栈顶元素返回
return objects.pop();
}
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:终结符实现类
*@Date: Created in 16:22 2018/4/17
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class TerminalExpression implements Expression {
String variable;
public TerminalExpression(String variable){
this.variable = variable;
}
@Override
public int interpreter(Context context) {
//因为要兼容之前的版本
Integer lookup = context.lookup(this);
if (lookup == null)
//若在map中能找到对应的数则返回
return Integer.valueOf(variable);
//找不到则直接返回(认为输入的就是数字)
return lookup;
}
}
/***
*
*@Author ChenjunWang
*@Description:测试类
*@Date: Created in 13:27 2018/4/8
*@Modified By:
*
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context context = new Context();
TerminalExpression a = new TerminalExpression("a");
TerminalExpression b = new TerminalExpression("b");
TerminalExpression c = new TerminalExpression("c");
String str = "4+8-2+9+9-8";
Expression build = Context.build(str);
System.out.println("4+8-2+9+9-8=" + build.interpreter(context));
context.add(a, 4);
context.add(b, 8);
context.add(c, 2);
System.out.println(new MinusOperation(new PlusOperation(a,b), c).interpreter(context));
}
}
运行结果如下
-----------------------------------------
4+8-2+9+9-8=20
10
/*文法规则
::= 的
::= 韶关|广州
::= 老人|妇女|儿童
*/
public class InterpreterPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Context bus = new Context();
bus.freeRide("韶关的老人");
bus.freeRide("韶关的年轻人");
bus.freeRide("广州的妇女");
bus.freeRide("广州的儿童");
bus.freeRide("山东的儿童");
}
}
//抽象表达式类
interface Expression {
public boolean interpret(String info);
}
//终结符表达式类
class TerminalExpression implements Expression {
private Set set = new HashSet();
public TerminalExpression(String[] data) {
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) set.add(data[i]);
}
public boolean interpret(String info) {
if (set.contains(info)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
//非终结符表达式类
class AndExpression implements Expression {
private Expression city = null;
private Expression person = null;
public AndExpression(Expression city, Expression person) {
this.city = city;
this.person = person;
}
public boolean interpret(String info) {
String s[] = info.split("的");
return city.interpret(s[0]) && person.interpret(s[1]);
}
}
//环境类
class Context {
private String[] citys = {"韶关", "广州"};
private String[] persons = {"老人", "妇女", "儿童"};
private Expression cityPerson;
public Context() {
Expression city = new TerminalExpression(citys);
Expression person = new TerminalExpression(persons);
cityPerson = new AndExpression(city, person);
}
public void freeRide(String info) {
boolean ok = cityPerson.interpret(info);
if (ok) System.out.println("您是" + info + ",您本次乘车免费!");
else System.out.println(info + ",您不是免费人员,本次乘车扣费2元!");
}
}
//上下文
public class Context {
private int result;//结果
private int index;//当前位置
private int mark;//标志位
private char[] inputChars;//输入的字符数组
private List operateNumbers = new ArrayList(2);//操作数
private char operator;//运算符
public Context(char[] inputChars) {
super();
this.inputChars = inputChars;
}
public int getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(int result) {
this.result = result;
}
public boolean hasNext(){
return index != inputChars.length;
}
public char next() {
return inputChars[index++];
}
public char current(){
return inputChars[index];
}
public List getOperateNumbers() {
return operateNumbers;
}
public void setLeftOperateNumber(int operateNumber) {
this.operateNumbers.add(0, operateNumber);
}
public void setRightOperateNumber(int operateNumber) {
this.operateNumbers.add(1, operateNumber);
}
public char getOperator() {
return operator;
}
public void setOperator(char operator) {
this.operator = operator;
}
public void mark(){
mark = index;
}
public void reset(){
index = mark;
}
}
//抽象表达式,定义一个解释操作
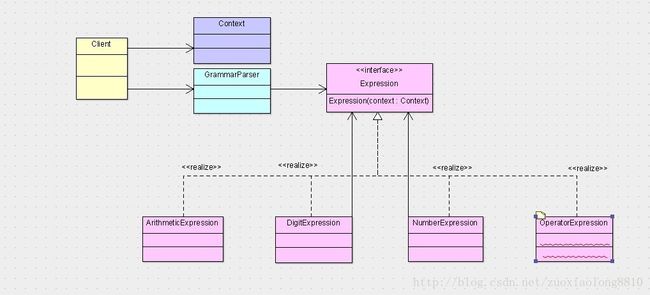
public interface Expression {
void interpreter(Context context);
}
//算数表达式(非终结符表达式,对应arithmetic)
public class ArithmeticExpression implements Expression {
public void interpreter(Context context) {
context.setResult(getResult(context));//计算结果
context.getOperateNumbers().clear();//清空操作数
context.setLeftOperateNumber(context.getResult());//将结果压入左操作数
}
private int getResult(Context context){
int result = 0;
switch (context.getOperator()) {
case '+':
result = context.getOperateNumbers().get(0) + context.getOperateNumbers().get(1);
break;
case '-':
result = context.getOperateNumbers().get(0) - context.getOperateNumbers().get(1);
break;
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
}
//非终结符表达式,对应number
public class NumberExpression implements Expression{
public void interpreter(Context context) {
//设置操作数
Integer operateNumber = Integer.valueOf(String.valueOf(context.current()));
if (context.getOperateNumbers().size() == 0) {
context.setLeftOperateNumber(operateNumber);
context.setResult(operateNumber);
}else {
context.setRightOperateNumber(operateNumber);
Expression expression = new ArithmeticExpression();//转换成算数表达式
expression.interpreter(context);
}
}
}
//终结符表达式,对应-、+
public class OperatorExpression implements Expression{
public void interpreter(Context context) {
context.setOperator(context.current());//设置运算符
}
}
//终结符表达式,对应0、1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9
public class DigitExpression implements Expression{
public void interpreter(Context context) {
Expression expression = new NumberExpression();//如果是数字,则直接转为number表达式
expression.interpreter(context);
}
}
//语法解析器(如果按照解释器模式的设计,这些代码应该是在客户端,为了更加清晰,我们添加一个语法解析器)
public class GrammarParser {
//语法解析
public void parse(Context context) throws Exception{
while (context.hasNext()) {
Expression expression = null;
switch (context.current()) {
case '+':
case '-':
checkGrammar(context);
expression = new OperatorExpression();
break;
case '0':
case '1':
case '2':
case '3':
case '4':
case '5':
case '6':
case '7':
case '8':
case '9':
context.mark();
checkGrammar(context, context.current());
context.reset();
expression = new DigitExpression();
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("语法错误!");//无效符号
}
expression.interpreter(context);
context.next();
}
}
//检查语法
private void checkGrammar(Context context,char current){
context.next();
if (context.hasNext() && context.current() != '+' && context.current() != '-') {
throw new RuntimeException("语法错误!");//第5条
}
try {
Integer.valueOf(String.valueOf(current));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("语法错误!");//第6条
}
}
//检查语法
private void checkGrammar(Context context){
if (context.getOperateNumbers().size() == 0) {//第4条
throw new RuntimeException("语法错误!");
}
if (context.current() != '+' && context.current() != '-') {//第7条
throw new RuntimeException("语法错误!");
}
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List inputList = new ArrayList();
//三个正确的,三个错误的
inputList.add("1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9");
inputList.add("1-2+3-4+5-6+7-8+9");
inputList.add("9");
inputList.add("-1+2+3+5");
inputList.add("1*2");
inputList.add("11+2+3+9");
GrammarParser grammarParser = new GrammarParser();//语法分析器
for (String input : inputList) {
Context context = new Context(input.toCharArray());
try {
grammarParser.parse(context);//语法分析器会调用解释器解释表达式
System.out.println(input + "=" + context.getResult());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("语法错误,请输入正确的表达式!");
}
}
}
}
输出结果:
1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9=45
1-2+3-4+5-6+7-8+9=5
9=9
语法错误,请输入正确的表达式!
语法错误,请输入正确的表达式!
语法错误,请输入正确的表达式!
根据以下文章总结:
-
Java设计模式:23种设计模式全面解析(超级详细)HYPERLINK http://c.biancheng.net/design_pattern/
-
3种设计模式详解 https://www.iteye.com/blog/zz563143188-1847029
-
Android系统编程思想:设计模式https://github.com/sucese/android-open-source-project-analysis/blob/master/doc/Android%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%E8%BD%AF%E4%BB%B6%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E7%AF%87/02Android%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%E8%BD%AF%E4%BB%B6%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E7%AF%87%EF%BC%9A%E8%AE%BE%E8%AE%A1%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F.md#35-%E8%A7%82%E5%AF%9F%E8%80%85%E6%A8%A1%E5%BC%8F
-
设计模式 https://blog.csdn.net/shusheng0007/category_8638565.html
-
java设计模式 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37909508/category_8976362.html
-
设计模式 https://www.cnblogs.com/zuoxiaolong/category/509144.html
-
设计模式 在源码中的应用 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36970993/category_10620886.html
-
Android系统设计中存在设计模式分析 https://www.2cto.com/kf/201208/150650.html
-
Android设计模式系列 - 基于android的各种代码分析各种设计模式 https://www.cnblogs.com/qianxudetianxia/category/312863.html